Grand Caravan FWD L4-2.4L VIN B (1997)
Fuel Injector: Description and Operation
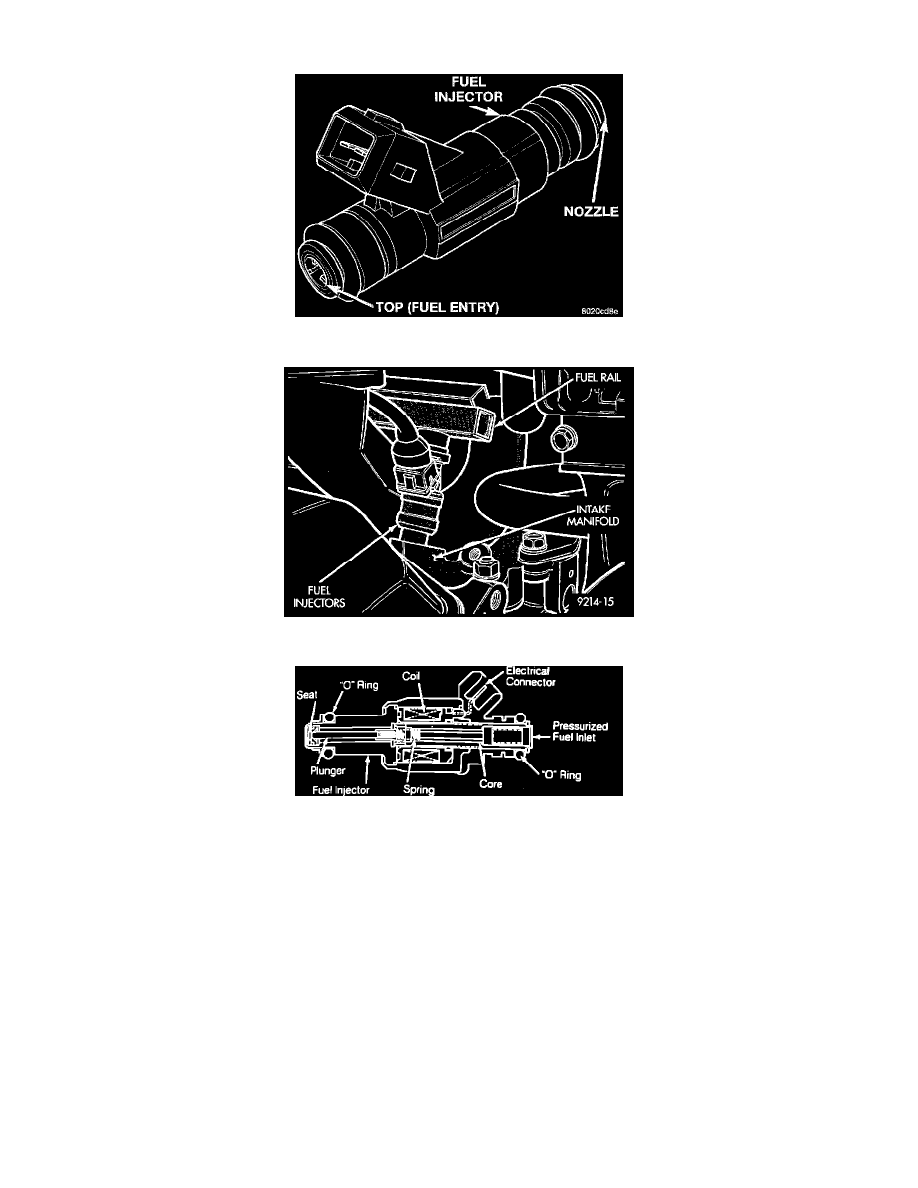
Fig 2 Fuel Injector
Fig 3 Fuel Injector Location -- Typical
Fuel Injector - Cutaway View
The fuel injectors are 12 ohm electrical solenoids (Fig. 2). The injector contains a pintle that closes off an orifice at the nozzle end. When electric
current is supplied to the injector, the armature and needle move a short distance against a spring, allowing fuel to flow out the orifice. Because the
fuel is under high pressure, a fine spray is developed in the shape of a hollow cone. The spraying action atomizes the fuel, adding it to the air
entering the combustion chamber. The injectors are positioned in the intake manifold.
The injectors are positioned in the intake manifold with the nozzle ends directly above the intake valve port (Fig. 3).
CIRCUIT OPERATION
When the ASD relay contacts CLOSE, they connect circuit #4 to circuit A142. Circuit A142 supplies battery voltage to the fuel injectors. The
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) controls the ground circuit of each injector.
-
Circuit K11 is the ground circuit for injector number one. Circuit K11 connects to cavity 13 of the PCM.
-
Circuit K12 is the ground circuit for injector number two. Circuit K12 connects to cavity 17 of the PCM.
-
Circuit K13 is the ground circuit for injector number three. Circuit K13 connects to cavity 7 of the PCM.
-
Circuit K14 is the ground circuit for injector number four. Circuit K14 connects to cavity 16 of the PCM.
Helpful Information
-
Circuit A142 splices to the ignition coil, upstream and downstream heated oxygen sensors, generator field and cavity 6 of the PCM
