Express 3/4 Ton Van V8-4.8L VIN V (2003)
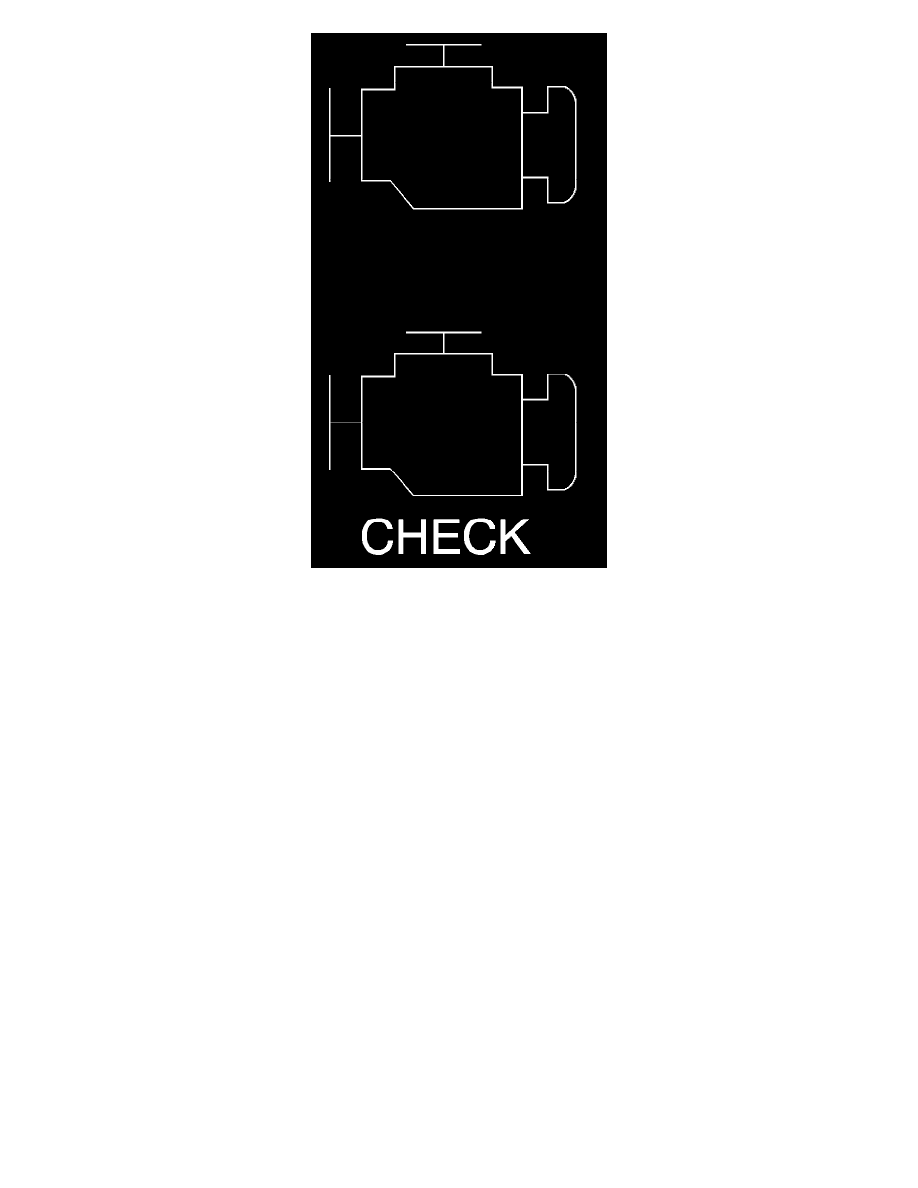
The malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) is located in the instrument panel cluster. The MIL will display as either SERVICE ENGINE SOON or one of
the following symbols when commanded ON:
The MIL indicates that an emissions related fault has occurred and vehicle service is required.
The following is a list of the modes of operation for the MIL:
-
The MIL illuminates when the ignition is turned ON, with the engine OFF. This is a bulb test to ensure the MIL is able to illuminate.
-
The MIL turns OFF after the engine is started if a diagnostic fault is not present.
-
The MIL remains illuminated after the engine is started if the control module detects a fault. A diagnostic trouble code (DTC) is stored any time
the control module illuminates the MIL due to an emissions related fault. The MIL turns OFF after three consecutive ignition cycles in which a
Test Passed has been reported for the diagnostic test that originally caused the MIL to illuminate.
-
The MIL flashes if the control module detects a misfire condition which could damage the catalytic converter.
-
When the MIL is illuminated and the engine stalls, the MIL will remain illuminated as long as the ignition is ON.
-
When the MIL is not illuminated and the engine stalls, the MIL will not illuminate until the ignition is cycled OFF and then ON.
TRIP
A trip is an interval of time during which the diagnostic test runs. A trip may consist of only a key cycle to power up the PCM, allow the diagnostic to
run, then cycle the key off to power down the PCM. A trip may also involve a PCM power up, meeting specific conditions to run the diagnostic test,
then powering down the PCM. The definition of a trip depends upon the diagnostic. Some diagnostic tests run only once per trip (i.e., catalyst
monitor) while other tests run continuously during each trip (i.e. misfire).
WARM-UP CYCLE
The PCM uses warm-up cycles to run some diagnostics and to clear any diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). A warm-up cycle occurs when the engine
coolant temperature increases 22°C (40°F) from the start-up temperature. The engine coolant must also achieve a minimum temperature of 71°C (160
°F). The PCM counts the number of warm-up cycles in order to clear the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL). The PCM will clear the DTCs when 40
consecutive warm-up cycles occur without a malfunction.
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTCs)
The PCM is programmed with test routines that test the operation of the various systems the PCM controls. Some tests monitor internal PCM
functions. Many tests are run continuously. Other tests run only under specific conditions, referred to as Conditions for Running the DTC. When the
vehicle is operating within the conditions for running a particular test, the PCM monitors certain parameters and determines if the values are within an
expected range. The parameters and values considered outside the range of normal operation are listed as Conditions for Setting the DTC. When the
Conditions for Setting the DTC occur, the PCM executes the Action Taken When the DTC Sets. Some DTCs alert the driver via the MIL or a
message. Other DTCs do not trigger a driver warning, but are stored in memory. The PCM also saves data and input parameters when most DTCs are
