Dynasty L4-153 2.5L SOHC VIN K TBI (1992)
Brake Master Cylinder: Description and Operation
With Antilock Brakes
Master Cylinder & Brake Booster Operation
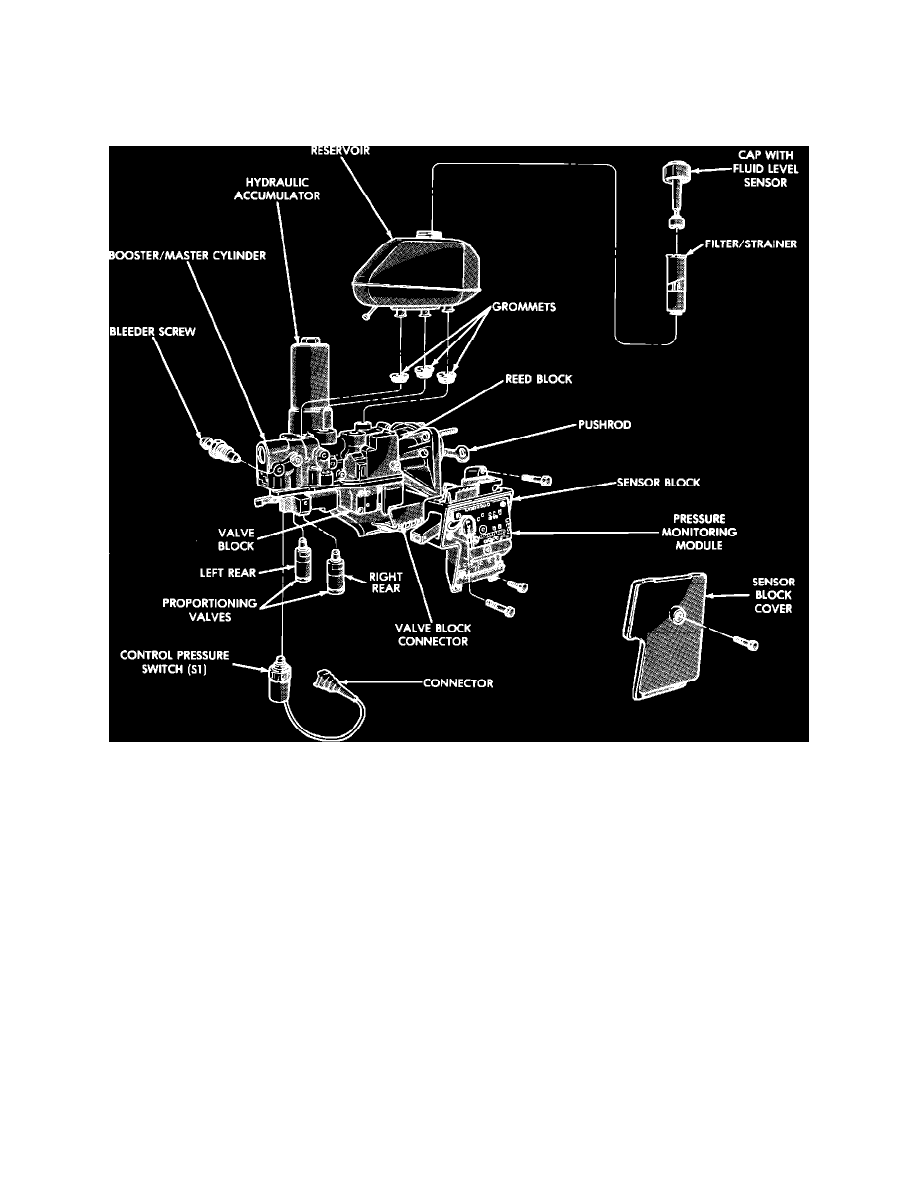
Hydraulic Assembly
NOTE: The booster/master cylinder portion of the hydraulic assembly is an integral component and should never be disassembled. The booster/master
cylinder is only serviced as a complete hydraulic assembly.
An electrohydraulic pump provides boost pressure by taking brake fluid from the hydraulic assembly reservoir, pressurizing the fluid, and supplying it
back to the hydraulic accumulator. The accumulator provides a supply of pressurized fluid for the booster servo circuit as required for power assist
braking and anti-lock braking. The amount of force applied to the brake pedal opens a spool valve, which controls the pressure in the booster servo
circuit.
The master cylinder portion of the hydraulic assembly uses a diagonally split configuration during normal braking. The two circuits are hydraulically
isolated so that a leak or malfunction in one circuit will allow continued braking ability on the other. Also included in the booster/master cylinder are the
boost piston travel switches which transmit master cylinder travel information to the Anti-lock Brake Control Module (ABM). These signals are used in
conjunction with the brake light switch and the control pressure switch to verify proper operation of the booster/master cylinder.
Hydraulic Assembly Operation
This Anti-lock Brake System (ABS) uses an integral hydraulic assembly which contains the wheel circuit valves used for brake pressure modulation.
