Blazer 4WD V6-4.3L VIN X (2005)
Body Control Module: Description and Operation
Body Control System
BODY CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
BCM FUNCTIONS
The body control module (BCM) performs multiple body control functions. The BCM can control devices directly connected to its outputs based on
input information. The BCM evaluates this information and controls certain body control systems by commanding outputs on or off. The BCM control
inputs can be:
-
Sensors and switches that are directly connected to the BCM
-
Class 2 serial data received from other control modules connected to the class 2 serial data link
The BCM is also capable of controlling other vehicle systems that are not directly wired to the BCM. The BCM does this by sending specific
messages on the class 2 serial data link. The control module capable of performing the required function will respond to the BCM message.
The BCM controls these functions:
-
Audible warnings-Refer to Audible Warnings Description and Operation in Instrument Panel, Gages and Console.
-
Automatic door locks-Refer to Power Door Locks Description and Operation in Doors.
-
Automatic headlamp control-Refer to Exterior Lighting Systems Description and Operation in Lighting Systems.
-
Interior lighting-Refer to Interior Lighting Systems Description and Operation in Lighting Systems.
-
Keyless entry (AUO option)-Refer to Keyless Entry System Description and Operation in Keyless Entry.
-
Passlock theft deterrent-Refer to Vehicle Theft Deterrent (VTD) Description and Operation in Theft Deterrent.
-
Retained accessory power (RAP)-Refer to Retained Accessory Power (RAP) Description and Operation.
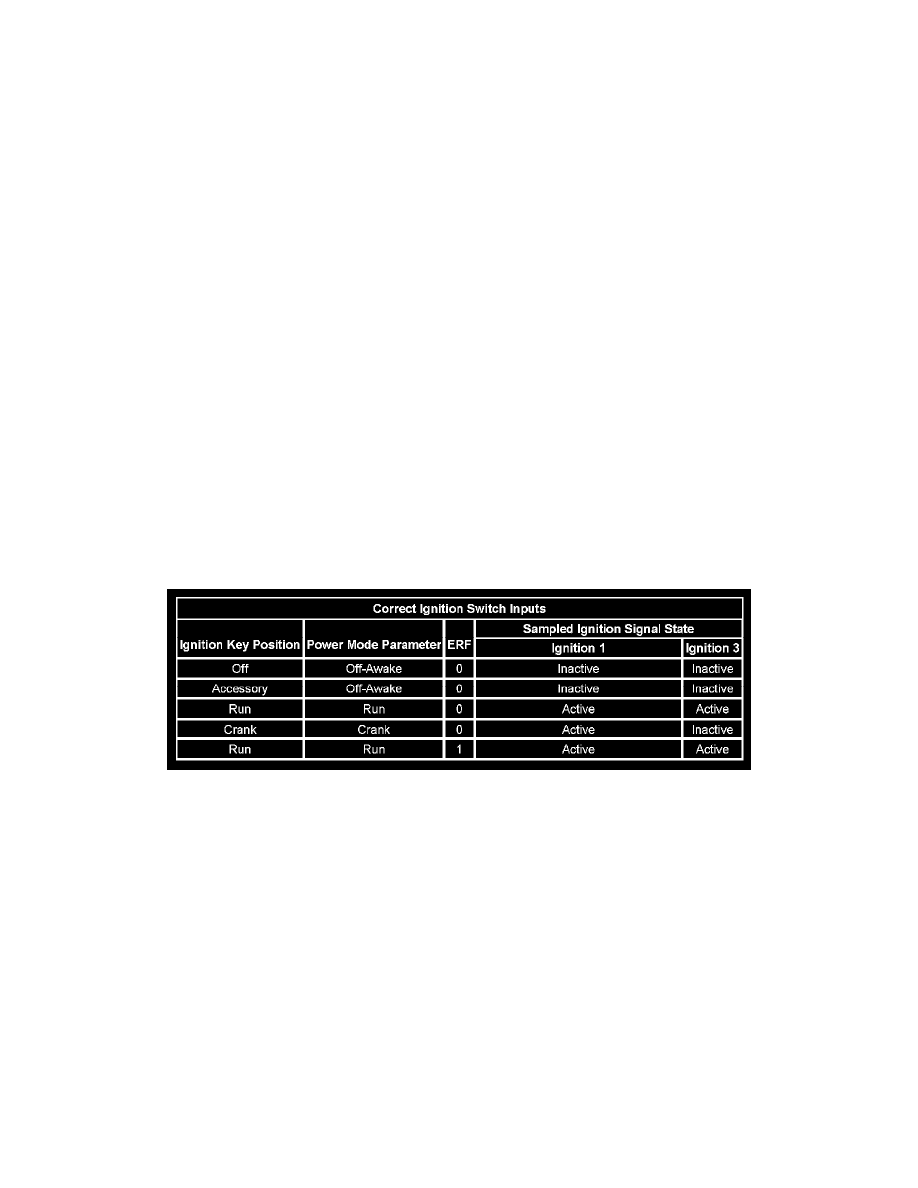
SERIAL DATA POWER MODE
On vehicles that have several control modules connected by serial data circuits, one module is the power mode master (PMM). On this vehicle the
PMM is the body control module (BCM). The BCM receives 2 signals from the ignition switch. These are the Ignition 1 and Ignition 3 circuits.
To determine the correct power mode the BCM uses:
-
The state of these signals/circuits, either switch closed or switch open.
-
The status of the engine run flag (ERF).
Correct Ignition Switch Inputs
The chart indicates the modes detected and transmitted by the BCM.
FAIL-SAFE OPERATION
Since the operation of the vehicle systems depends on the power mode, there is a fail-safe plan in place should the body control module (BCM) fail to
send a power mode message. The fail-safe plan covers modules with discrete ignition signal inputs as well as those modules using exclusively serial
data control of power mode.
SERIAL DATA MESSAGES
The modules that depend exclusively on serial data messages for power modes stay in the state dictated by the last valid BCM message until they
receive the engine status from the powertrain control module (PCM). If the BCM fails, the modules monitor the serial data circuit for the engine run
flag serial data. If the engine run flag serial data is true, indicating that the engine is running, the modules fail-safe to Run. In this state the modules
and their subsystems can support all operator requirements. If the engine run flag serial data is false, indicating that the engine is not running, the
modules fail-safe to OFF-AWAKE. In this state the modules are constantly checking for a change status message on the serial data circuits and can
respond to both local inputs and serial data inputs from other modules on the vehicle.
DISCRETE IGNITION SIGNALS
Those modules that have discrete ignition signal inputs also remain in the state dictated by the last valid BCM message received on the serial data
circuits. They then check the state of their discrete ignition input to determine the current valid state. If the discrete ignition input is active, B+, the
modules will fail-safe to the RUN power mode. If the discrete ignition input is not active, open or 0 voltage, the modules will fail-safe to
