NSX V6-3.0L DOHC (1991)
ABS Motor: Description and Operation
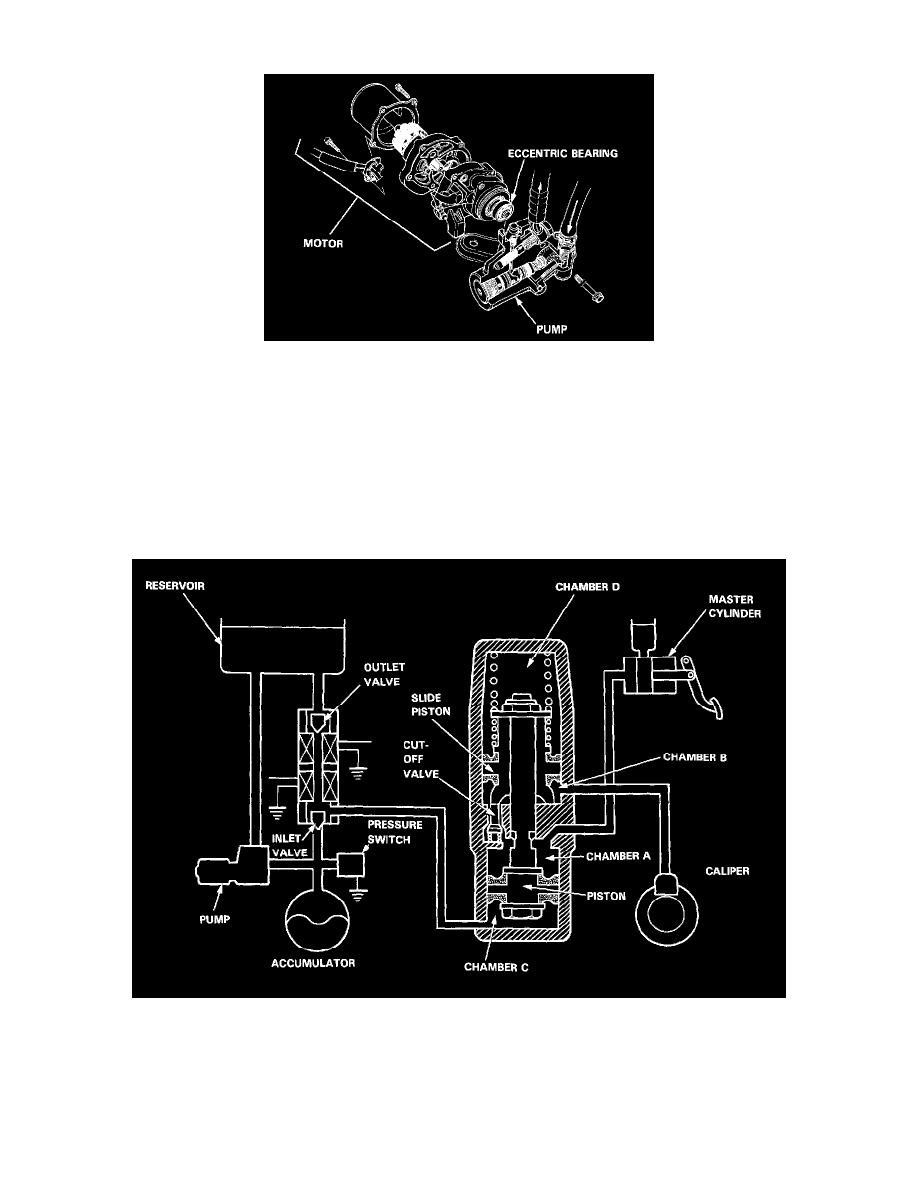
The power unit consists of a motor and a plunger-type pump. This unit transmits the revolution of the motor to the plunger by way of an eccentric
bearing and supplies high-pressure brake fluid to the accumulator by the effect of the reciprocating movement of the plunger.
When the pressure in the accumulator drops below the prescribed pressure level, the pressure switch gives an Off signal. The ABS control unit turns
the motor relay ON to start the operation of the pump, upon the reception of this signal and a signal from the wheel sensor that the vehicle is running at
a speed greater than 6 mph (10 km/h). When the pressure in the accumulator attains the prescribed pressure, the ABS control unit turns the motor relay
OFF approximately three seconds after the unit receives an ON-signal from the pressure switch. By this, the high-pressure in the accumulator is
maintained.
The ABS control unit turns the pump off and lights the system indicator light if the accumulator pressure does not reach the prescribed level after the
pump has run continuously for 120 seconds.
In ordinary brake operations, the cut-off out valve in the modulator is open to transmit the hydraulic pressure from the master cylinder to the brake
calipers via the chamber A and the chamber B.
The chamber C is connected to the reservoir through the outlet valve which is normally open. It is also connected to the hydraulic pressure source
(pump, accumulator, pressure switch, etc.l via the inlet valve which is normally closed. The chamber D serves as an air chamber. Under these
conditions, the pressures of the chambers C and D are maintained at about the atmospheric pressure, permitting regular braking operations.
