Roadmaster Estate Wagon V8-305 5.0L (1991)
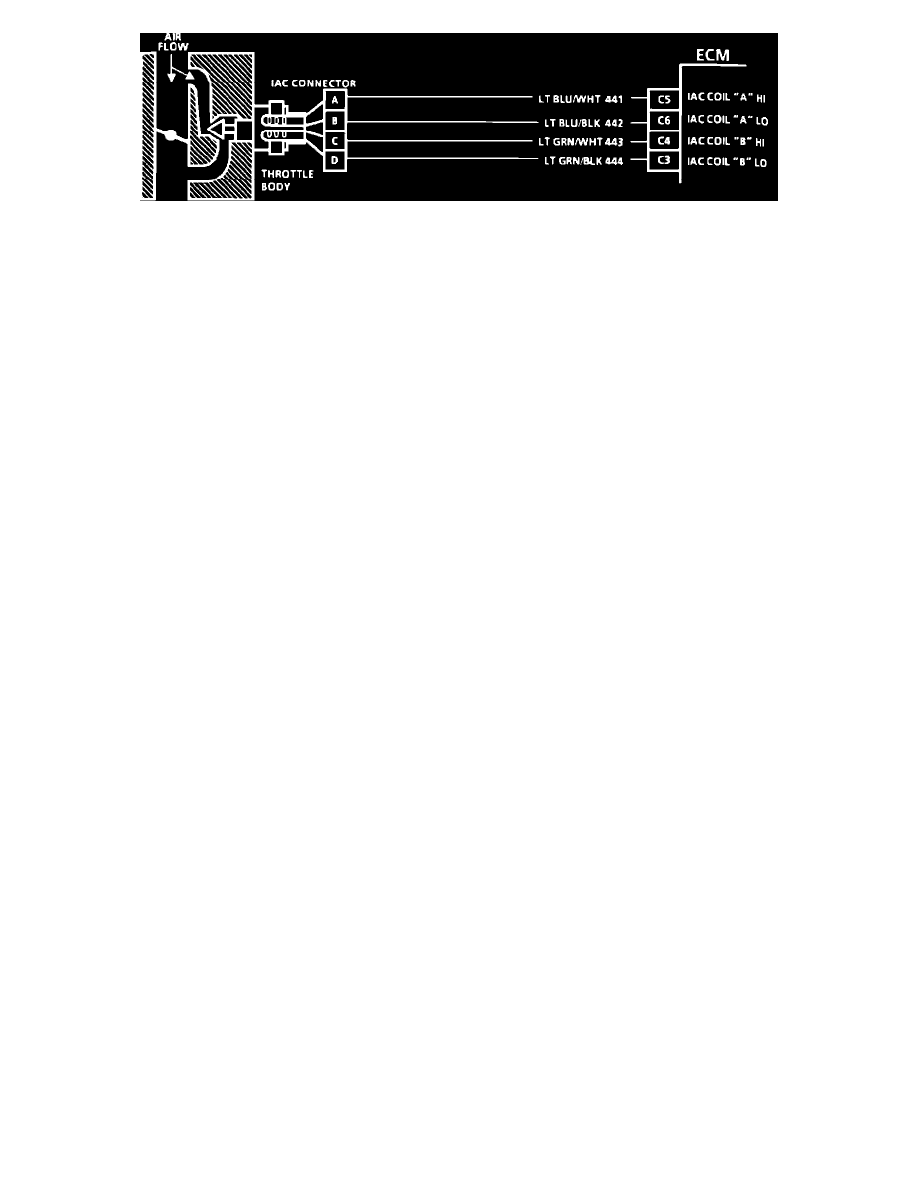
Wiring Diagram For IAC
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The ECM controls engine idle speed with the Idle Air Control (IAC) valve. To increase idle speed, the ECM retracts the IAC valve pintle away from its
seat, allowing more air to pass by the throttle body. To decrease idle speed, it extends the IAC valve pintle towards its seat, reducing bypass air flow. A
"Scan" tool will read the ECM commands to the IAC valve in counts. The higher the counts indicate more air bypass (higher idle). The lower the counts
indicate less air is allowed to bypass (lower idle).
TEST DESCRIPTION: The numbers below refer to circled numbers on the diagnostic chart.
1.
The IAC tester is used to extend and retract the IAC valve. Valve movement is verified by an engine speed change. If no engine speed occurs, the
valve can be retested when removed from the throttle body.
2.
This step checks the quality of the IAC movement in step 1. Between 700 and 1500 rpm, the engine speed should change smoothly with each flash
of the tester light for both extend and retract. If the IAC valve is retracted beyond the control range (approximately 1500 rpm), it may take many
flashes in the extend position before the engine speed drops. This is normal on certain engines; fully extending the IAC may cause the engine to
stall.
3.
Steps 1 and 2 verified proper IAC valve operation. This step checks the IAC circuit. Each lamp on the node light should flash red and green while
the IAC valve is cycled. While the sequence of colors are not important, if either the light is "OFF" or does not flash red and green, check the
circuits for faults. Check for poor terminal contacts.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
A slow, unstable idle may be caused by a non-IAC system problem that cannot be overcome by the IAC valve. Out of control range IAC "Scan" tool
counts will be above 60 if idle is too low, and "0" counts if the idle is too high. If the idle speed is too high, turn the ignition "OFF" to stop the engine.
Turn the ignition "ON" without the engine running. Wait 45 seconds for the IAC valve pintle to seat, then disconnect the IAC valve. The following
checks should be made to repair a non-IAC system problem:
a.
Vacuum leak (High Idle) - If idle is too high, stop the engine. Fully extend (low) IAC with tester. Start engine. If idle speed is above 800 rpm,
locate and correct vacuum leak including PCV system. Also check for binding of throttle blade or linkage.
b.
System Too Lean (High Air/Fuel Ratio) - The idle speed may be too high or too low. Engine speed may vary up and down and disconnecting
the IAC valve does not help. A Code 44 may set. "Scan" O2 voltage will be less than 300 mv (0.3 volt). Check for low regulated fuel pressure
, or water in fuel. A fixed oxygen sonsor voltage above 800 mv (0.8 volts) may be contaminated by silicone. A Code 45 may be stored in the
computer.
c.
System Too Rich (Low Air/Fuel Ratio - The idle speed will be too low. Scaning IAC counts will usually be above 80. System is obviously
rich and may exhibit black smoke in exhaust. "Scan" tool O2 voltage will be fixed above 800 mv (0.8 volt). Check for high fuel pressure,
leaking or sticking injector. Silicone contaminated O2 sensors "Scan" voltage will be slow to respond.
d.
Throttle Body - Remove IAC valve and inspect bore for foreign material.
e.
IAC Valve Electrical Connections - IAC valve harness connections should be carefully checked for proper contact.
f.
PCV Valve - An incorrect or faulty PCV valve may result in an incorrect idle speed.
g.
Refer to "Rough, Unstable, Incorrect Idle or Stalling" in DIAGNOSIS BY SYMPTOM.
