RAM 2500 Truck 2WD L6-5.9L DSL Turbo VIN C (2002)
Brake Caliper: Description and Operation
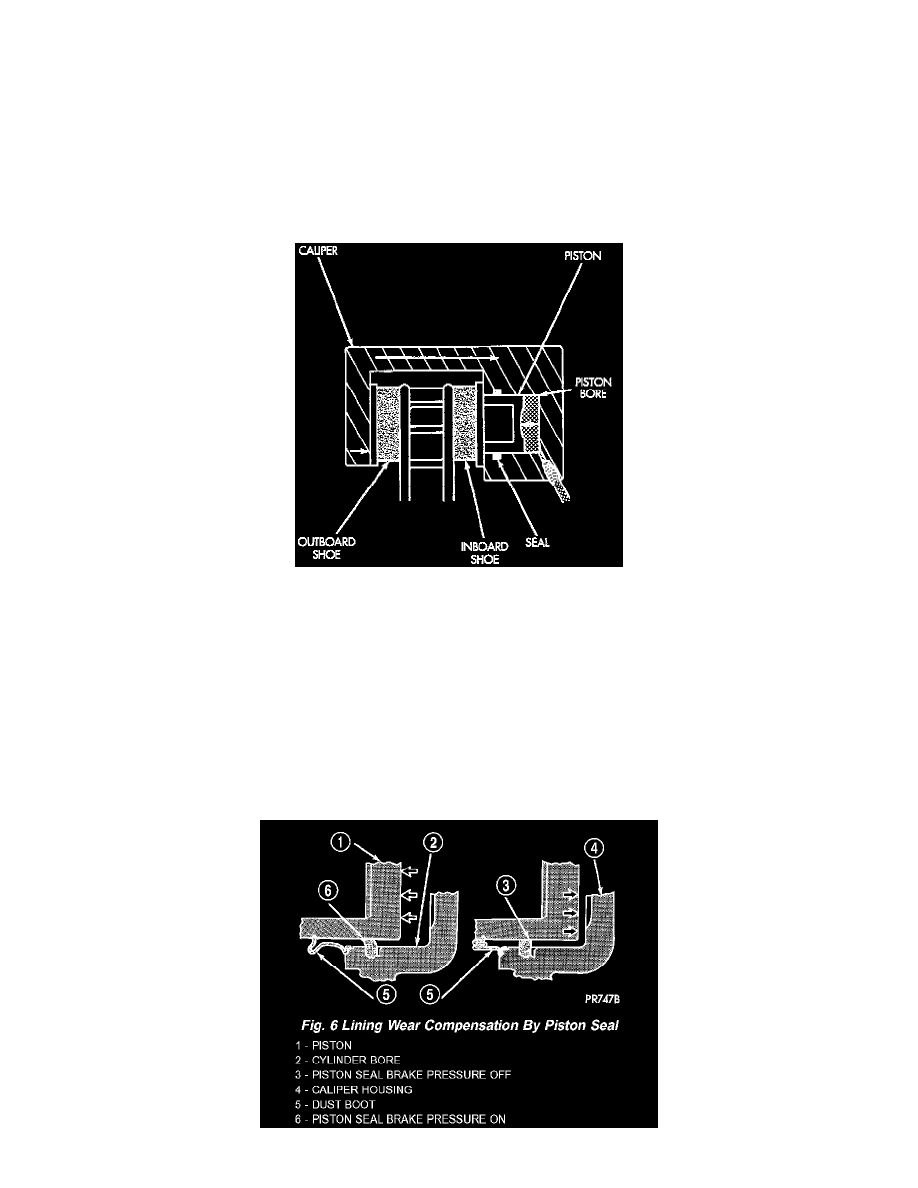
DISC BRAKE CALIPERS
DESCRIPTION
The caliper is a one-piece casting. The piston bores are located in the inboard side. A square-cut piston seal is located in a machined groove in the
cylinder bore. The caliper pistons dust boot prevents dirt, water and road splash from entering the piston bore. The boot is seated in a groove
machined at the outer end of the caliper piston. The boot retaining flange is seated in a counterbore machined in the outer end of the caliper piston
bore. Ventilated disc brake rotors are used for all applications. The rotors are serviceable and can be machined to restore surface finish when
necessary.
OPERATION
Disc Brake Caliper
When the brakes are applied fluid pressure is exerted against the caliper piston. The fluid pressure is exerted equally and in all directions. This means
pressure exerted against the caliper piston and within the caliper bore will be equal.
Fluid pressure applied to the piston is transmitted directly to the inboard brake shoe. This forces the shoe lining against the inner surface of the disc
brake rotor. At the same time, fluid pressure within the piston bore forces the caliper to slide inward on the mounting bolts. This action brings the
outboard brake shoe lining into contact with the outer surface of the disc brake rotor.
In summary, fluid pressure acting simultaneously on both piston and caliper, produces a strong clamping action. When sufficient force is applied,
friction will attempt to stop the rotors from turning and bring the vehicle to a stop.
Application and release of the brake pedal generates only a very slight movement of the caliper and piston. Upon release of the pedal, the caliper and
piston return to a rest position. The brake shoes do not retract an appreciable distance from the rotor. In fact, clearance is usually at, or close to zero.
The reasons for this are to keep road debris from getting between the rotor and lining and in wiping the rotor surface clear each revolution. The
caliper piston seal controls the amount of piston extension needed to compensate for normal lining wear.
