Escalade EXT AWD V8-6.2L (2009)
A circuit breaker is a protective device that is designed to open the circuit when a current load is in excess of the rated breaker capacity. If there is a short
or other type of overload condition in the circuit, the excessive current will open the circuit between the circuit breaker terminals. Two types of circuit
breakers are used.
Circuit Breaker
-
This type opens when excessive current passes through it for a period of time. It closes again after a few seconds, and if the cause of the high
current is still present, it will open again. The circuit breaker will continue to cycle open and closed until the condition causing the high current is
removed.
Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC) Circuit Breaker
-
This type greatly increases its resistance when excessive current passes through it. The excessive current heats the PTC device, as the device heats
its resistance increases. Eventually the resistance gets so high that the circuit is effectively open. Unlike the ordinary circuit breaker the PTC unit
will not reset until the circuit is opened, by removing the voltage from its terminals. Once the voltage is removed the circuit breaker will re-close
within a second or 2.
Circuit Protection - Fuses
Circuit Protection - Fuses
The fuse is the most common method of an automotive wiring circuit protection. Whenever there is an excessive amount of current flowing through a
circuit the fusible element will melt and create an open or incomplete circuit. Fuses are an one time protection device and must be replaced each time the
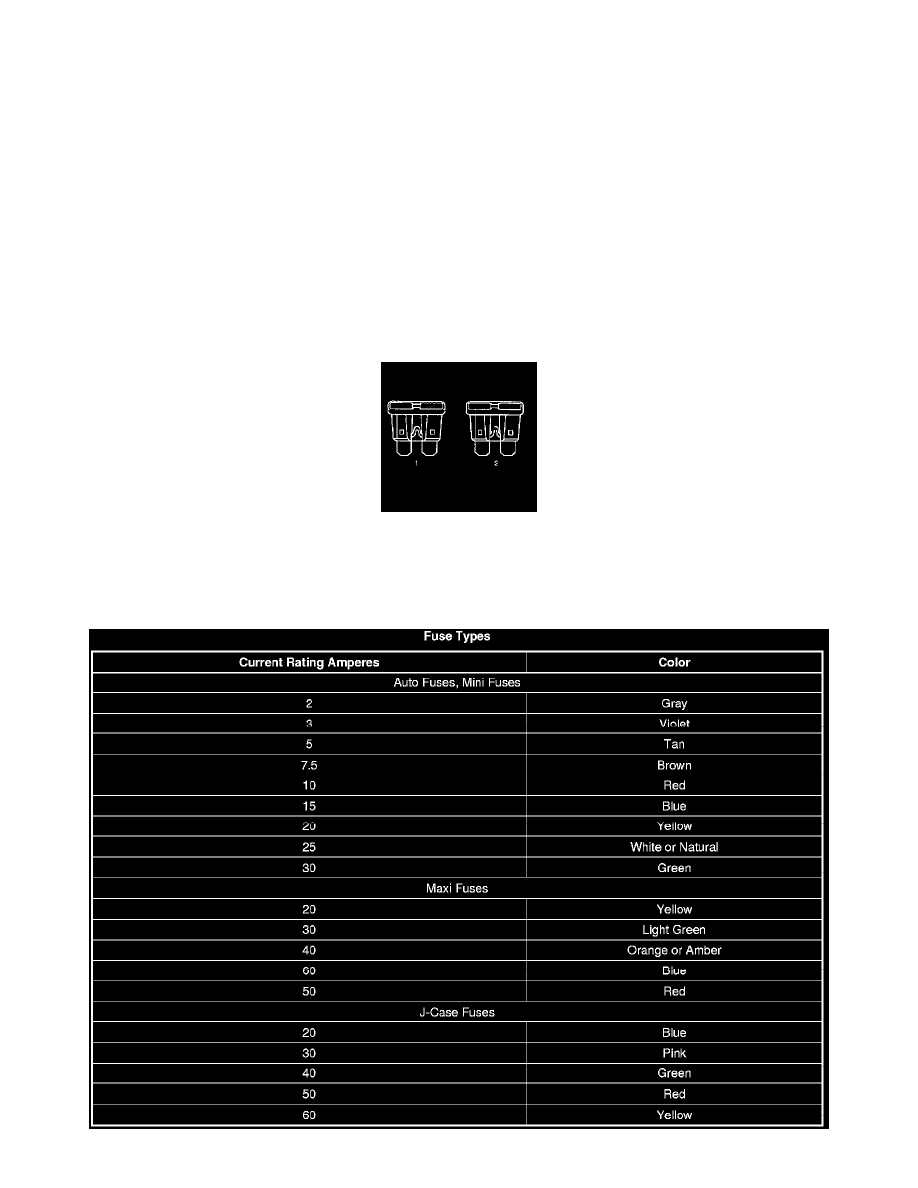
circuit is overloaded. To determine if a fuse is open, remove the suspected fuse and examine the element in the fuse for an open (2). If not broken (1),
also check for continuity using a DMM or a continuity tester. If the element is open or continuity is suspect, replace the fuse with one of equal current
rating.
