Sebring Sedan L4-2.4L (2007)
Wheel Speed Sensor: Description and Operation
Rear Wheel Speed
Description
DESCRIPTION
The antilock brake system uses two-wire wheel speed sensors, known as active wheel speed sensors. The sensors use an electronic principle known as
magnetoresistive to help increase performance and durability. The sensors convert wheel speed into a small digital signal. A Wheel Speed Sensor (WSS)
is used at each wheel. A magnetic pole encoder serves as the trigger mechanism for each sensor. At each wheel of the vehicle there is one wheel speed
sensor and one encoder.
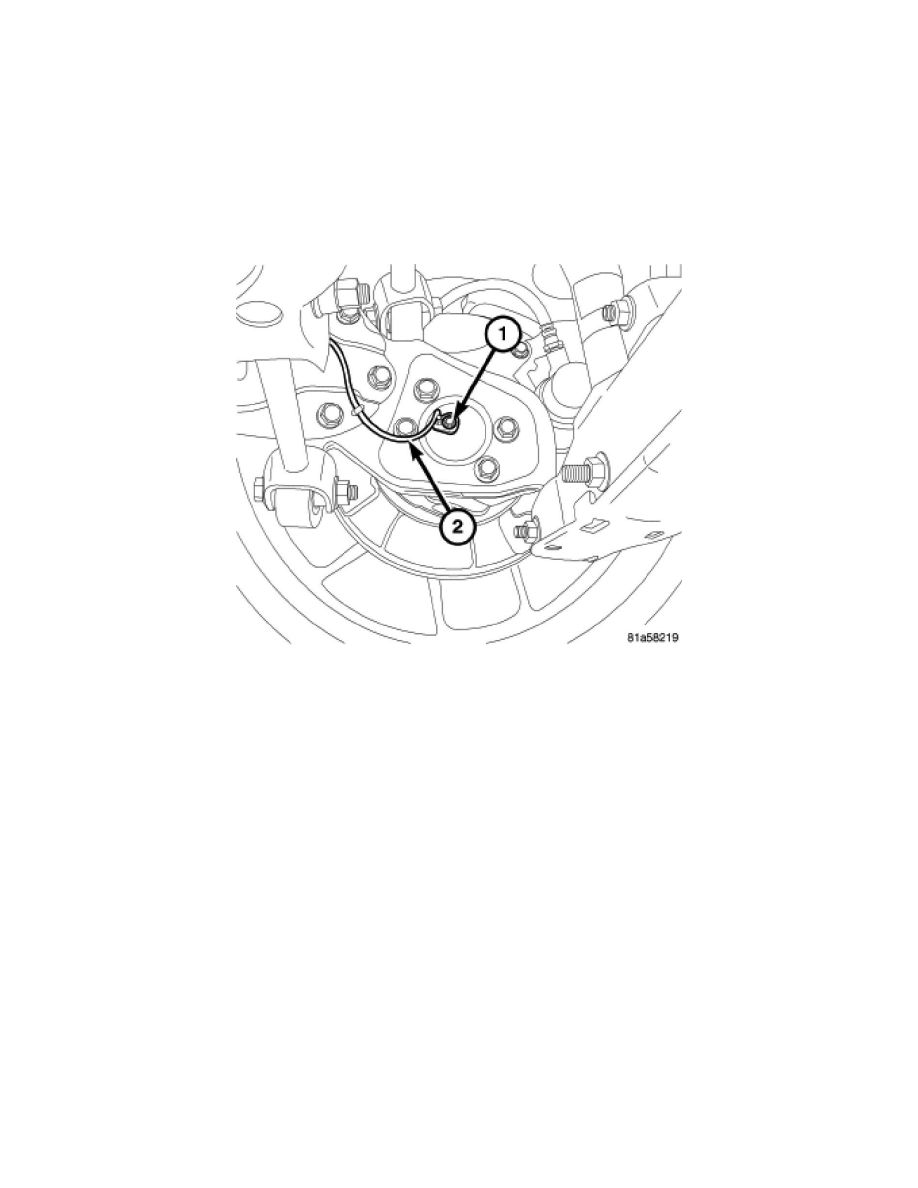
The rear wheel speed sensor (2) head is mounted to the rear of the hub and bearing by a screw (1). The encoder is integral to the hub and bearing
assembly. The encoder is serviced as part of the rear hub and bearing.
WSS air gaps are not adjustable.
Operation
OPERATION
The ABM sends 12 volts to power an Integrated Circuit (IC) in the sensor. The IC supplies a constant 7 mA power supply to the ABM. The relationship
of the magnetic pole encoder to the permanent magnet in the sensor, signals the IC to enable a second 7 mA power supply. The output of the sensor, sent
to the ABM, is a DC voltage signal with changing voltage and current levels. The ground for the IC and the current sense circuit is provided by the
ABM.
When a pole is properly aligned with the sensor, the voltage signal is approximately 0.8 volts and a constant 7 mA current is sent to the ABM. As the
magnetic pole encoder rotates, the encoder shifts the magnetic field and the IC enables a second 7 mA current source. The ABM senses a voltage signal
of approximately 1.6 volts and 14 mA. The ABM measures the amperage of the digital signal for each wheel. The resulting signal is interpreted by the
ABM as the wheel speed.
