SRT-4 L4-2.4L Turbo VIN S (2004)
Crankshaft Position Sensor: Description and Operation
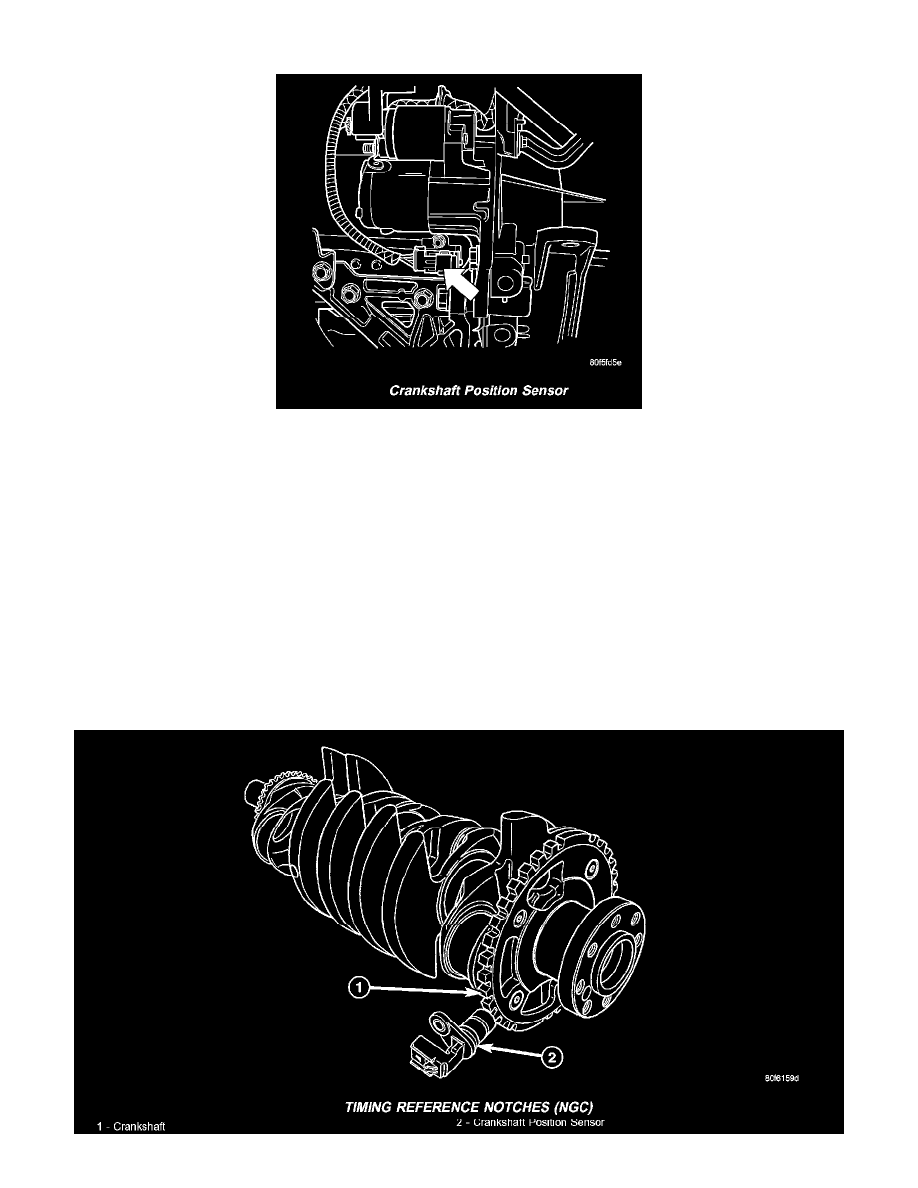
Crankshaft Position Sensor
The crankshaft position sensor mounts to the engine block near the starter.
The PCM uses the Crankshaft Position sensor to calculate the following:
-
Engine RPM
-
TDC number 1 and 4
-
Ignition coil synchronization
-
Injector synchronization
-
Camshaft-to-crankshaft misalignment (Timing belt skipped 1 tooth or more diagnostic trouble code).
The PCM sends approximately 5 volts to the Hall-effect sensor. This voltage is required to operate the Hall-effect chip and the electronics inside the
sensor. A ground for the sensor is provided through the sensor return circuit. The input to the PCM occurs on a 5 volt output reference circuit that
operates as follows: The Hall-effect sensor contains a powerful magnet. As the magnetic field passes over the dense portion of the counterweight, the
5-volt signal is pulled to ground (.3 volts) through a transistor in the sensor. When the magnetic field passes over the notches in the crankshaft counter
weight, the magnetic field turns off the transistor in the sensor, causing the PCM to register the 5-volt signal. The PCM identifies crankshaft position by
registering the change from 5 to 0 volts, as signaled from the Crankshaft Position sensor.
