300M Special V6-3.5L VIN G (2002)
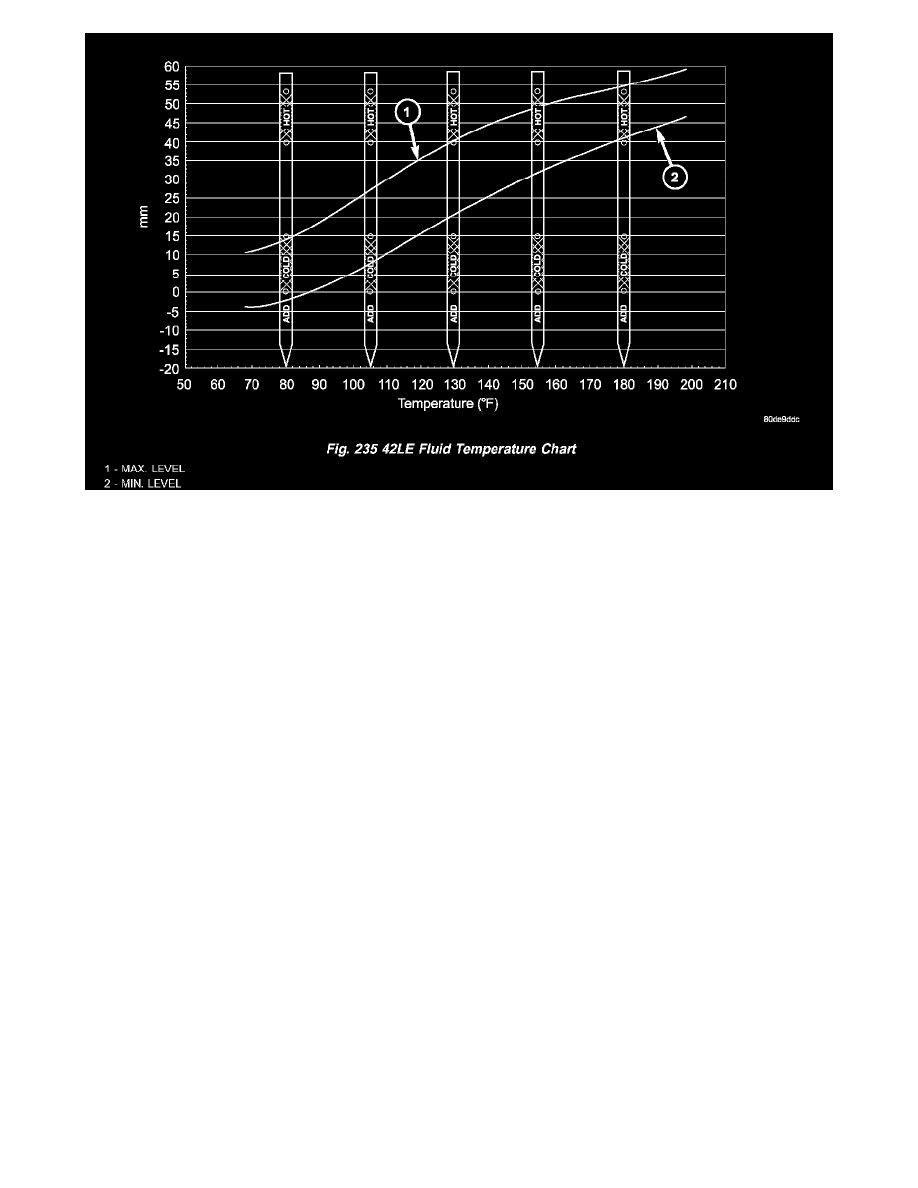
6. Adjust transmission fluid level shown on the dipstick according to the chart (Fig. 235). Use only Mopar (R) ATF+4 Automatic Transmission Fluid
(MS 9602).
7. Check transmission for leaks.
Low fluid level can cause a variety of conditions because it allows the pump to take in air along with the fluid. As in any hydraulic system, air bubbles
make the fluid spongy, therefore, pressures will be low and build up slowly.
Improper filling can also raise the fluid level too high. When the transaxle has too much fluid, the gears churn up foam and cause the same conditions
which occur with a low fluid level.
In either case, air bubbles can cause overheating and/or fluid oxidation, and varnishing. This can interfere with normal valve, clutch, and accumulator
operation. Foaming can also result in fluid escaping from the transaxle vent where it may be mistaken for a leak.
Along with fluid level, it is important to check the condition of the fluid. When the fluid smells burned, and is contaminated with metal or friction
material particles, a complete transaxle recondition is needed.
Be sure to examine the fluid on the dipstick closely. If there is any doubt about its condition, drain out a sample for a double check.
Mopar (R) ATF+4 (Automatic Transmission Fluid Type 9602) when new is red in color. The ATF is dyed red so it can be identified from other fluids
used in the vehicle such as engine oil or antifreeze. The red color is not permanent and is not an indicator of fluid condition. As the vehicle is driven, the
ATF will begin to look darker in color and may eventually become brown. This is normal. ATF+4 also has a unique odor that may change with age.
Consequently, odor and color cannot be used to indicate the fluid condition or the need for a fluid change.
After the fluid has been checked, seat the dipstick fully to seal out water and dirt.
