Town & Country AWD V6-3.8L VIN L (2003)
When the front wheels lose traction and begin to slip, the propeller shaft and rear axle pinion speed difference decreases to zero. At this point the input
shaft (cam) becomes the driving member of the BOC (Fig. 30), compressing the rollers against the outer race. This locks the input shaft with the outer
race and transmits torque to the housing of the viscous coupler, that in turn transmits torque to the rear axle pinion. It should also be noted that when the
device is locked, the inner shaft and the outer race are rotating at the same speed. The rollers are pinched at this point and will stay locked until a torque
reversal (no front wheel slip) occurs. When locked, the viscous coupler slips during the torque transfer and the amount of torque transferred is dependent
on the coupling characteristic and the amount of front wheel slip.
STEADY STATE, HIGH SPEED, NO WHEEL SLIP
The roller cage positions the rollers on the input shaft flats during low and high speed overrunning and during initial BOC lockup. The roller cage is
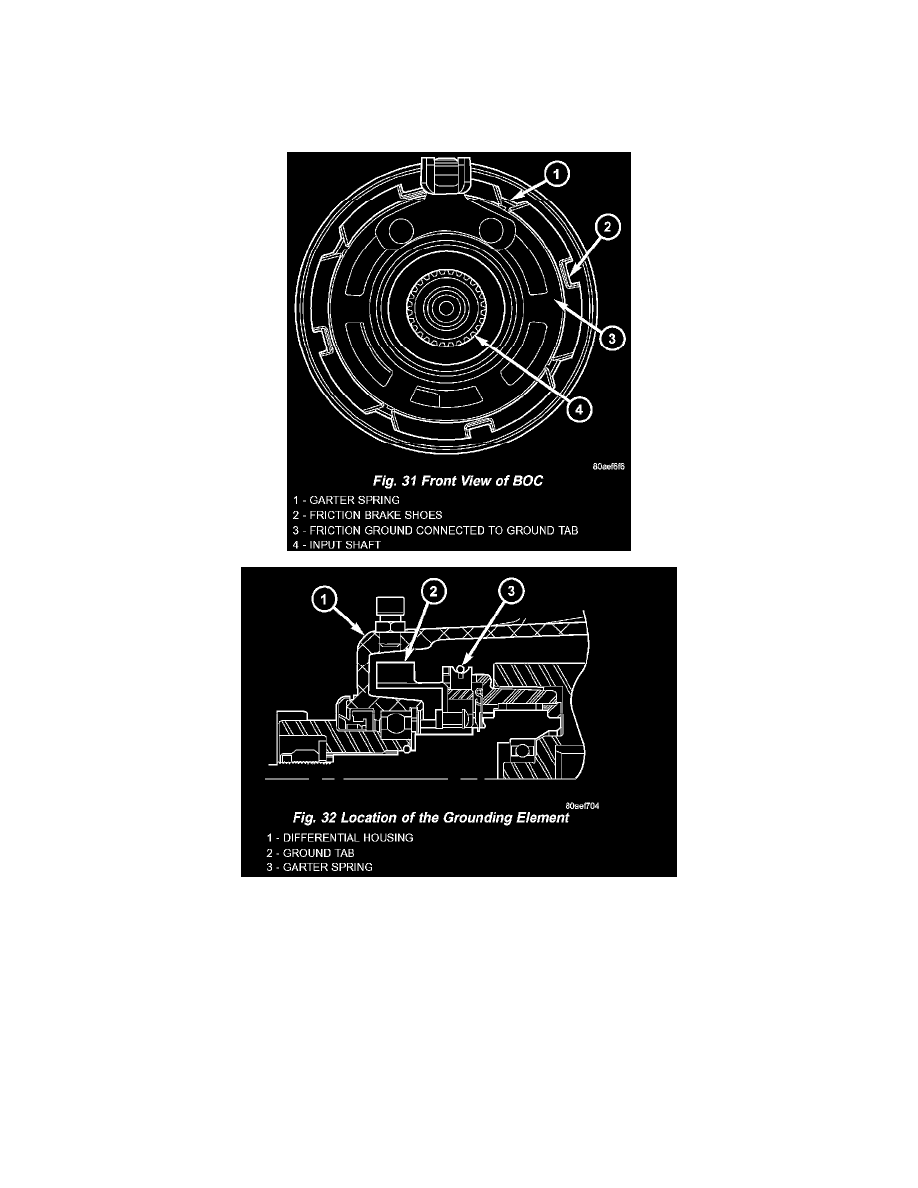
rotating at input shaft (propeller shaft) speed at all times. At low speeds, the friction shoes (Fig. 31) are pressed against the friction ground via the garter
spring (Fig. 32), creating a drag force on the roller cage. The drag force positions the cage, which in turn positions the rollers to one side of the flat. The
direction of this drag force (position of the roller) is dependent on the input (propeller shaft) rotational direction. Since the rollers are always in contact
with the outer race, due to centrifugal forces, the rollers want to follow the outer race due to drag. During overrunning operation, the outer race is
rotating faster than the input; causing the rollers to want to traverse the flat from one side to the other. During low speeds, the brake shoes counteract this
effect. To avoid excessive wear, the ground shoes are designed to lift off from the friction ground due to centrifugal forces at higher rotational speeds.
