Corvette V8-6.2L (2008)
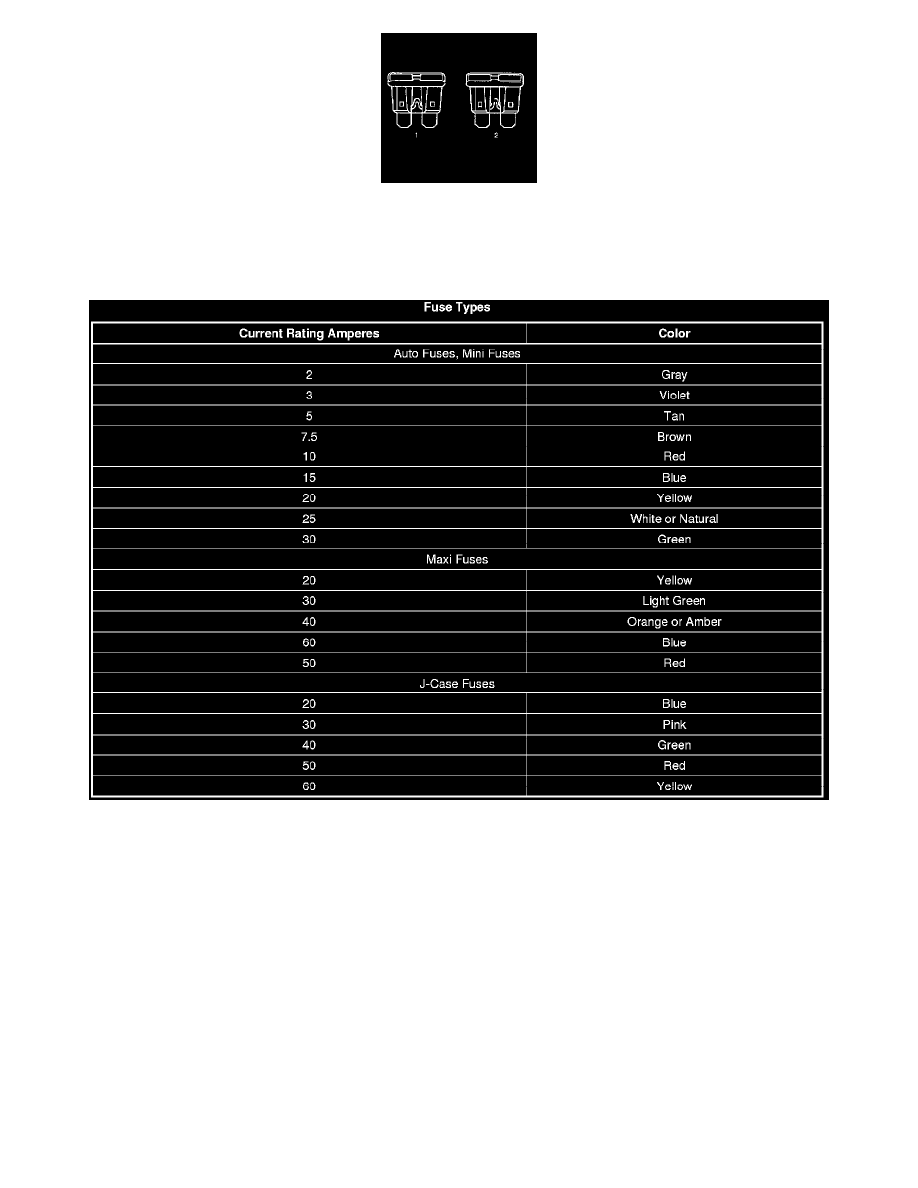
The fuse is the most common method of an automotive wiring circuit protection. Whenever there is an excessive amount of current flowing through a
circuit the fusible element will melt and create an open or incomplete circuit. Fuses are an one time protection device and must be replaced each time the
circuit is overloaded. To determine if a fuse is open, remove the suspected fuse and examine the element in the fuse for an open (2). If not broken (1),
also check for continuity using a DMM or a continuity tester. If the element is open or continuity is suspect, replace the fuse with one of equal current
rating.
Circuit Protection - Fusible Links
Circuit Protection - Fusible Links
Fusible link is wire designed to melt and break continuity when excessive current is applied. It is often located between or near the battery and starter or
electrical center. Use a continuity tester or a DMM at each end of the wire containing the fusible link in order to determine if it is broken. If broken, it
must be replaced with fusible link of the same gage size.
Repairing a Fusible Link
Important: Fusible links cut longer than 225 mm (approximately 9 in) will not provide sufficient overload protection.
Refer to Splicing Copper Wire Using Splice Clips (See: Testing and Inspection/Component Tests and General Diagnostics).
Flat Wire Repairs
Flat Wire Repairs
