Eagle L4-150 2.5L (1983)
When the brakes are initially applied, the metering valve stem moves to the left, preventing fluid to flow through the valve to the front disc brakes. This
is accomplished by the smooth end of the metering valve stem contacting the metering valve seal lip at 4 to 30 psi. The metering valve spring holds the
retainer against the seal until a predetermined pressure is produced at the valve inlet port which overcomes the spring pressure and permits hydraulic
pressure to actuate the front disc brakes. The increased pressure into the valve is metered through the valve seal, to the front disc brakes, producing an
increased force on the diaphragm. The diaphragm then pulls the pin, in turn pulling the retainer and reduces the spring pressure on the metering valve
seal. Eventually, the pressure reaches a point at which the spring is pulled away by the diaphragm pin and retainer, leaving the metering valve
unrestricted, permitting full pressure to pass through the metering valve.
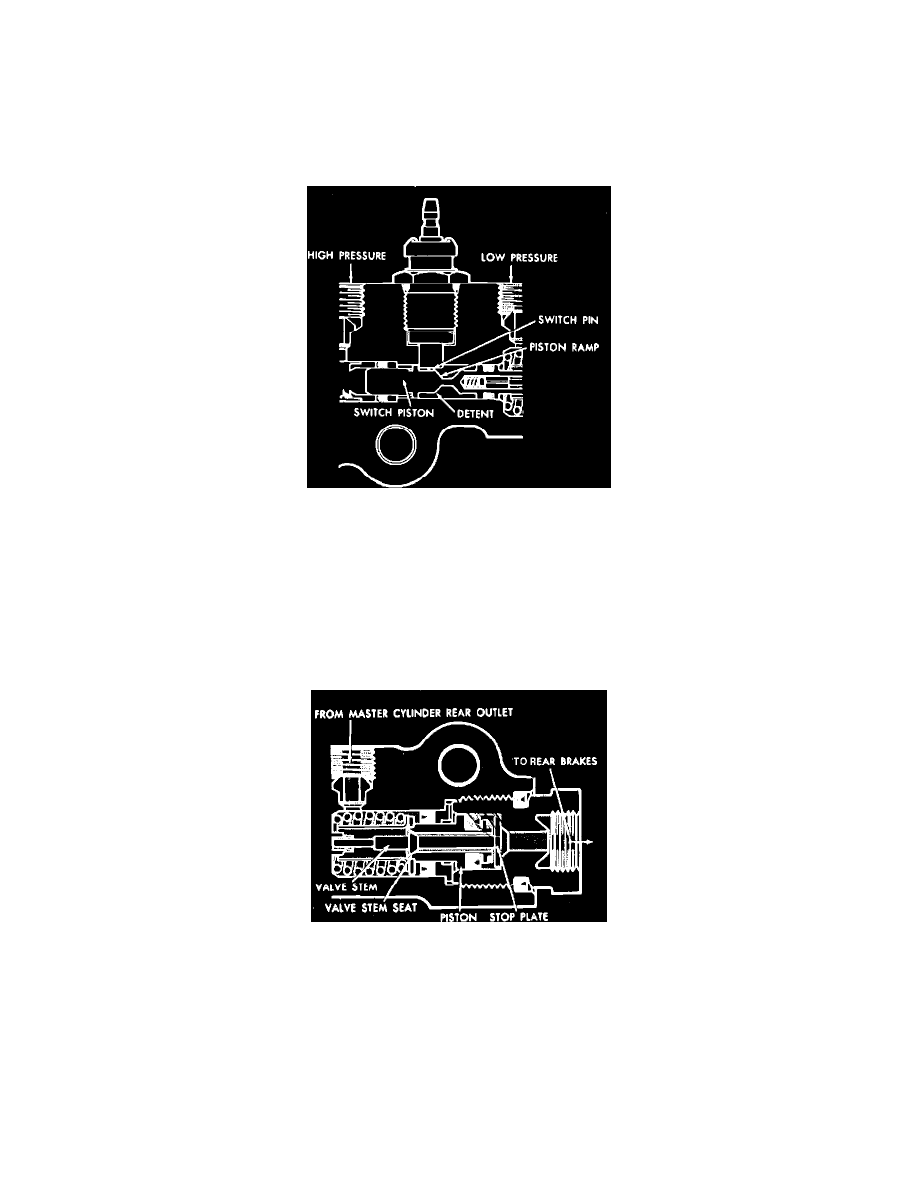
Fig. 12 Failure warning switch, rear system failure
FAILURE WARNING SWITCH
If the rear brake system fails, the front system pressure forces the switch piston to the right. The switch pin is then forced up into the switch, completing
the electrical circuit and activates the dash warning lamp.
When repairs are made and pressure returns to the system, the piston moves to the left, resetting the switch. The detent on the piston requires
approximately 100 to 450 PSI to permit full reset of the piston. In event of front brake system failure, the piston moves to the left and the same sequence
of events is followed as for rear system failure except the piston resets to the right.
Fig. 13 Proportioner, rapid deceleration
