Astro Van 2WD V6-4.3L VIN X (2002)
Misfire Monitor Diagnostic Operation
The misfire monitor diagnostic is based on crankshaft rotational velocity, aka reference period, variations. The PCM determines crankshaft rotational
velocity using the Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor and Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor. When a cylinder misfires, the crankshaft slows down
momentarily. By monitoring the crankshaft and camshaft position sensor signals, the PCM can calculate when a misfire occurs.
For a non-catalyst damaging misfire, the diagnostic is required to monitor a misfire present for between 1,000 - 3,200 engine revolutions.
For catalyst damage misfire, the diagnostic responds to the misfire within 200 engine revolutions.
Rough roads may cause false misfire detection. A rough road applies sudden torque variations to the drive wheels and drivetrain. This torque can
intermittently decrease the crankshaft rotational velocity. The Antilock Braking (ABS) System detects uneven speed between the vehicles wheels and
sends data via the serial data bus to the PCM to disable the misfire monitor until the rough road is no longer detected.
On automatic transmission equipped vehicles, the Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) disables whenever a misfire is detected. Disabling the TCC isolates
the engine from the rest of the drive line and minimizes the effect of the drive wheel inputs on crankshaft rotation.
When the TCC has disabled as a result of misfire detection, the TCC is re-enabled after approximately 3,200 engine revolutions if no misfire is detected.
The TCC remains disabled whenever the misfire is detected, with or without a DTC set. This allows the misfire diagnostic to reevaluate the system.
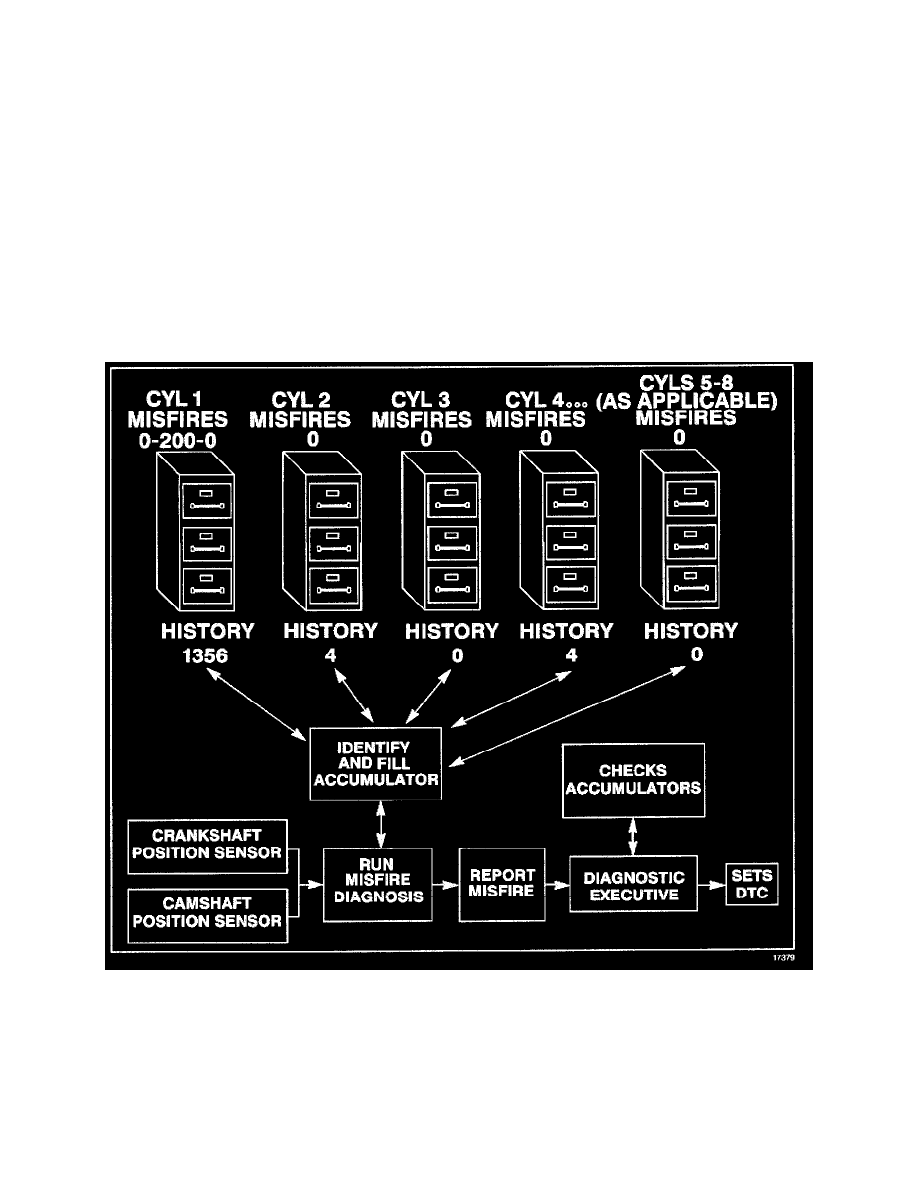
Whenever a cylinder misfires, the misfire diagnostic counts the misfire and notes the crankshaft position at the time the misfire occurred.
A current and a history misfire counter is maintained for each cylinder. The misfire current counters, Misfire Cur #1 - 8, indicate the number of firing
events out of the last 200 cylinder firing events which were misfires. The misfire current counters displays real time data without a misfire DTC stored.
The misfire history counters, Misfire Hist #1 - 8. indicate the total number of cylinder firing events which were misfires. The misfire history counters
display 0 until the misfire diagnostic has failed and a DTC P0300 is set. Once the misfire DTC sets, the misfire history counters will be updated every
200 cylinder firing events. The Misfire counters graphic illustrates how these misfire counters are maintained.
When crankshaft rotation is erratic, the PCM detects a misfire condition. Because of this erratic condition, the data that is collected by the diagnostic can
