Stratus L4-2.4L VIN X (1998)
EGR Control Solenoid: Description and Operation
Electronic EGR Transducer (EET) Solenoid Operation
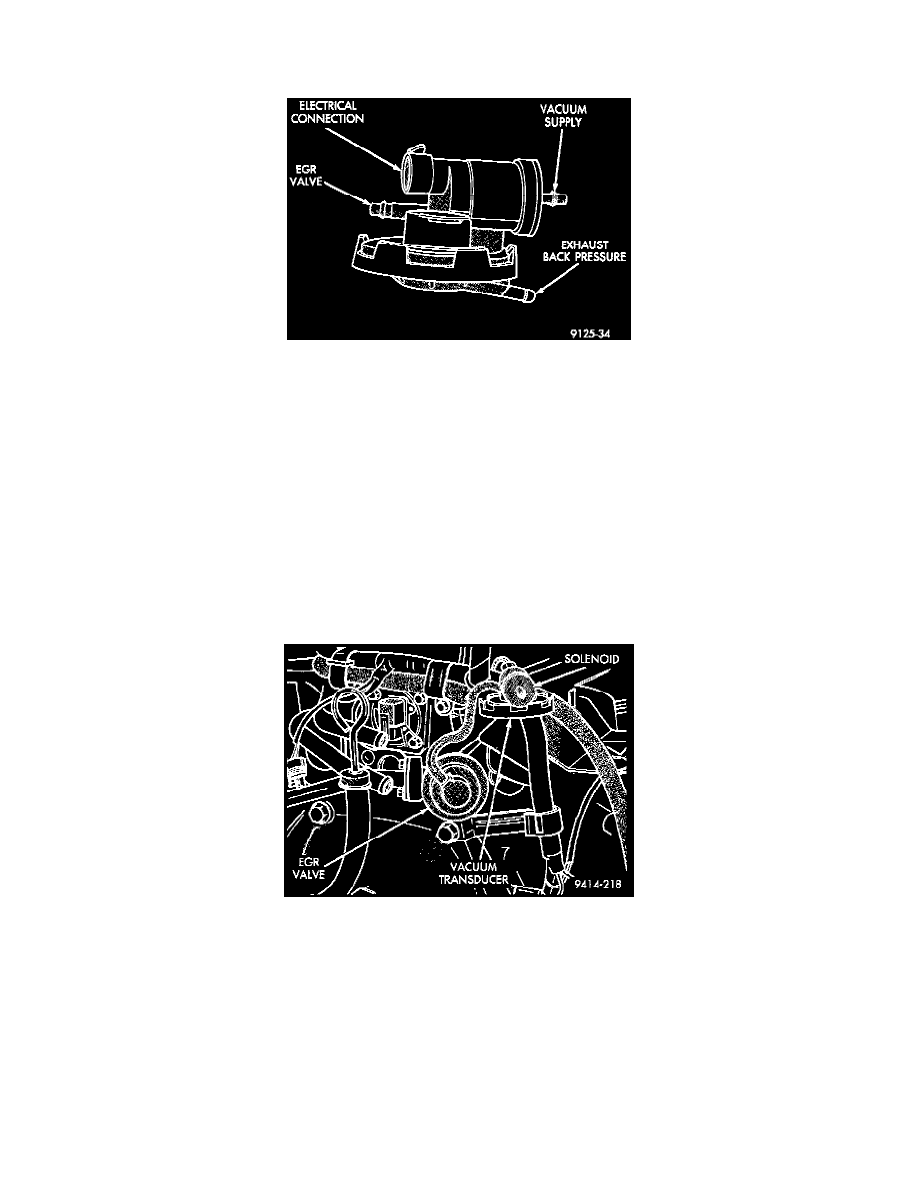
Fig. 27 Electronic EGR Transducer
OPERATION
The Electric EGR Transducer contains an electrically operated solenoid and a back-pressure controlled vacuum transducer Fig. 27. The PCM
operates the solenoid based on inputs from the multi-port fuel injection system. The solenoid/transducer and EGR valve are serviced as an
assembly.
When the PCM energizes the solenoid, vacuum does not reach the transducer. Vacuum flows to the transducer when the PCM de-energizes the
solenoid.
When exhaust system back-pressure becomes high enough, it fully closes a bleed valve in the vacuum transducer. When the PCM de-energizes the
solenoid and back-pressure closes the transducer bleed valve, vacuum flows through the transducer to operate the EGR valve.
De-energizing the solenoid, but not fully closing the transducer bleed hole (because of low back-pressure), varies the strength of the vacuum signal
applied to the EGR valve. Varying the strength of the vacuum signal changes the amount of EGR supplied to the engine. This provides the correct
amount of exhaust gas recirculation for different operating conditions.
Fig. 28 Electric EGR Transducer
The solenoid/transducer and EGR valve mount to the rear of the cylinder head Fig. 28.
