RAM 2500 Truck 2WD L6-5.9L DSL Turbo VIN 7 (2001)
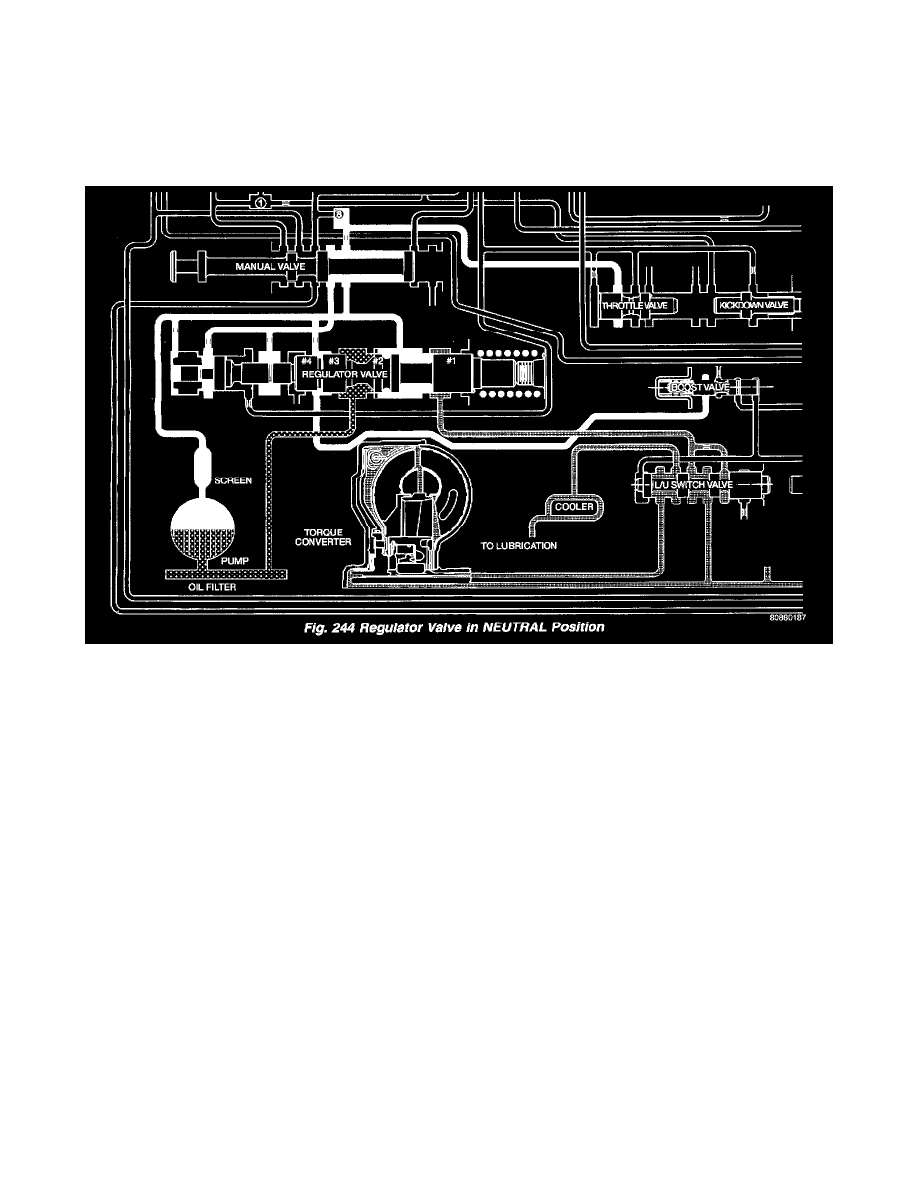
The regulator valve (Fig. 243) has a spring on one end that pushes the valve to the left. This closes a dump (vent) that is used to lower pressure. The
closing of the dump will cause the oil pressure to increase. Oil pressure on the opposite end of the valve pushes the valve to the right, opening the
dump and lowering oil pressure. The result is spring pressure working against oil pressure to maintain the oil at specific pressures. With the engine
running, fluid flows from the pump to the pressure regulator valve, manual valve, and the interconnected circuits. As fluid is sent through passages to
the regulator valve, the pressure pushes the valve to the right against the large spring. It is also sent to the reaction areas on the left side of the throttle
pressure plug and the line pressure plug. With the gear selector in the PARK position, fluid recirculates through the regulator and manual valves back
to the sump.
Meanwhile, the torque converter is filled slowly. In all other gear positions (Fig. 244), fluid flows between two right side lands to the switch valve and
torque converter. At low pump speeds, the flow is controlled by the pressure valve groove to reduce pressure to the torque converter. After the torque
converter and switch valve fill with fluid, the switch valve becomes the controlling metering device for torque converter pressure. The regulator valve
then begins to control the line pressure for the other transmission circuits. The balance of the fluid pressure pushing the valve to the right and the
spring pressure pushing to the left determines the size of the metering passage at land # 2 (land # 1 being at the far right of the valve in the diagram).
As fluid leaks past the land, it moves into a groove connected to the filter or sump. As the land meters the fluid to the sump, it causes the pressure to
reduce and the spring decreases the size of the metering passage. When the size of the metering passage is reduced, the pressure rises again and the
size of the land is increased again. Pressure is regulated by this constant balance of hydraulic and spring pressure.
