Sebring Sedan V6-2.7L VIN R (2004)
Axle Shaft: Description and Operation
HALF SHAFT
DESCRIPTION
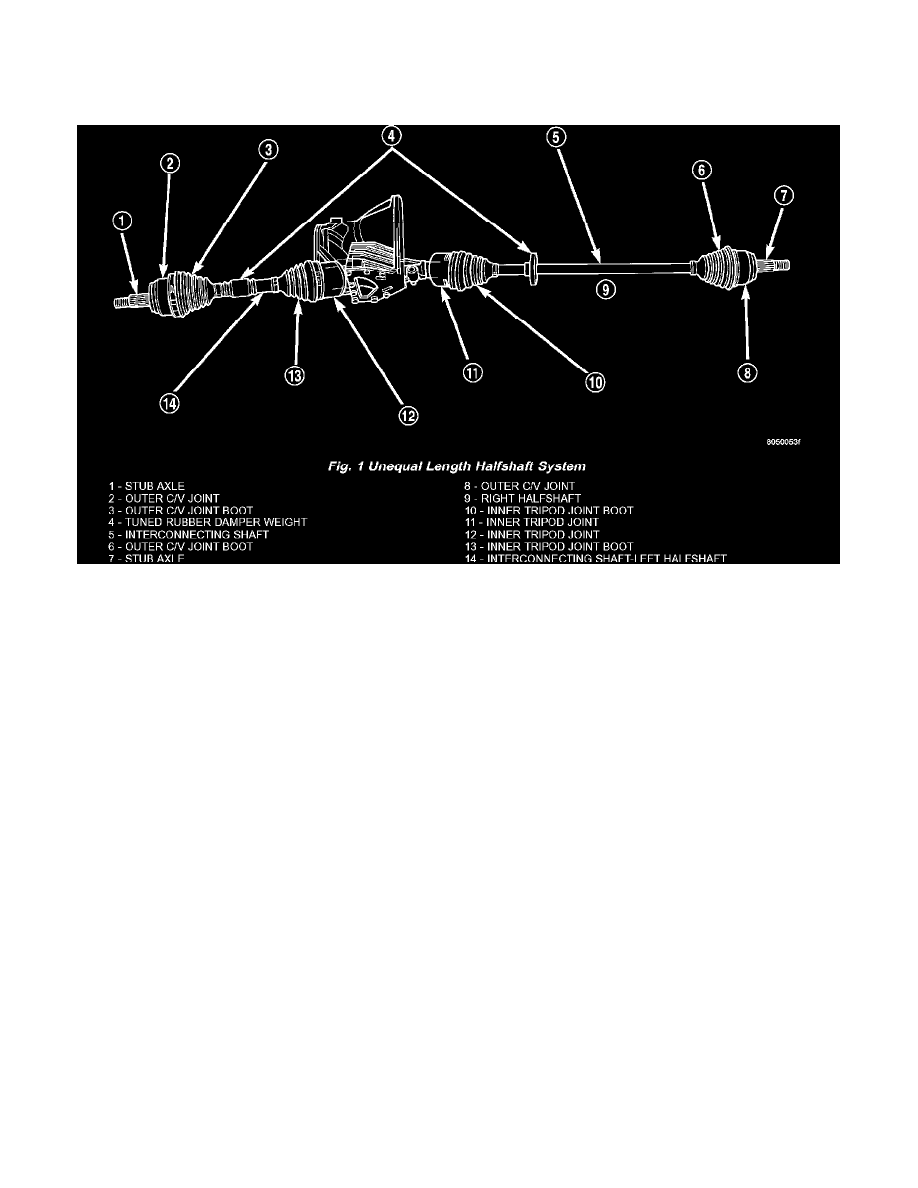
This vehicle is equipped with an unequal length halfshaft system (Fig. 1). These halfshafts consist of two constant velocity joints connected by a solid
shaft. A solid short interconnecting shaft is used on the left side. A long solid interconnecting shaft is used on the right side.
Some halfshafts use a tuned rubber damper weight. When replacing a halfshaft assembly, be sure the replacement halfshaft has the same damper
weight as the original.
Both halfshaft assemblies use the same type of inner and outer joints. The inner joint of both halfshaft assemblies is a tripod joint, and the outer joint
of both halfshaft assemblies is a Rzeppa joint. Both tripod joints and Rzeppa joints are true Constant Velocity (C/V) joint assemblies. The inner tripod
joint allows for the changes in halfshaft length through the jounce and rebound travel of the front suspension.
On vehicles equipped with ABS brakes, the outer C/V joint is equipped with a tone wheel used to determine vehicle speed for ABS brake operation.
The inner tripod joint of both halfshafts is splined into the transaxle side gears. The inner tripod joints are retained in the side gears of the transaxle
using a snap ring located in the stub shaft of the tripod joint. The outer C/V joint has a stub shaft that is splined into the wheel hub and retained by a
steel hub nut.
OPERATION
Halfshaft assemblies are designed to transmit power from the transaxle to the front wheels, while allowing for powertrain and suspension flex.
