Neon R/T L4-2.0L VIN F HO (2001)
Crankshaft Position Sensor: Description and Operation
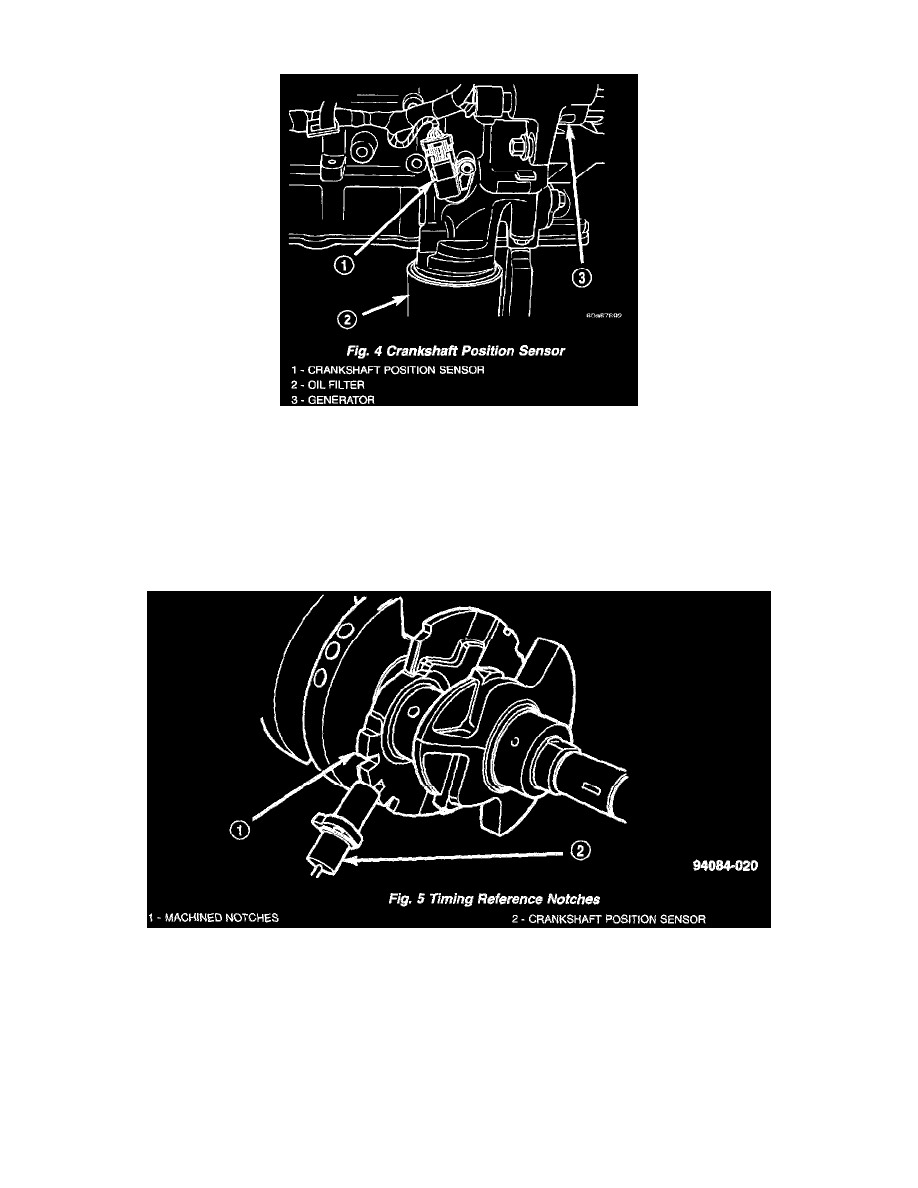
Fig. 4 Crankshaft Position Sensor
The crankshaft position sensor mounts to the engine block behind the generator, just above the oil filter.
The PCM uses the Crankshaft Position sensor to calculate the following:
-
Engine RPM
-
TDC number 1 and 4
-
Ignition coil synchronization Injector synchronization
-
Camshaft-to-crankshaft misalignment (Timing belt skipped 1 tooth or more diagnostic trouble code).
Fig. 5 Timing Reference Notches
The Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor is a Hall-effect sensor. The second crankshaft counterweight has two sets of four timing reference notches
including a 60 degree signature notch.
The PCM sends approximately 8 volts to the Hall-effect sensor. This voltage is required to operate the Hall-effect chip and the electronics inside the
sensor. A ground for the sensor is provided through the sensor return circuit. The input to the PCM occurs on a 5 volt output reference circuit.
The notches generate pulses from high to low in the crankshaft position sensor output voltage. When a metal portion of the counterweight aligns with the
crankshaft position sensor, the sensor output voltage goes low (less than 0.5 volts). When a notch aligns with the sensor, voltage goes high (5.0 volts).
As a group of notches pass under the sensor, the output voltage switches from low (metal) to high (notch) then back to low.
