E 350 V8-5.4L (2008)
The ESM is an integrated differential pressure feedback EGR system that functions in the same manner as a conventional differential pressure
feedback EGR system. The various system components have been integrated into a single component called the ESM. The flange of the valve portion
of the ESM bolts directly to the intake manifold with a metal gasket that forms the metering orifice. This arrangement increases system reliability,
response time, and system precision. By relocating the EGR orifice from the exhaust to the intake side of the EGR valve, the downstream pressure
signal measures manifold absolute pressure (MAP). This MAP signal is used for EGR correction and inferred barometric pressure (BARO) at key on.
The system provides the powertrain control module (PCM) with a differential pressure feedback EGR signal, identical to a traditional differential
pressure feedback EGR system.
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Valve
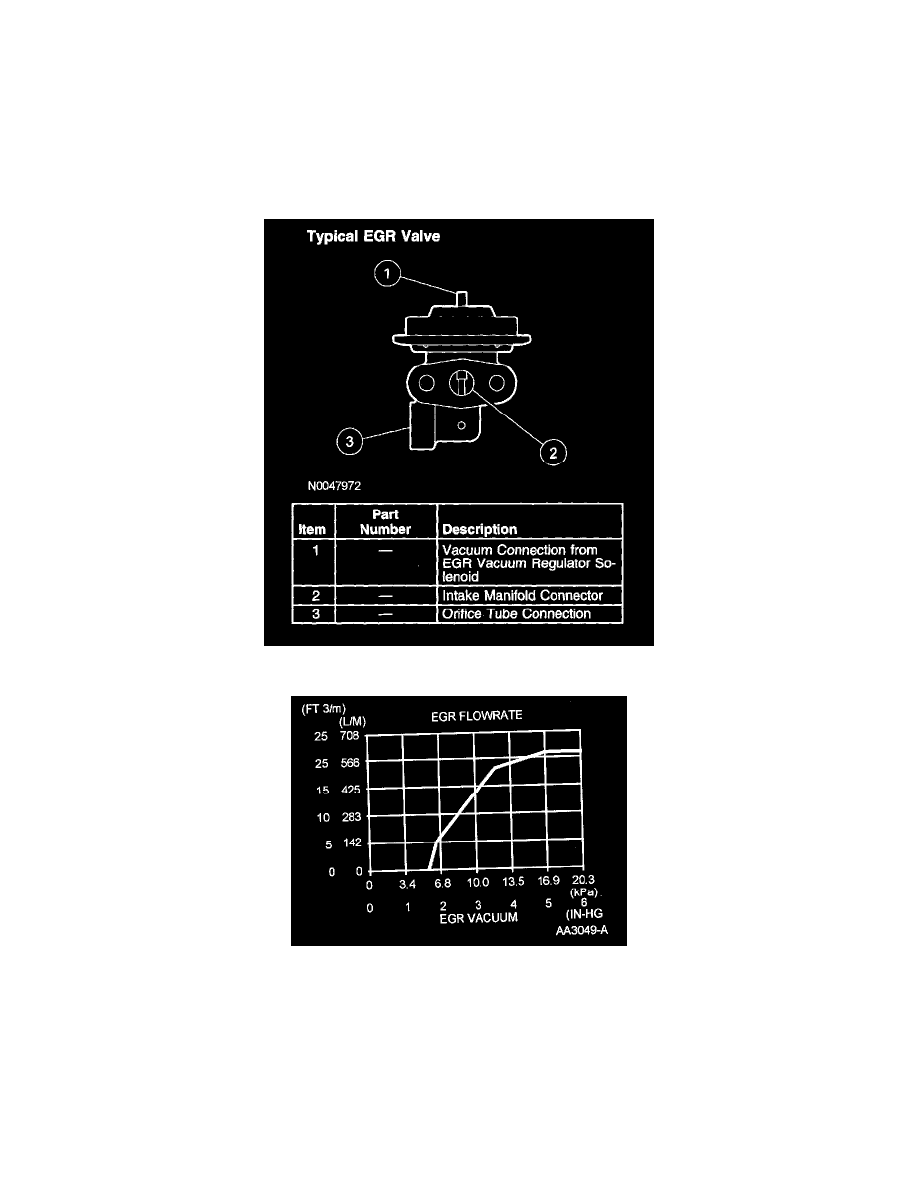
Typical EGR Valve
EGR Flowrate
The EGR valve in the differential pressure feedback EGR system is a conventional, vacuum-actuated. The valve increases or decreases the flow of
EGR. As vacuum applied to the EGR valve diaphragm overcomes the spring force, the valve begins to open. As the vacuum signal weakens, at 5.4
kPa (1.6 in-Hg) or less, the spring force closes the valve. The EGR valve is fully open at about 15 kPa (4.5 in-Hg).
Since EGR flow requirement varies greatly, providing repair specifications on flow rate is impractical. The on board diagnostic (OBD) system
monitors the EGR valve function and triggers a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) if the test criteria is not met. The EGR valve flow rate is not measured
directly as part of the diagnostic procedures.
