E 150 1/2 Ton Van V6-4.2L VIN 2 (1997)
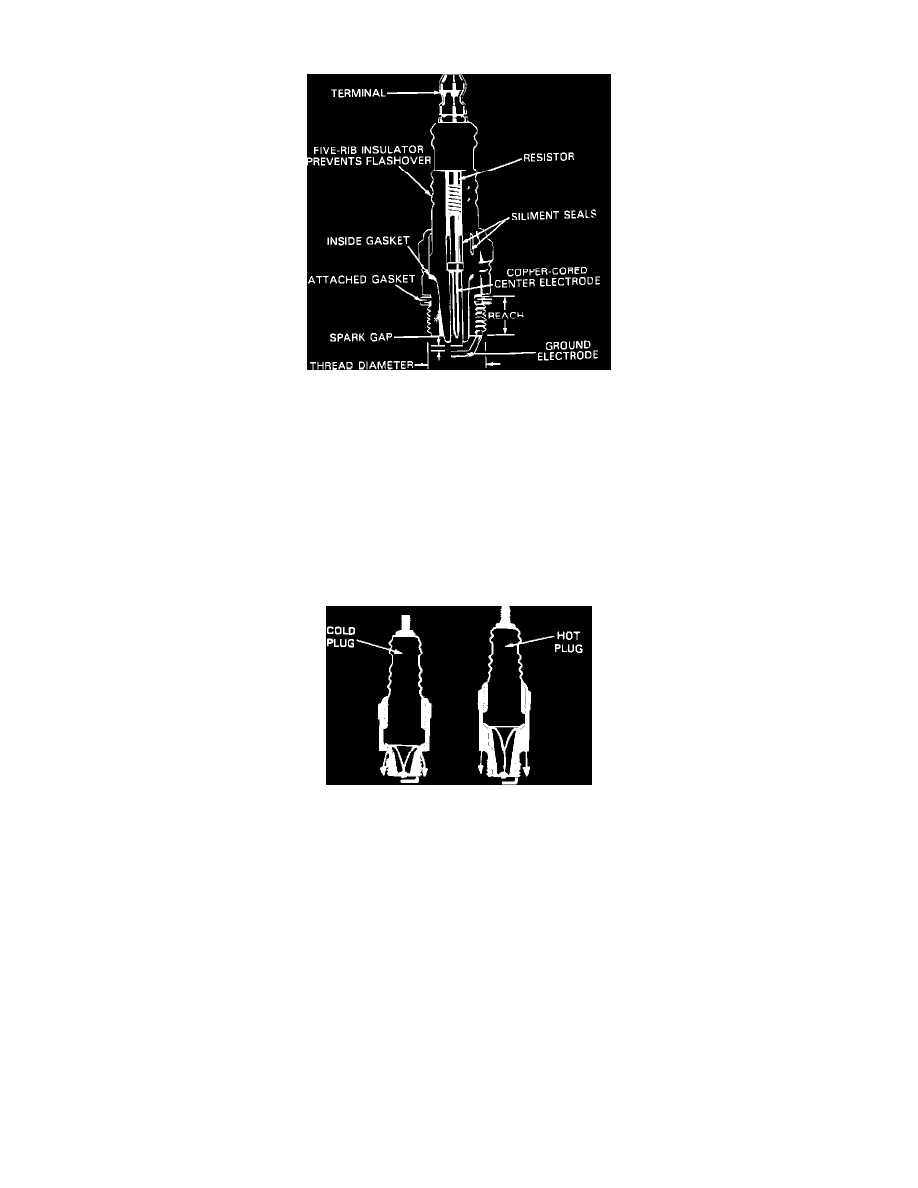
Spark Plug: Description and Operation
Spark Plug Construction
PURPOSE
Ignites the combustion mixture.
LOCATION
Threaded into the cylinder head, at the combustion chamber.
OPERATION
The spark plug provides a path for the high current of the secondary circuit to flow to ground. The only paths for this current are through the
ground electrode and center electrode across the spark gap. The spark produced when the current jumps the gap and ignites the air/fuel mixture in
the cylinder.
Spark Plug Heat Range
CONSTRUCTION
The temperature of the spark plug is determined by the length of the insulator and the size of the heatsink area. The longer the insulator is, the
smaller the heatsink area will be and this will cause the spark plug to be hotter.
- Change high voltage pulses to spark at gap which ignites fuel and air mixture.
- Have a platinum enhanced active electrode for long life.
FEATURES
The active electrode is different for LH and RH sides:
-
The spark plugs on the RH side (cylinders 1, 2 and 3) spark plugs are AWSF-42EG.
-
The spark plugs on the LH side (cylinders 4, 5 and 6) are AWSF-42E.
NOTE: AWSF-42EE spark plugs are used for replacement; the electrodes are platinum enhanced so they can replace either a RH or LH spark
plug.
