RAM 2500 Truck 2WD V8-5.2L VIN Y (2000)
CAUTION: Never use a motorized wire wheel brush to clean the spark plugs. Metallic deposits will remain on the spark plug insulator and will
cause plug misfire.
SPARK PLUG CABLES
Spark plug cables are sometimes referred to as secondary ignition wires.
The spark plug cables transfer electrical current from the ignition coil(s) and/or distributor, to individual spark plugs at each cylinder. The resistive
spark plug cables are of nonmetallic construction. The cables provide suppression of radio frequency emissions from the ignition system.
IGNITION COIL
A single ignition coil is used. The coil is not oil filled. The coil windings are embedded in an epoxy compound. This provides heat and vibration
resistance that allows the coil to be mounted on the engine.
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) opens and closes the ignition coil ground circuit for ignition coil operation.
Battery voltage is supplied to the ignition coil positive terminal from the ASD relay. If the PCM does not see a signal from the crankshaft and
camshaft sensors (indicating the ignition key is ON but the engine is not running), it will shut down the ASD circuit.
Base ignition timing is not adjustable on any engine. By controlling the coil ground circuit, the PCM is able to set the base timing and adjust the
ignition timing advance. This is done to meet changing engine operating conditions.
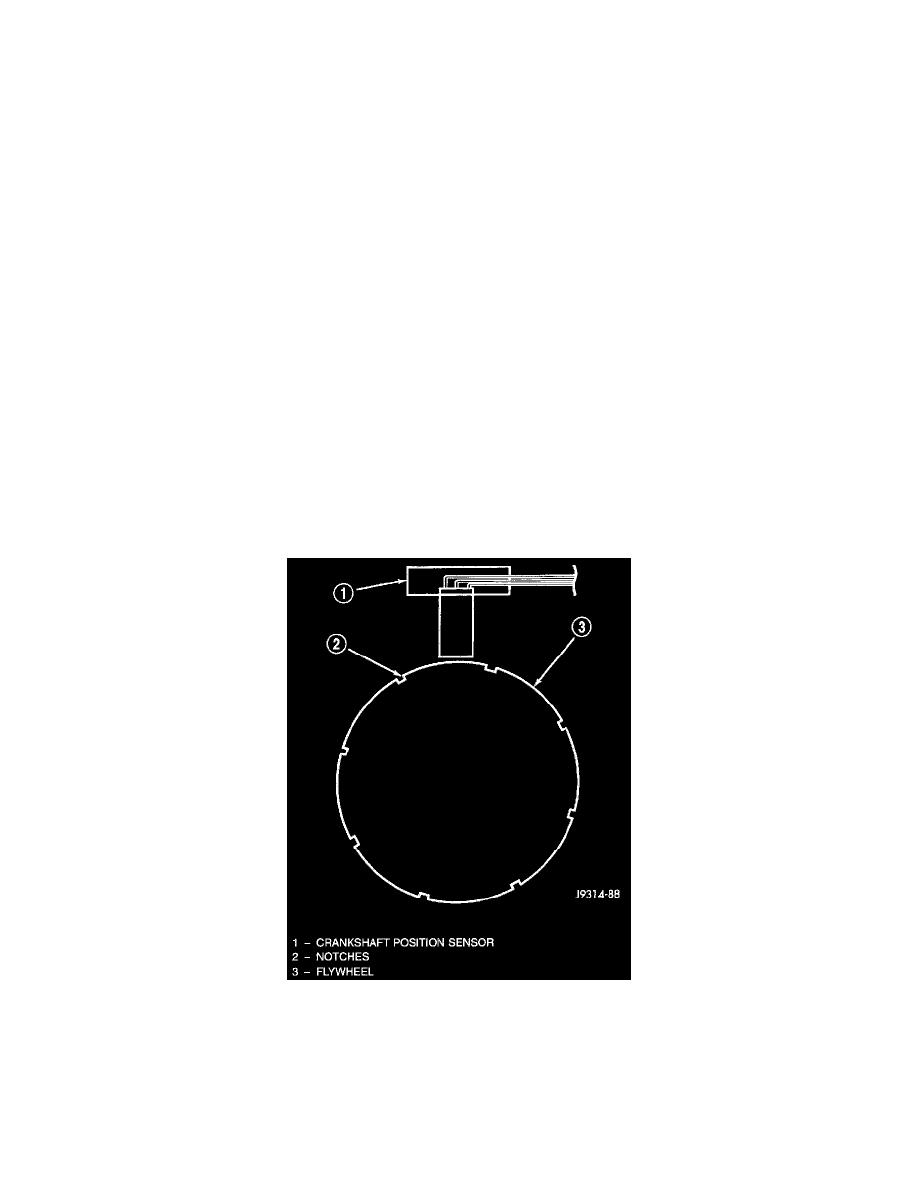
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
The Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor is located near the outer edge of the flywheel (starter ringear).
Engine speed and crankshaft position are provided through the CKP sensor. The sensor generates pulses that are the input sent to the Powertrain
Control Module (PCM). The PCM interprets the sensor input to determine the crankshaft position. The PCM then uses this position, along with
other inputs, to determine injector sequence and ignition timing.
The sensor is a hall effect device combined with an internal magnet. It is also sensitive to steel within a certain distance from it.
CKP Sensor Operation
On 5.2/5.9L V-8 engines, the flywheel/drive plate has 8 single notches, spaced every 45 degrees, at its outer edge.
The notches cause a pulse to be generated when they pass under the sensor. The pulses are the input to the PCM. For each engine revolution, there
are 8 pulses generated on V-8 engines.
The engine will not operate if the PCM does not receive a CKP sensor input.
