Sprinter 3500 V6-3.0L DSL Turbo VIN 45 (2007)
Fuel Injector: Description and Operation
Operation
OPERATION
The injectors incorporate piezoelectric actuators required for high-speed activation. The higher switching speed allows the intervals between individual
fuel injections to be reduced and controlled more precisely. This feature contributes to a quiet and more efficient engine.
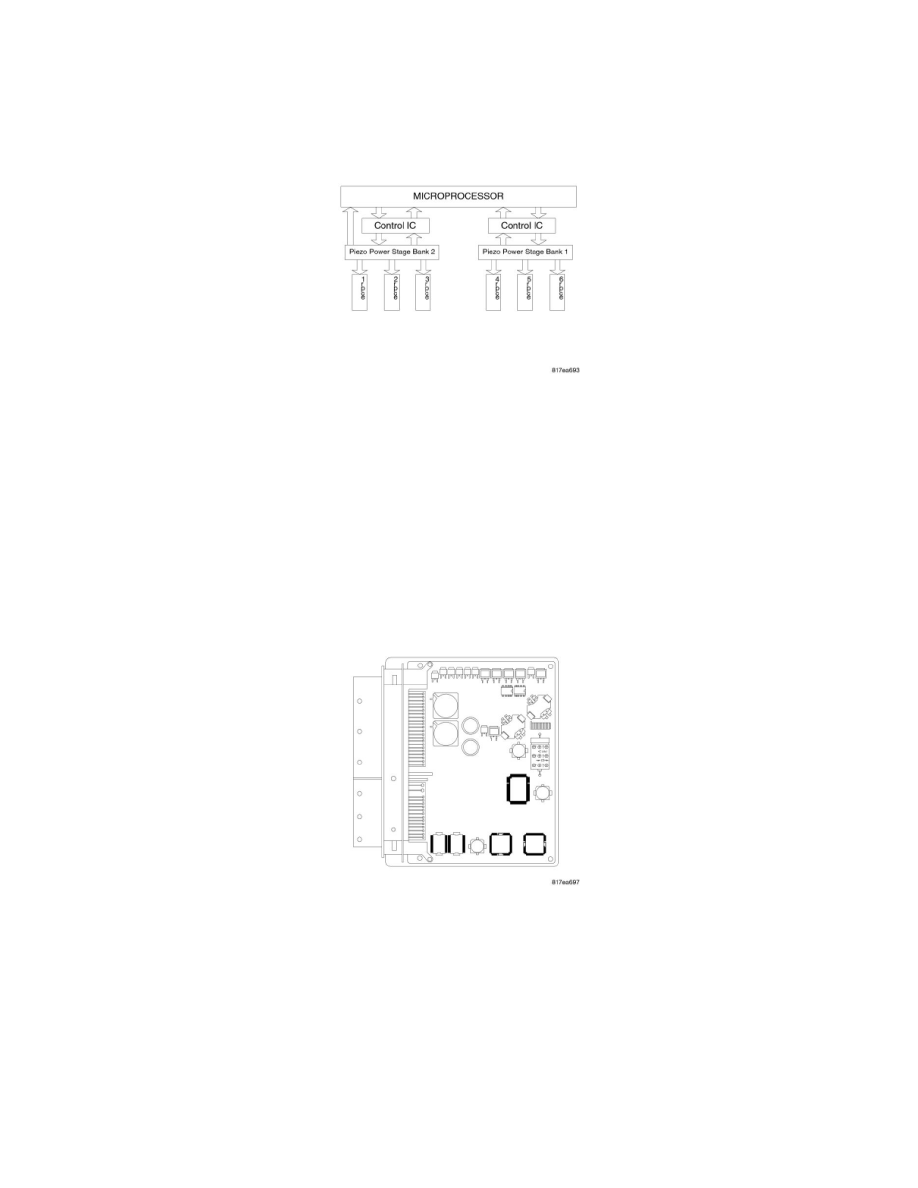
The fuel injector drive circuit is arranged in two separate banks. Each bank is controlled by a control integrated circuit, which drives the power stage to
activate the piezoelectric actuators. Bank 1 is comprised of injectors 4, 5 and 6, while bank 2 is comprised of injectors 1, 2 and 3. The microprocessor
receives information concerning the operation of the control integrated circuits and power stages.
The engine requires a high number of injections during normal operation. At an engine speed of 1000 rpm for example, the ECM may activate the
injectors up to 250 times every second. Enough energy needs to be quickly stored to activate the injectors within these time constraints. The piezoelectric
actuators also require high-voltage for proper operation. To supply the demand of power, each injector bank contains the following stages:
-
Booster stage
-
Charge/discharge driver stage
-
Piezoelectric-driver stage
The control IC of each bank controls the operation of its corresponding booster stage, charge driver stage and piezoelectric actuator driver stage. The
booster stage is controlled via the charge pump. The charge driver stage is controlled via the charge and discharge power transistors. In the piezoelectric
actuator driver stage, the control IC controls the power and ground side of each piezoelectric actuator via high-side and low-side power transistors. The
high side selects the bank, while the low side selects the individual cylinders. The ECM monitors the current flow throughout the injector drive circuit
via the shunt resistors to determine the state of charge of the booster capacitor.
