Diplomat V8-318 5.2L VIN K 2-bbl (1982)
Catalytic Converter: Description and Operation
Three-Way Catalytic (TWC) Pellet Type
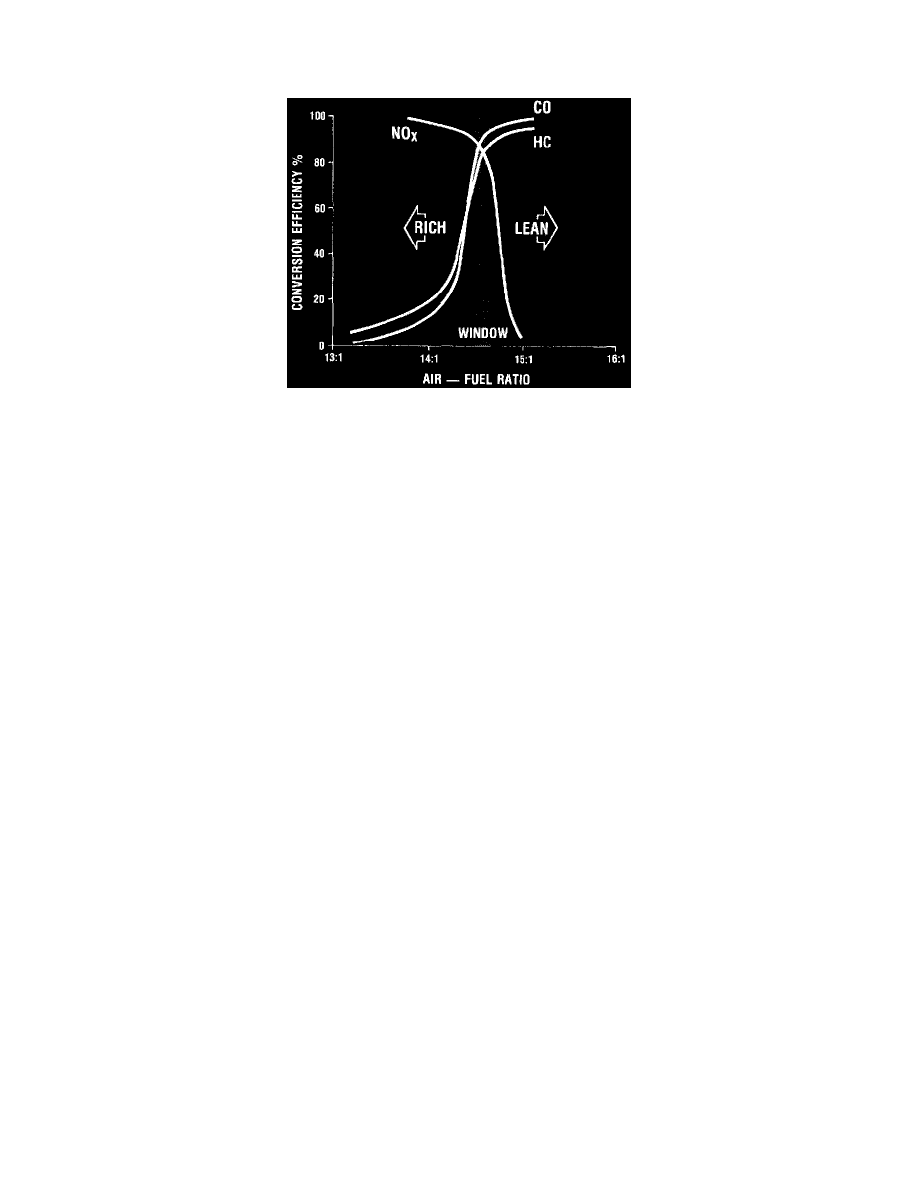
Fig. 3 - Conversion Efficiency Range Of Three-way Catalyst
The three-way catalytic converter contains rhodium which reduces or separates oxides of nitrogen (NOx) into nitrogen and oxygen. This action
provides better exhaust emission control than is obtainable by using only exhaust gas recirculation, an oxidation catalyst or engine modifications.
Its use allows richer air-fuel mixtures, more spark advance and less exhaust gas recirculation. All these improve both driveability and fuel
economy.
Effective catalytic control of all three pollutants is possible when the correct balance of excess CO is reached for reduction and excess oxygen is
reduced. Therefore, it is necessary to maintain precise control of the air-fuel mixture entering the engine, keeping it very close to the
stoichiometric range (chemically correct for theoretical complete combustion).
The properties of a three-way catalyst are shown in Fig. 3. The curve of efficiency as a function of air-fuel indicates that when the air-fuel mixture
is lean (excess of oxygen), HC and CO pollutants are low, but NOx pollutants are high. When the air-fuel mixture is rich (oxygen deficiency), HC
and CO pollutants are high, but NOx pollutants are low. At the chemically correct mixture, a narrow range exists where the control of all pollutants
is good. Maintaining the exhaust constituents at this range is the purpose of the EFC system.
The downstream catalyst, along with oxygen supplied by an air pump used to remove the remaining HC and O2 left after the exhaust gases have
passed through the three- way catalyst.
