RAM 2500 Truck 2WD L6-5.9L DSL Turbo VIN 7 (2001)
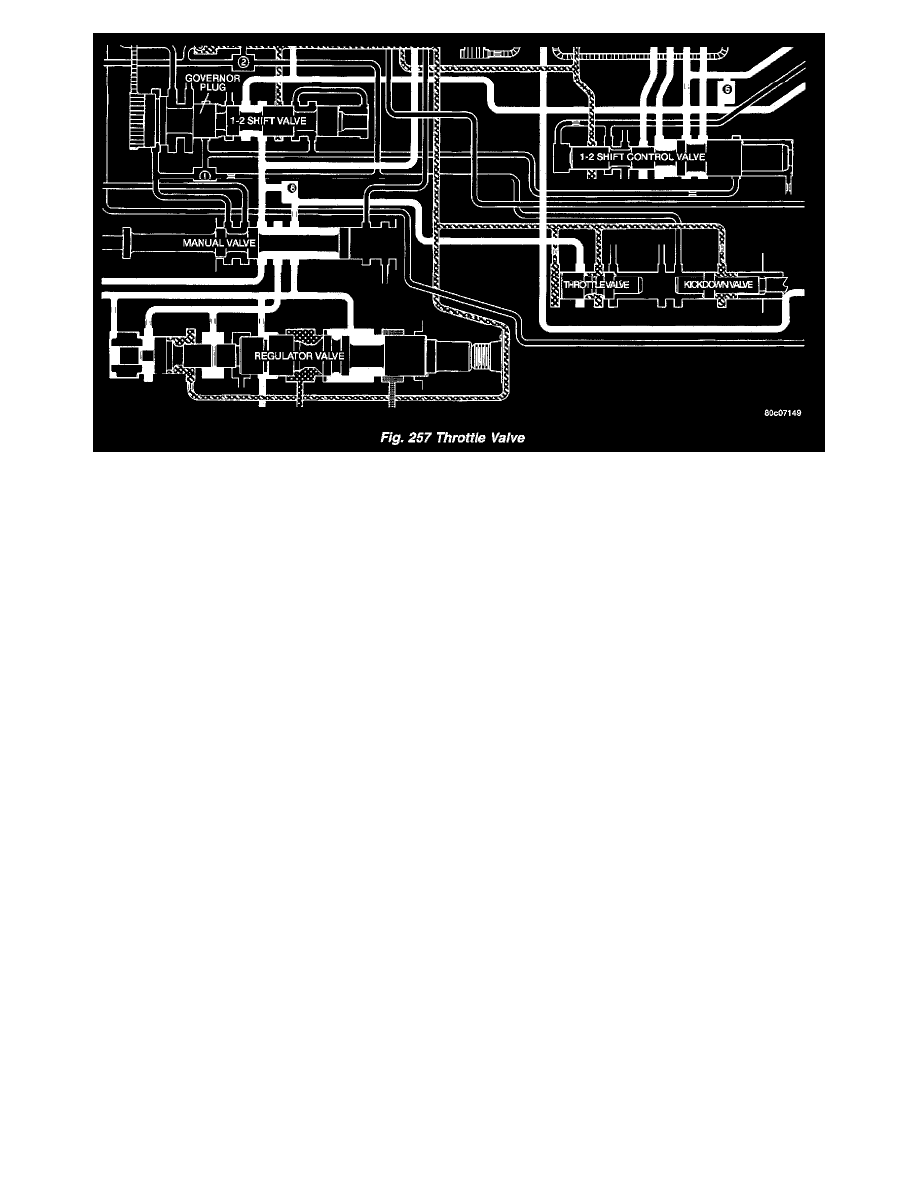
In all gear positions the throttle valve (Fig. 257) is being supplied with line pressure. The throttle valve meters and reduces the line pressure that now
becomes throttle pressure. The throttle valve is moved by a spring and the kickdown valve, which is mechanically connected to the throttle. The larger
the throttle opening, the higher the throttle pressure (to a maximum of line pressure). The smaller the throttle opening, the lower the throttle pressure
(to a minimum of zero at idle). As engine speed increases, the increase in pump speed increases pump output. The increase in pressure and volume
must be regulated to maintain the balance within the transmission. To do this, throttle pressure is routed to the reaction area on the right side of the
throttle pressure plug (in the regulator valve).
The higher engine speed and line pressure would open the vent too far and reduce line pressure too much. Throttle pressure, which increases with
engine speed (throttle opening), is used to oppose the movement of the pressure valve to help control the metering passage at the vent. The throttle
pressure is combined with spring pressure to reduce the force of the throttle pressure plug on the pressure valve. The larger spring at the right closes
the regulator valve passage and maintains or increases line pressure. The increased line pressure works against the reaction area of the line pressure
plug and the reaction area left of land # 3 simultaneously moves the regulator valve train to the right and controls the metering passage.
The kickdown valve, along with the throttle valve, serve to delay upshifts until the correct vehicle speed has been reached. It also controls downshifts
upon driver demand, or increased engine load. If these valves were not in place, the shift points would be at the same speed for all throttle positions.
The kickdown valve is actuated by a cam connected to the throttle. This is accomplished through either a linkage or a cable. The cam forces the
kickdown valve toward the throttle valve compressing the spring between them and moving the throttle valve. As the throttle valve land starts to
uncover its port, line pressure is "metered" out into the circuits and viewed as throttle pressure. This increased throttle pressure is metered out into the
circuits it is applied to: the 1-2 and 2-3 shift valves. When the throttle pressure is high enough, a 3-2 downshift, will occur. If the vehicle speed is low
enough, a 2-1 downshift will occur.
SWITCH VALVE
