Camaro V8-305 5.0L VIN E TBI (1989)
Fuel Supply Line: Description and Operation
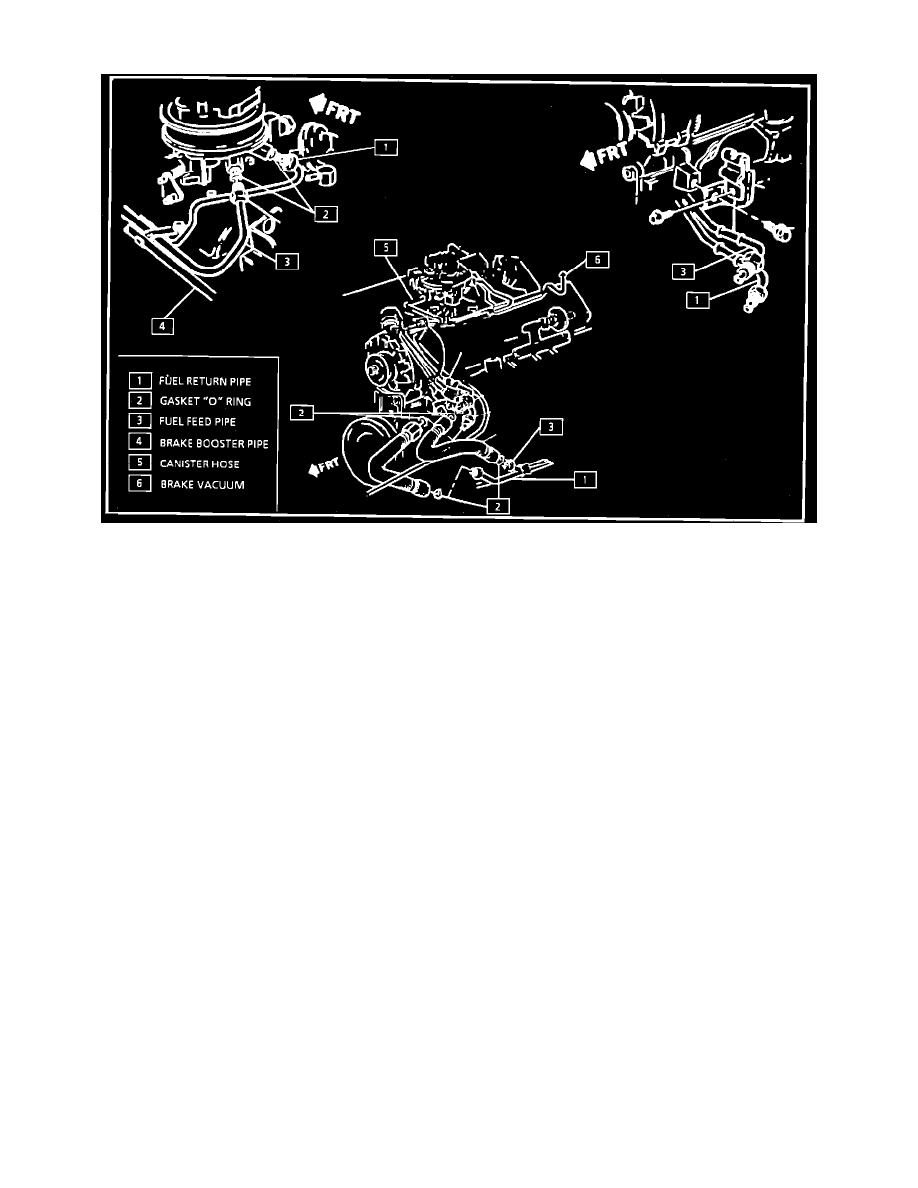
Vehicle Fuel Lines
FUEL TANK
The fuel tank is located under the rear of the vehicle and is the fuel reservoir. The tank has a vertical baffle installed to prevent fuel slosh. The fuel pump
and fuel level sending unit assembly are mounted in the fuel tank as one assembly. The fuel tank assembly also consists of the fuel filler neck and filler
cap.
FUEL FILLER NECK
To help prevent refueling with leaded fuel, the fuel filler neck has a built-in restrictor and deflector. The opening of the restrictor will accept only the
smaller unleaded gasoline nozzle which must be fully inserted to bypass the deflector. Attempted refueling with a leaded fuel nozzle will result in fuel
splashing back out of the filler neck.
FUEL TANK FILLER CAP
The fuel tank filler neck is equipped with a screw type cap. The threaded part of the cap requires several turns counterclockwise to remove. The long
threaded area was designed to allow any remaining fuel tank pressure to escape during the cap removal operation. A ratchet type torque limiting device
prevents over-tightening. To install, turn the cap clockwise until a clicking noise is heard. This signals that the correct torque has been reached and the
cap is fully seated.
NOTE: If a fuel filler cap requires replacement, only a cap with the same features should be used. Failure to use the correct cap can result in a serious
malfunction of the system.
FUEL AND VAPOR PIPES
The fuel feed and return pipes extend from the fuel pump/gauge sending unit to the engine compartment. The pipes are secured to the underbody with
clip and screw assemblies. Both fuel feed pipes and return pipe must be properly routed and retained, and should be inspected occasionally for leaks,
kinks, or dents. If evidence of dirt is found in the fuel injector assembly or fuel filter during disassembly, the pipes should be disconnected and blown
out. Check the fuel strainer on the fuel pump/fuel gauge assembly for damage or omission.
The vapor pipe extends from the fuel pump/gauge assembly to the canister. However, it may not follow the same route as the fuel feed pipe.
Due to the fact that the fuel pipes/hoses are under high pressure on fuel injected systems these systems require special consideration for service.
NOTE: All fuel feed and return line attachments in the system are screw type fittings. Always use a backup wrench when loosening or tightening the
