Challenger V8-5.7L (2010)
The torque converter lockup clutch regulating valve (6) regulates the torque converter lock-up clutch working pressure (p-TCC) in relation to the torque
converter clutch control pressure (p-S/TCC). According to the size of the working pressure (p-A), the torque converter lockup clutch is either Engaged,
Disengaged, or Slipping. When the regulating valve (6) is in the lower position, lubricating oil flows through the torque converter and oil cooler (7) into
the transmission (torque converter lockup clutch unpressurized). In its regulating position (slipping, torque converter lockup clutch pressurized), a
reduced volume of lubricating oil flows through the annular passage bypassing the torque converter and passing direct through the oil cooler into the
transmission. The rest of the lubricating oil is directed via the throttle "a" into the torque converter in order to cool the torque converter lockup clutch.
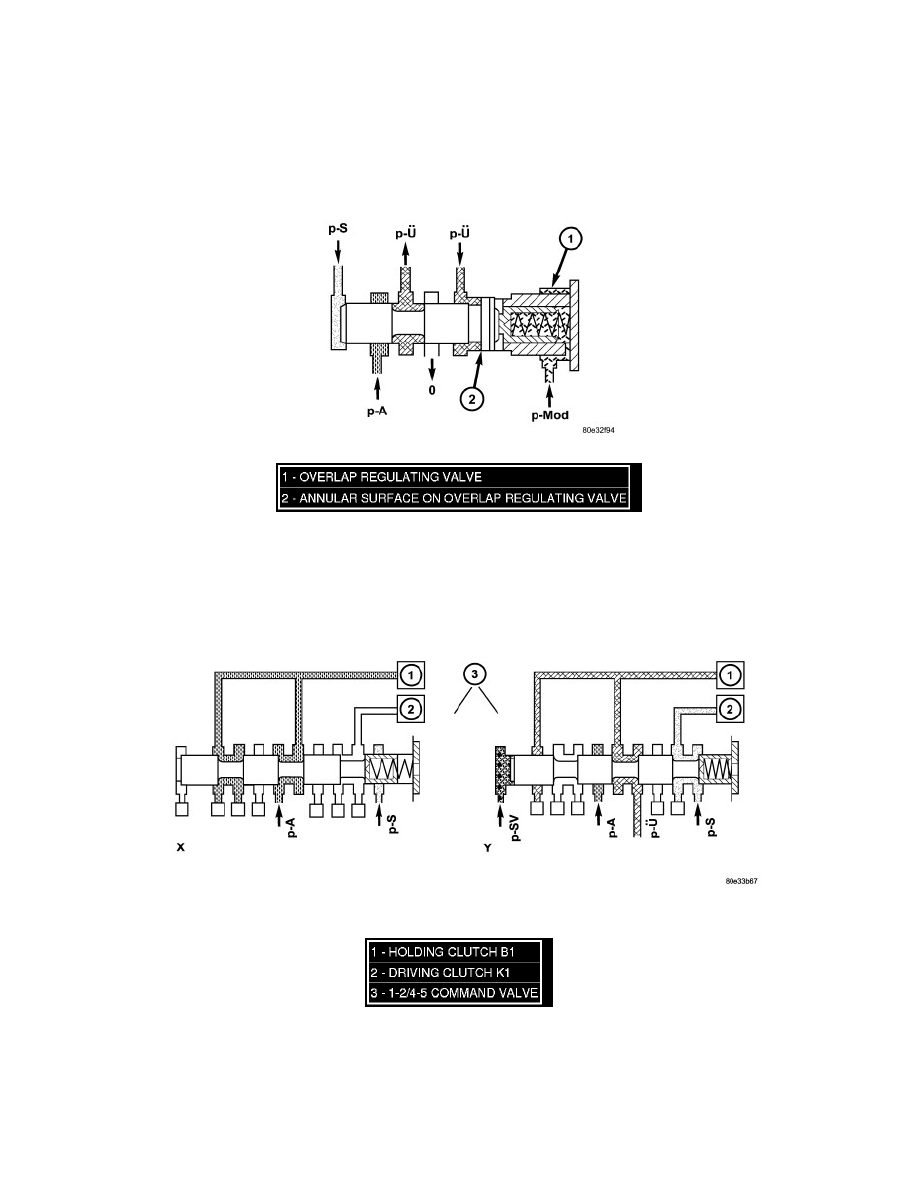
Overlap Regulating Valve
During the shift phase the pressure in the deactivating shift actuator is regulated in relation to the engine load (modulating pressure, p-Mod) and the
pressure in the activating actuator. The regulated pressure is inversely proportional to the transfer capacity of the activating shift actuator (regulated
overlap).
Command Valve
Command Valve
When the end face is unpressurized (stationary phase), the working pressure (p-A) is directed to the actuated shift element. If the end face of the
command valve is subjected to the shift valve pressure (p-SV) (shift phase), then the shift pressure (p-S) is switched to the activating element and the
overlap pressure (p-U) is switched to the deactivating element.
Shift Valve Holding Pressure
