Neon L4-2.0L SOHC (1995)
Positive Crankcase Ventilation: Description and Operation
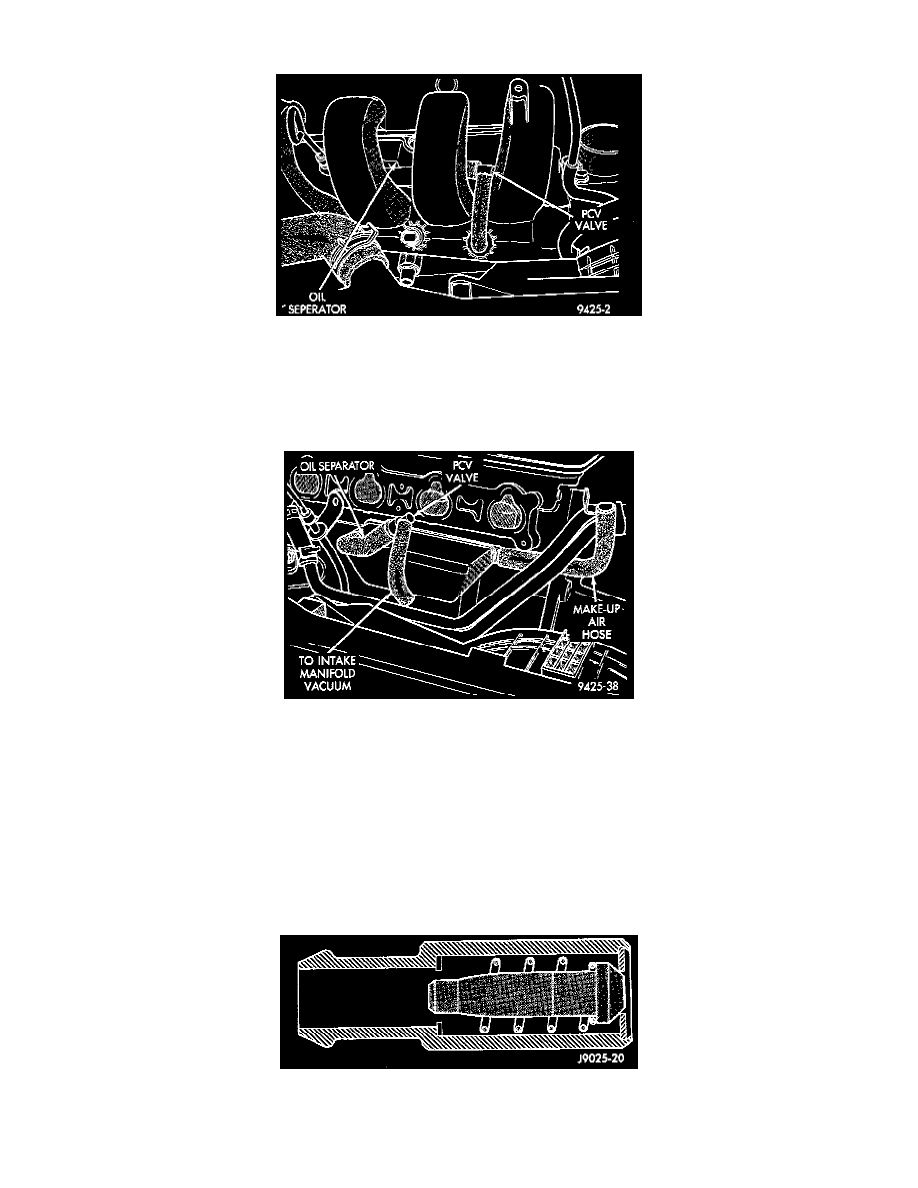
Fig. 5 Oil Separator
This engine PCV system contains an oil separator (Fig. 5). The oil separator attaches to the engine, behind the intake manifold.
Crankcase vapors enter the bottom of the separator. Oil collected in the separator drains back into the crankcase from an outlet in the bottom of the
separator.
Fig. 6 PCV Valve And Oil Separator (Intake Manifold Removed)
The PCV valve connects to the separator and to intake manifold vacuum (Fig. 6). Make-up air is supplied to the separator by a hose connected to
the air cleaner air tube.
Intake manifold vacuum removes crankcase vapors and piston blow-by from the separator. Emissions pass through the PCV valve into the intake
manifold plenum. The vapors become part of the calibrated air-fuel mixture, are burned and then expelled with the exhaust gases. The air cleaner
supplies make up air when the engine does not have enough vapor or blow-by gases.
PCV VALVE
The PCV valve contains a spring loaded plunger. The plunger meters the amount of crankcase vapors routed into the combustion chamber based
on intake manifold vacuum.
Fig. 7 Engine Off Or Engine Backfire - No Vapor Flow
When the engine is not operating or during an engine backfire, the spring forces the plunger back against the seat. This prevents vapors from
