RAM 3500 Truck 2WD L6-5.9L DSL Turbo VIN 7 (2002)
other bus wire.
The voltage drop through the termination resistor creates 2.51 volts on Bus (-), and 2.49 volts on Bus (+). The voltage difference between the two
circuits is 0.02 volts. When the data bus voltage differential is a steady 0.02 volts, the CCD system is considered "idle." When no input is received from
any module and the ignition switch is in the OFF position for a pre-programmed length of time, the bus data becomes inactive or enters the "sleep mode."
Electronic control modules that provide bus bias can be programmed to "wake up" the data bus and become active upon receiving any predetermined
input or when the ignition switch is turned to the ON position.
Bus Messaging
The electronic control modules used in the CCD data bus system contain microprocessors. Digital signals are the means by which microprocessors
operate internally and communicate messages to other microprocessors. Digital signals are limited to two states, voltage high or voltage low,
corresponding to either a one or a zero. Unlike conventional binary code, the CCD data bus systems translate a small voltage difference as a one (1), and
a larger voltage difference as a zero (0). The use of the 0 and 1 is referred to as binary coding. Each binary number is called a bit, and eight bits make up
a byte. For example: 01011101 represents a message. The controllers in the multiplex system are able to send thousands of these bytes strung together to
communicate a variety of messages. Through the use of binary data transmission, all electronic control modules on the data bus can communicate with
each other.
The microprocessors in the CCD data bus system translate the binary messages into Hexadecimal Code (or Hex Code). Hex code is the means by which
microprocessors communicate and interpret messages. When fault codes are received by the DRBIII scan tool, they are translated into text for display on
the DRBIII screen. Although not displayed by the DRBIII for Body Systems, hex codes are shown by the DRBIII for Engine System faults.
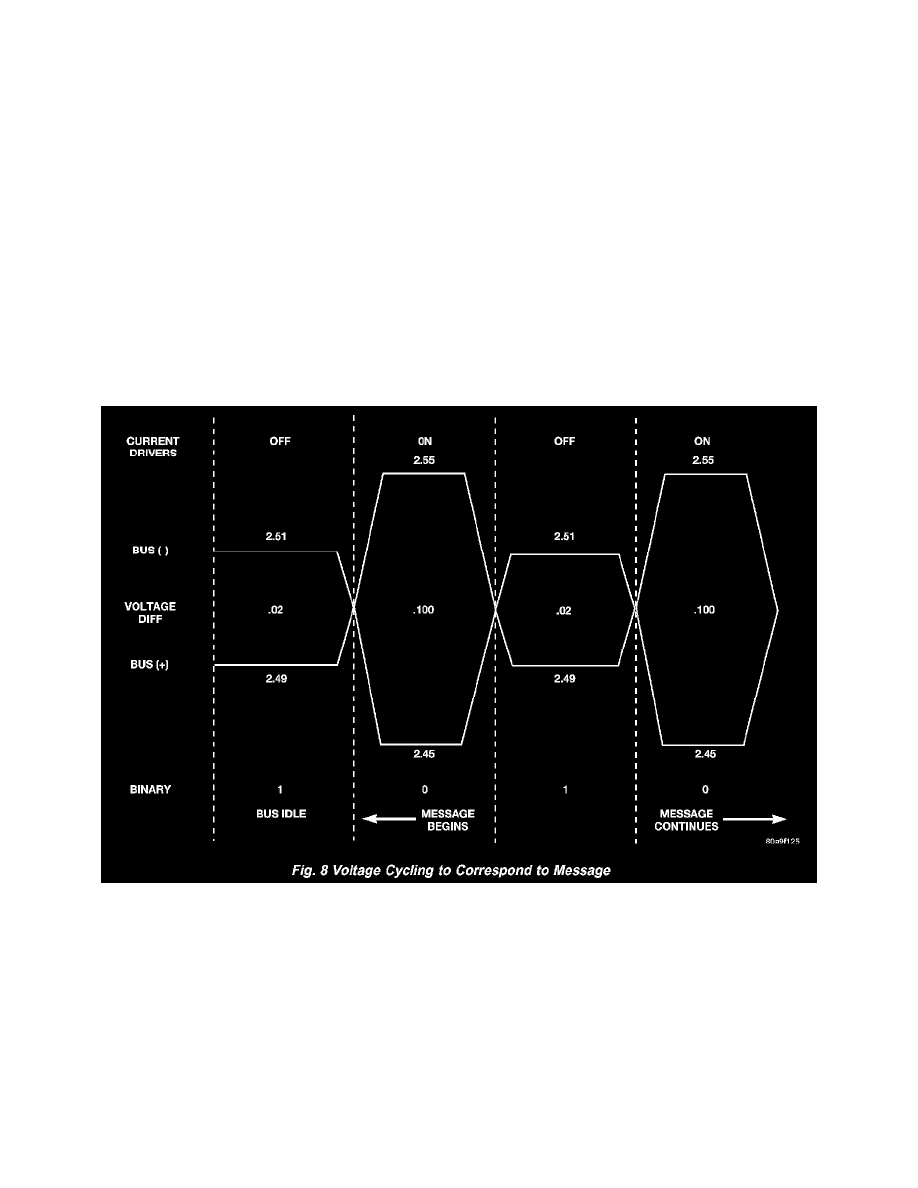
Fig. 8 Voltage Cycling To Correspond To Message
When the microprocessor signals the transceiver in the CCD chip to broadcast a message, the transceiver turns the current drivers ON and OFF, which
cycles the voltage on the CCD data bus circuits to correspond to the message. At idle, the CCD system recognizes the 0.02 voltage differential as a
binary bit 1. When the current drivers are actuated, the voltage differential from idle must increase by 0.02 volt for the CCD system to recognize a binary
bit 0. The nominal voltage differential for a 0 bit is 0.100 volts. However, data bus voltage differentials can range anywhere between 0.02 and 0.120
volt.
Bus Message Coding
The first part of a data bus message has an Identification (ID) byte. The ID byte contains message priority, message identification, message content and
message length information. All messages sent over the data bus are coded for both priority and identification.
Priority
