300M V6-3.5L VIN G (2000)
^
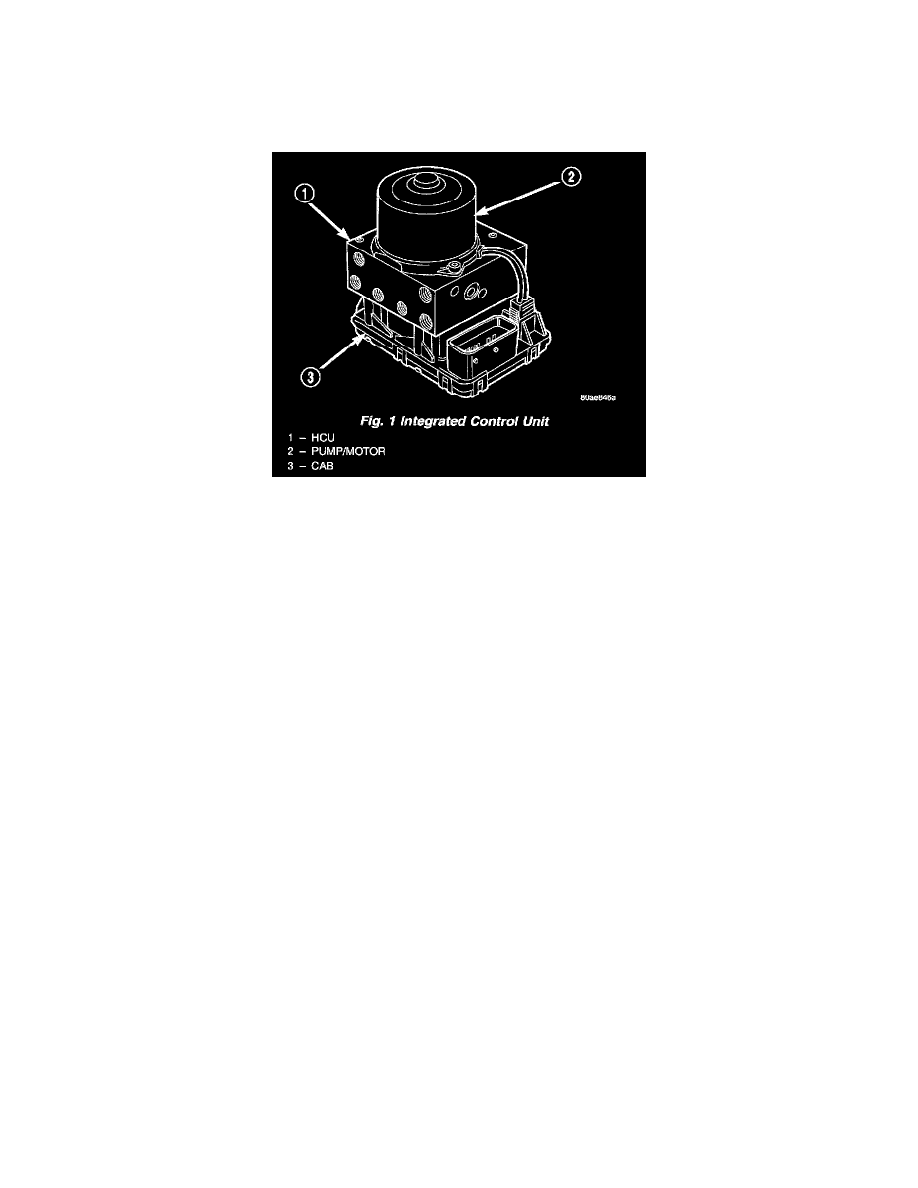
HYDRAULIC CONTROL UNIT (HCU)
For information on the ICU's hydraulic circuits, refer to Antilock Brake System, Description and Operation.
CONTROLLER ANTILOCK BRAKE (CAB)
DESCRIPTION
The Controller Antilock Brake (CAB) is a microprocessor-based device which monitors the ABS system during normal braking and controls it when
the vehicle is in an ABS stop. The CAB is mounted to the bottom of the HCU. The CAB uses a 25-way electrical connector on the vehicle wiring
harness. The power source for the CAB is through the ignition switch in the RUN or ON position. The CAB is on the PCI bus.
OPERATION
The primary functions of the CAB are to:
^
Monitor the antilock brake system for proper operation.
^
Detect wheel locking or wheel slipping tendencies by monitoring the speed of all four wheels of the vehicle.
^
Control fluid modulation to the wheel brakes while the system is in an ABS mode.
^
Store diagnostic information.
^
Provide communication to the DRB scan tool while in diagnostic mode.
^
Illuminate the amber ABS warning lamp.
^
(with traction control only) Illuminate the TRAC ON lamp in the message center on the instrument panel when a traction control event occurs.
^
(with traction control only) Illuminate the TRAC OFF lamp when the amber ABS warning lamp illuminates.
The CAB constantly monitors the antilock brake system for proper operation. If the CAB detects a fault, it will turn on the amber ABS warning lamp
and disable the antilock braking system. The normal base braking system will remain operational.
NOTE: If the vehicle is equipped with traction control, the TRAC OFF lamp will illuminate anytime the amber ABS warning lamp illuminates.
The CAB continuously monitors the speed of each wheel through the signals generated by the wheel speed sensors to determine if any wheel is
beginning to lock. When a wheel locking tendency is detected, the CAB commands the CAB command coils to actuate. The coils then open and close
the valves in the HCU that modulate brake fluid pressure in some or all of the hydraulic circuits. The CAB continues to control pressure in individual
hydraulic circuits until a locking tendency is no longer present.
The CAB contains a self-diagnostic program that monitors the antilock brake system for system faults. When a fault is detected, the amber ABS
warning lamp is turned on and the fault Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) is then stored in a diagnostic program memory. These DTC's will remain in
the CAB memory even after the ignition has been turned off. The DTC's can be read and cleared from the CAB memory by a technician using the
DRB scan tool. If not cleared with a DRB scan tool, the fault occurrence and DTC will be automatically cleared from the CAB memory after the
identical fault has not been seen during the next 3,600 miles.
CONTROLLER ANTILOCK BRAKE INPUTS
^
wheel speed sensors (four)
^
brake lamp switch
^
ignition switch
^
system and pump voltage
^
ground
^
traction control switch (if equipped)
^
diagnostic communication (PCI)
