Somerset V6-181 3.0L (1986)
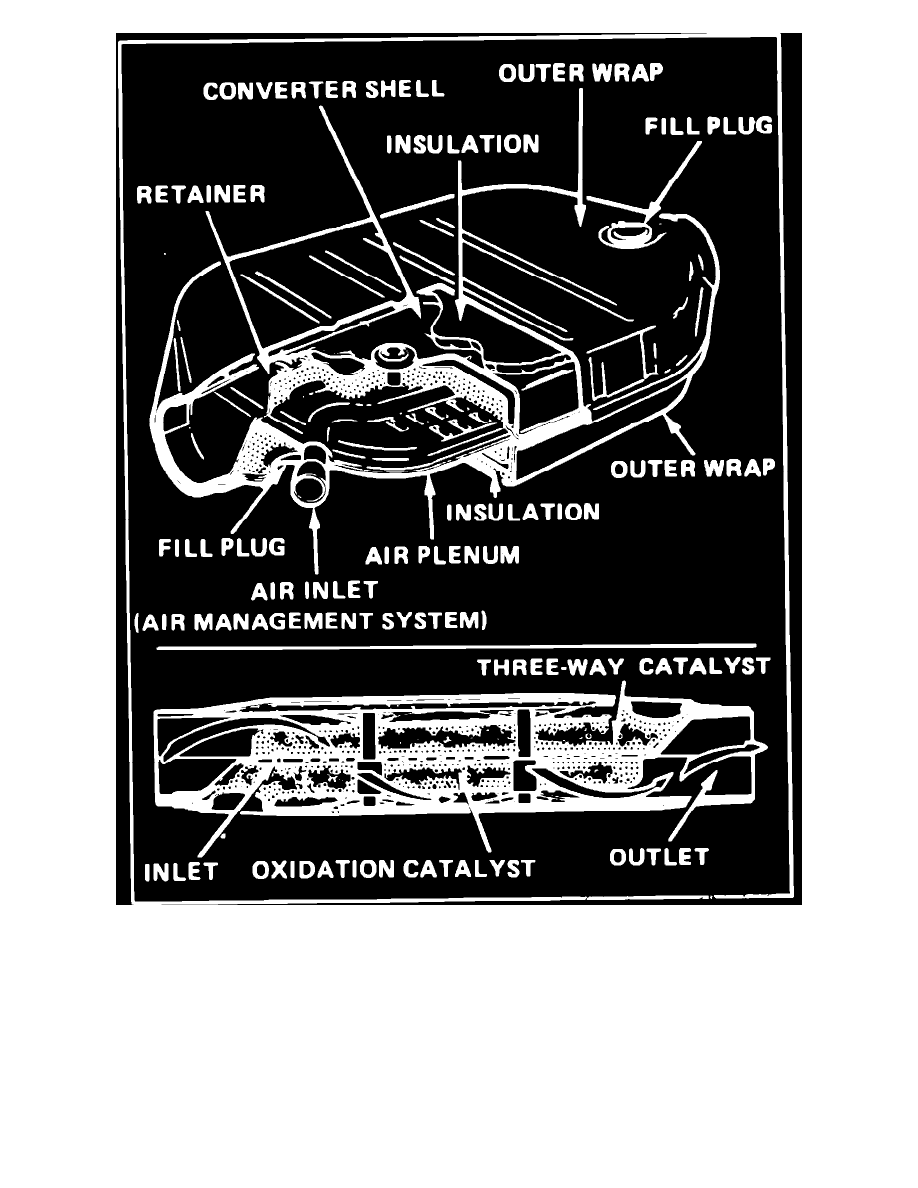
Fig. 22 Dual bed pellet type catalytic converter
The catalytic converter is an emission control device added to the exhaust system to effectively reduce the levels of carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons,
and in some cases oxides of nitrogen, entering the atmosphere. The converter serves two purposes: it permits a faster chemical reaction to take place and
although it enters into the chemical reaction, it remains unchanged, ready to repeat the process.
This device sometimes requires the use of heat shields, due to its high operating temperatures. The heat shields are necessary to protect chassis
components, passenger compartment and other areas from heat related damage.
General Motors uses four different converter designs in conjunction with two types of catalysts. The four converter designs, Figs. 19 through 22, are:
single bed monolith, dual bed monolith, single bed pellet and dual bed pellet. The two types of catalysts used are an oxidation catalyst and a three-way
(reduction) catalyst. The oxidation catalyst is coated with material containing platinum and palladium which lowers levels of carbon monoxide and
hydrocarbons. The Three-way (reduction) catalyst is coated with platinum and rhodium which lowers levels of oxides of nitrogen (NOx), as well as
carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons.
All dual bed converters, whether monolith or pellet type, contain both oxidation and three-way catalysts.
