Stratus Sedan L4-2.4L VIN X (2003)
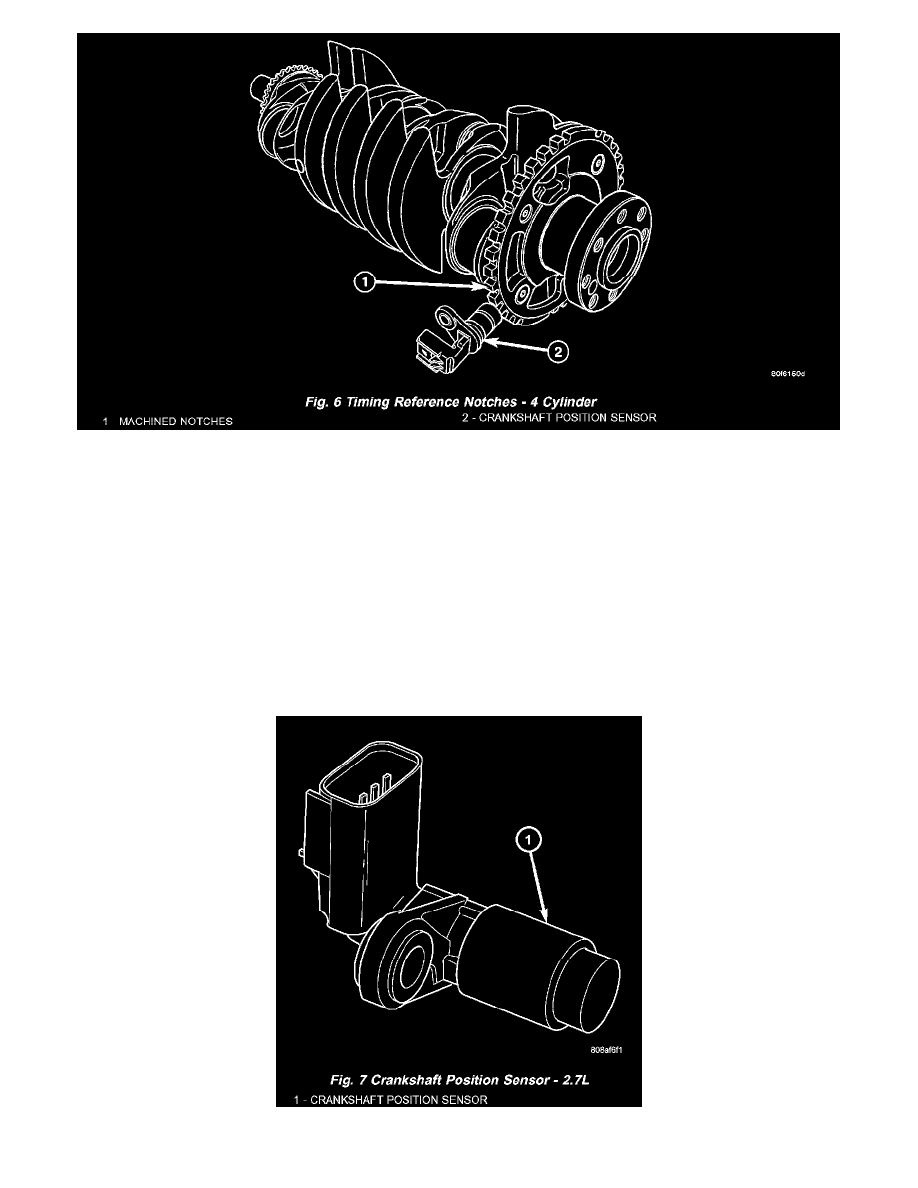
Fig.6 Timing Reference Notches - 4 Cylinder
The notches generate pulses from high to low in the crankshaft position sensor output voltage.
When a metal portion of the counterweight aligns with the crankshaft position sensor, the sensor output voltage goes low (less than 0.5 volts). When a
notch aligns with the sensor, voltage goes high (5.0 volts). As a group of notches pass under the sensor, the output voltage switches from low (metal) to
high (notch) then back to low.
If available, an oscilloscope can display the square wave patterns of each voltage pulses. From the width of the output voltage pulses, the PCM calculates
engine speed. The width of the pulses represent the amount of time the output voltage stays high before switching back to low. The period of time the
sensor output voltage stays high before switching back to low is referred to as pulse width. The faster the engine is operating, the smaller the pulse width
on the oscilloscope.
For SBEC vehicles, each group of timing reference notches, the first notch represents 69 °BTDC (Before Top Dead Center). The second notch
represents 49 °BTDC. The third notch represents 29 °BTDC. The last notch in each set represents 9 °BTDC. There is also a notch at 11 °BTDC.
Fig.7 Crankshaft Position Sensor - 2.7L
