Leganza CDX L4-2.2L DOHC D-TEC MFI (1999)
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor: Description and Operation
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE SENSOR
The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor measures the changes in the intake manifold pressure which result from engine load and speed changes
and converts these to a voltage output.
A closed throttle on engine coast down produces a relatively low MAP output. MAP is the opposite of vacuum. When manifold pressure is high, vacuum
is low. The MAP sensor is also used to measure barometric pressure. This is performed as part of MAP sensor calculations. With the ignition ON and the
engine not running, the engine control module (ECM) will read the manifold pressure as barometric pressure and adjust the air/fuel ratio accordingly.
This compensation for altitude allows the system to maintain driving performance while holding emissions low. The barometric function will update
periodically during steady driving or under a wide open throttle condition. In the case of a fault in the barometric portion of the MAP sensor, the ECM
will set to the default value.
A failure in the MAP sensor circuit sets a diagnostic trouble codes P0107, P0108 or P0106.
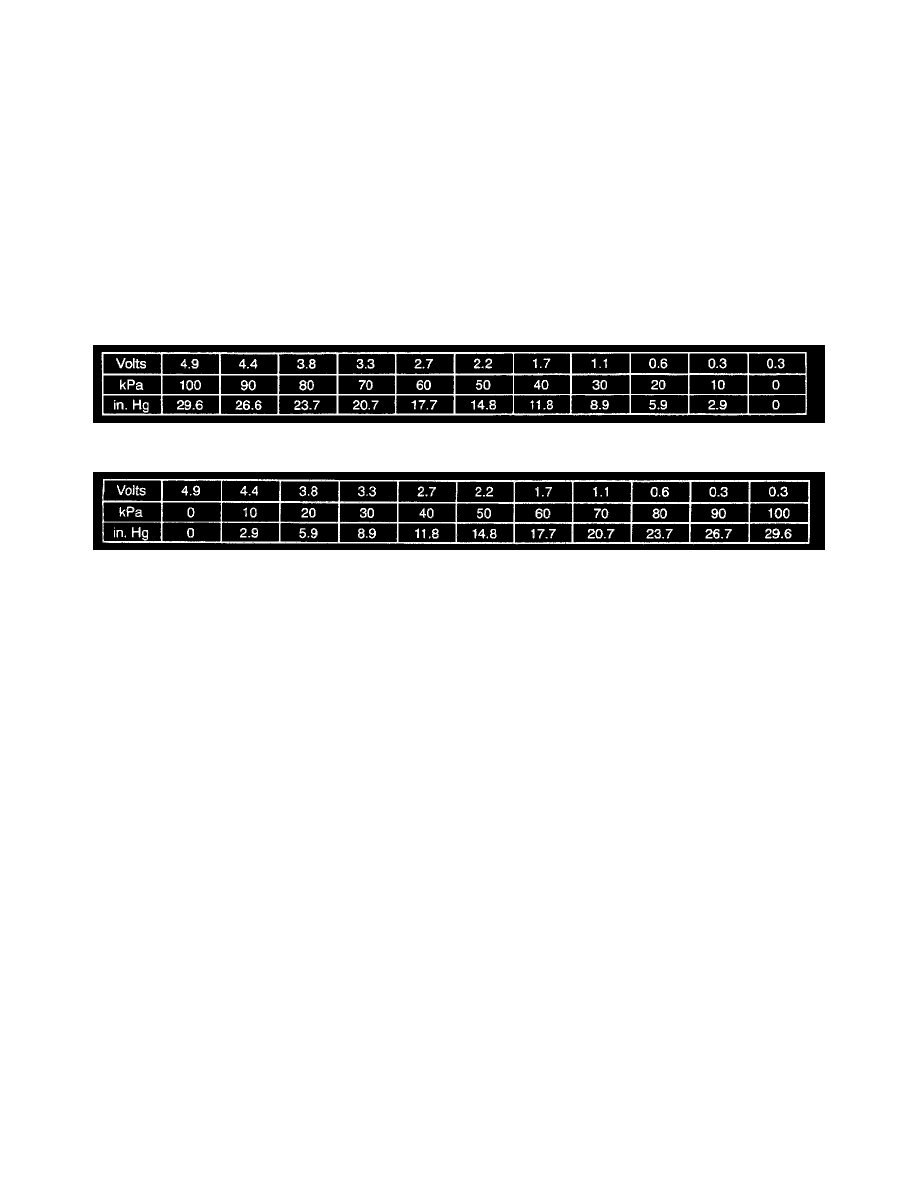
The following tables show the difference between absolute pressure and vacuum related to MAP sensor output, which appears as the top row of both
tables.
MAP
VACUUM
