Grand Caravan FWD V6-3.0L VIN 3 (1999)
Spark Plug: Testing and Inspection
Spark Plug Condition
Remove the spark plugs and examine them for burned electrodes and fouled, cracked or broken porcelain insulators. Keep plugs arranged in the
order in which they were removed from the engine. An isolated plug displaying an abnormal condition indicates that a problem exists in the
corresponding cylinder. Replace spark plugs at the intervals recommended.
Normal Operating Conditions
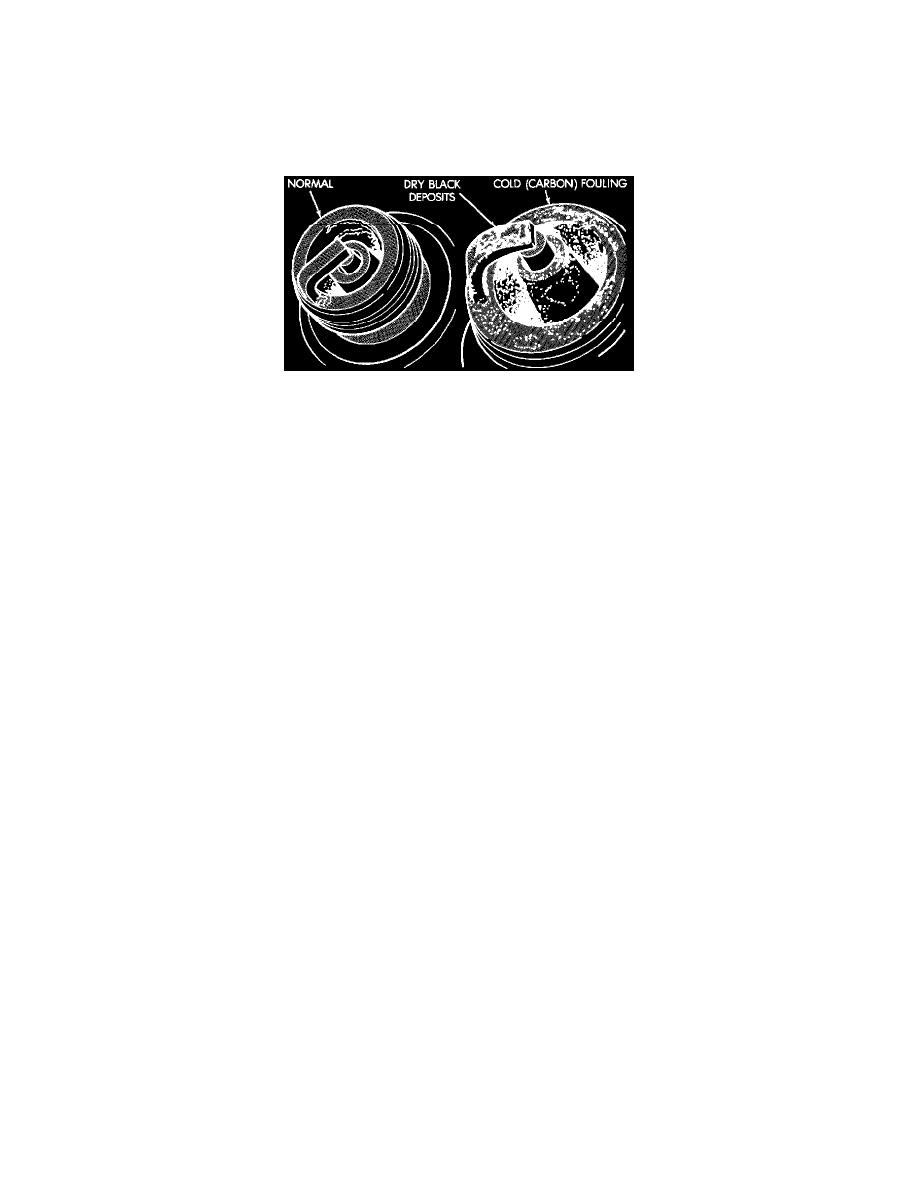
Normal Operation And Cold (Carbon) Fouling
The few deposits present will be probably light tan or slightly gray in color with most grades of commercial gasoline. There will not be evidence
of electrode burning. Gap growth will not average more than approximately 0.025 mm (.001 in) per 1600 km (1000 miles) of operation for non
platinum spark plugs. Non-platinum spark plugs that have normal wear can usually be cleaned, and then reinstalled.
CAUTION: Never attempt to tile the electrodes or use a wire brush for cleaning platinum spark plugs. This would damage the platinum pads
which would shorten spark plug life.
Some fuel refiners in several areas of the United States have introduced a manganese additive (MMT) for unleaded fuel. During combustion, fuel
with MMT may coat the entire tip of the spark plug with a rust colored deposit. The rust color deposits can be mis diagnosed as being caused by
coolant in the combustion chamber. Spark plug performance may be affected by MMT deposits.
Cold Fouling (Carbon Fouling)
Cold fouling is sometimes referred to as carbon fouling because the deposits that cause cold fouling are basically carbon. A dry, black deposit on
one or two plugs in a set may be caused by sticking valves or misfire conditions. Cold (carbon) fouling of the entire set may be caused by a
clogged air cleaner.
Cold fouling is normal after short operating periods. The spark plugs do not reach a high enough operating temperature during short operating
periods. Replace carbon fouled plugs with new spark plugs.
Fuel Fouling
A spark plug that is coated with excessive wet fuel is called fuel fouled. This condition is normally observed during hard start periods. Clean fuel
fouled spark plugs with compressed air and reinstall them in the engine.
Oil Fouling
A spark plug that is coated with excessive wet oil is oil fouled. In older engines, wet fouling can be caused by worn rings or excessive cylinder
wear. Break-in fouling of new engines may occur before normal oil control is achieved. Replace oil fouled spark plugs with new ones.
Oil Or Ash Encrusted
