Sebring LX Convertible L4-2.4L VIN X (2002)
EGR Valve: Description and Operation
The EGR valve consists of three major components. First there is the pintle, valve seat, and housing which contains and regulates the gas flow. Second
there is the armature, return spring, and solenoid coil to provide the operating force to regulate the flow by changing the pintle position. The solenoid
coil assembly is in parallel with a diode and connects to the two connectors in the connector assembly The third major component which senses pintle
position and is connected to the three connectors in the electrical connector is the EGR Monitor.
The engines use Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) systems. The EGR system reduces Oxides Of Nitrogen (NOx) in engine exhaust and helps prevent
detonation (engine knock). Under normal operating conditions, engine cylinder temperature can reach more than 3000 °F. Formation of NOx increases
proportionally with combustion temperature. To reduce the emission of these oxides, the cylinder temperature must be lowered. The system allows a
predetermined amount of hot exhaust gas to recirculate and dilute the incoming air/fuel mixture. The diluted air/fuel mixture reduces peak flame
temperature during combustion.
This system does not allow EGR at idle.
A failed or malfunctioning EGR system can cause engine spark knock, sags or hesitation, rough idle, engine stalling and increased emissions.
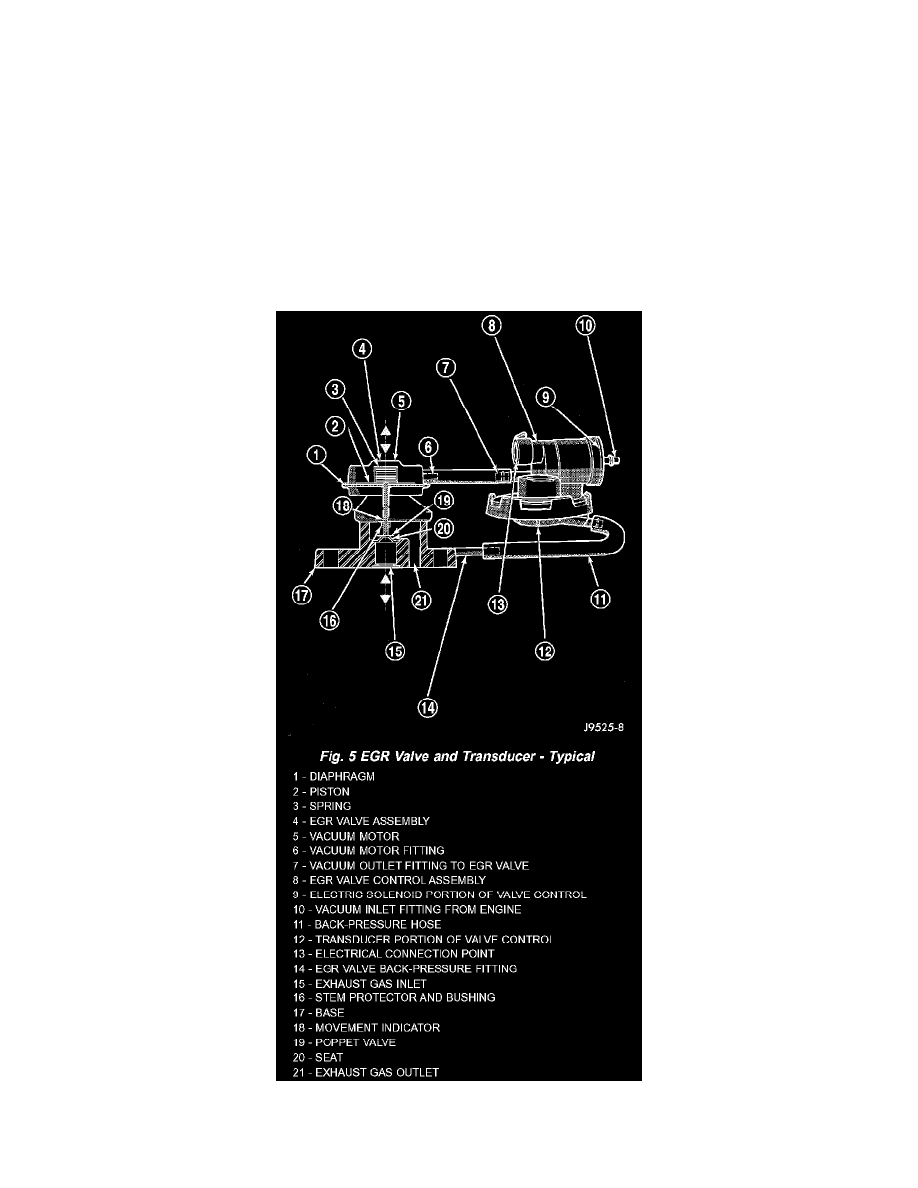
Fig.5 EGR Valve And Transducer - Typical
4 - CYLINDER The electric EGR transducer contains an electrically operated solenoid and a back-pressure transducer. The Powertrain Control Module
