K Tahoe 4WD V8-4.8L VIN V (2000)
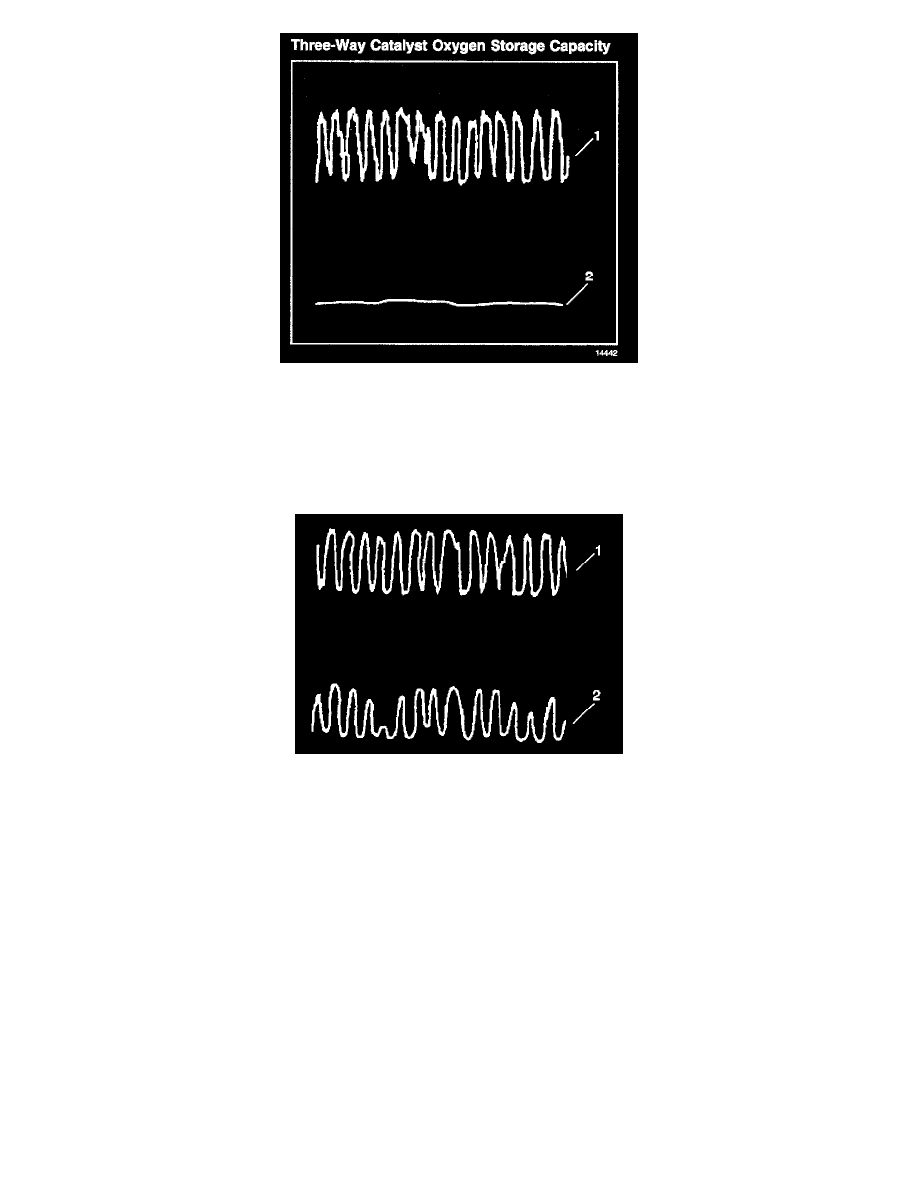
Three-Way Catalyst Oxygen Storage Capacity
The PCM must monitor the 3-way Catalyst System (TWC) for efficiency. In order to accomplish this, the PCM monitors the pre-catalyst and
post-catalyst oxygen sensors. When the TWC is operating properly, the post-catalyst (2) oxygen sensor shows significantly less activity than the
pre-catalyst (1) oxygen sensor. The TWC stores oxygen during the normal reduction and oxidation process. The TWC releases oxygen during its normal
reduction and oxidation process. The PCM calculates the oxygen storage capacity using the difference between the pre-catalyst and post-catalyst oxygen
sensor voltage levels.
Whenever the sensor activity of the post-catalyst (2) oxygen sensor nears the sensor activity of the pre-catalyst (1) oxygen sensor, the catalysts efficiency
is degraded.
After market HO2S characteristics may be different from the original equipment manufacturer sensor. This may lead to a false pass or a false fail of the
catalyst monitor diagnostic. Similarly, if an after market catalyst does not contain the same amount of precious metal content as the original part, the
correlation between oxygen storage and conversion efficiency may be altered enough to set a false DTC.
Misfire Monitor Diagnostic Operation
The misfire monitor diagnostic is based on crankshaft rotational velocity, aka reference period, variations. The PCM determines crankshaft rotational
velocity using the Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor and Camshaft Position (CMP) sensor. When a cylinder misfires, the crankshaft slows down
momentarily. By monitoring the crankshaft and camshaft position sensor signals, the PCM can calculate when a misfire occurs.
For a non-catalyst damaging misfire, the diagnostic is required to monitor a misfire present for between 1,000-3,200 engine revolutions.
For catalyst damage misfire, the diagnostic responds to the misfire within 200 engine revolutions.
Rough roads may cause false misfire detection. A rough road applies sudden torque variations to the drive wheels and drivetrain. This torque can
intermittently decrease the crankshaft rotational velocity. The Antilock Braking (ABS) system detects uneven speed between the vehicles wheels and
sends data via the serial data bus to the PCM to disable the misfire monitor until the rough road is no longer detected.
On automatic transmission equipped vehicles, the Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) disables whenever a misfire is detected. Disabling the TCC isolates
the engine from the rest of the drive line and minimizes the effect of the drive wheel inputs on crankshaft rotation.
