K 2500 Suburban 4WD V8-6.0L VIN U (2001)
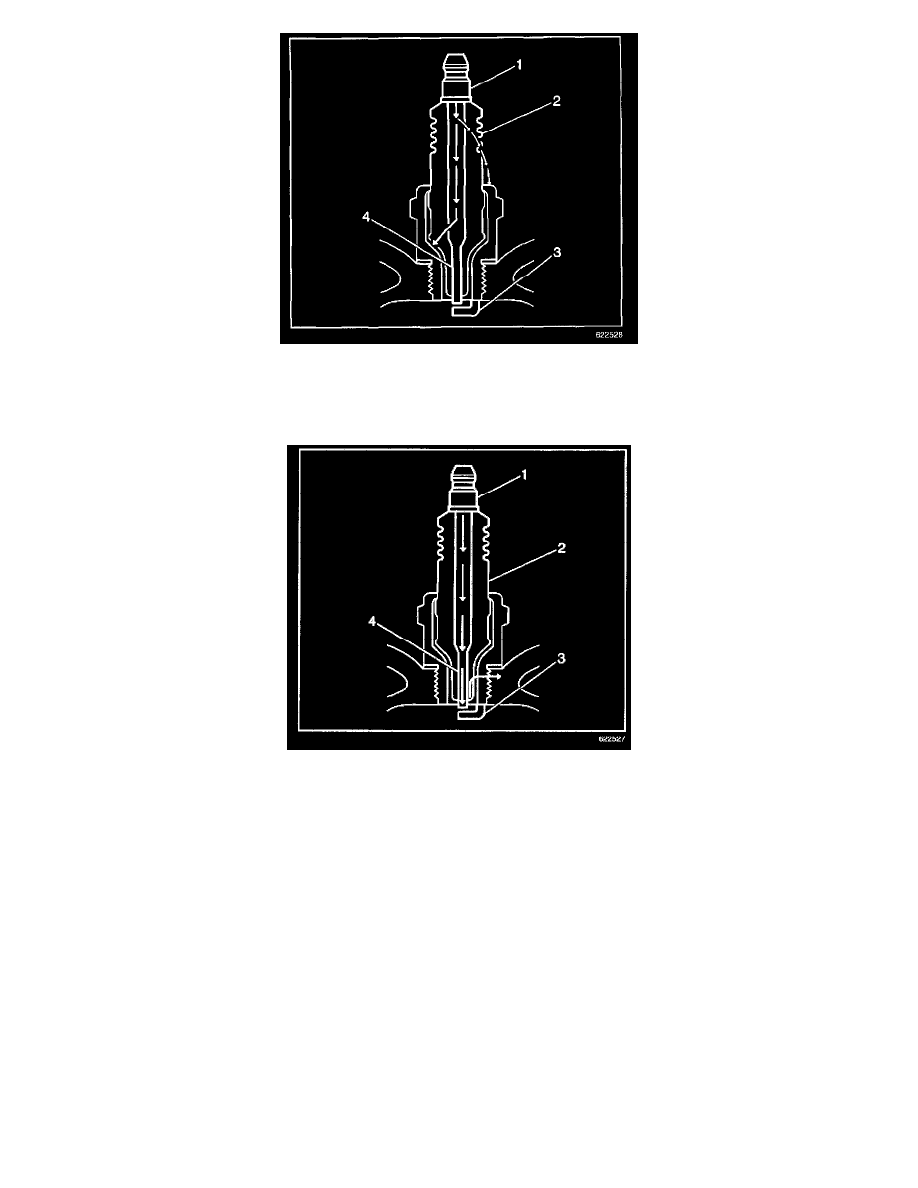
-
Inspect the spark plug boot for damage.
-
Inspect the spark plug recess area of the cylinder head for moisture, such as oil, coolant, or water. A spark plug boot that is saturated causes
arcing to ground.
^
Inspect the insulator (2) for cracks. All or part of the electrical charge may arc through the crack instead of the electrodes (3, 4).
^
Inspect for evidence of improper arcing.
-
Measure the gap between the center electrode (4) and the side electrode (3) terminals. Refer to Ignition System Specifications. An excessively
wide electrode gap can prevent correct spark plug operation.
-
Inspect for the correct spark plug torque. Refer to Ignition System Specifications. Insufficient torque can prevent correct spark plug operation.
An over torqued spark plug, causes the insulator (2) to crack.
-
Inspect for signs of tracking that occurred near the insulator tip instead of the center electrode (4).
-
Inspect for a broken or worn side electrode (3).
-
Inspect for a broken, worn, or loose center electrode (4) by shaking the spark plug.
^
A rattling sound indicates internal damage.
^
A loose center electrode (4) reduces the spark intensity.
-
Inspect for bridged electrodes (3, 4). Deposits on the electrodes (3, 4) reduce or eliminates the gap.
-
Inspect for worn or missing platinum pads on the electrodes (3, 4), if equipped.
-
Inspect for excessive fouling.
^
Inspect the spark plug recess area of the cylinder head for debris. Dirty or damaged threads can cause the spark plug not to seat correctly during
installation.
SPARK PLUG VISUAL INSPECTION
