Explorer AWD V6-4.0L VIN K Flex Fuel (2003)
Throttle Body: Description and Operation
THROTTLE BODY SYSTEM OVERVIEW
The throttle body system meters air to the engine during idle, part throttle, and Wide Open Throttle (WOT) conditions. The throttle body system consists
of an Idle air control (IAC) valve assembly, idle air orifice, single or dual bores with butterfly valve throttle plates and a Throttle Position (TP) sensor.
One other source of idle air flow is the Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) system. The combined idle air flow (from idle air orifice IAC flow and
PCV flow) is measured by the MAF sensor on all applications.
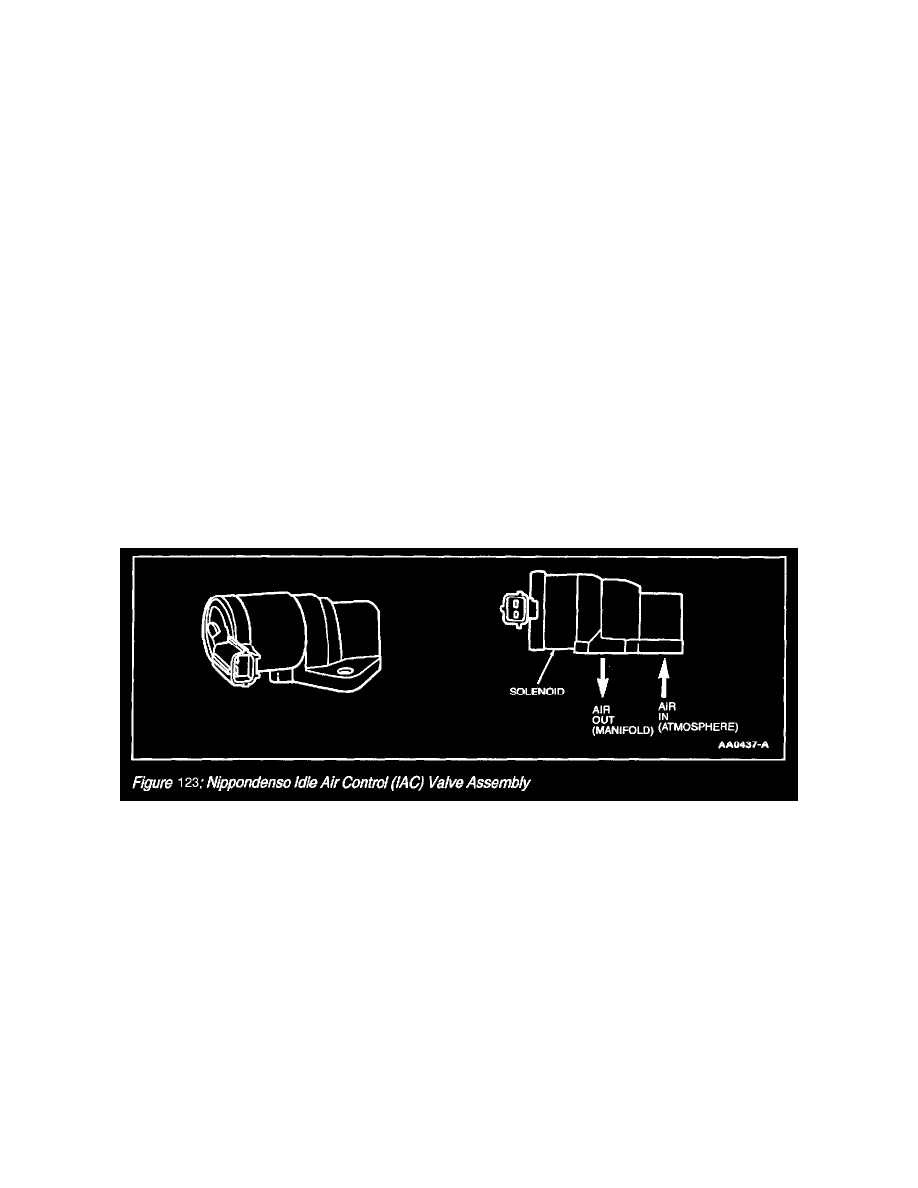
During idle, the throttle body assembly provides a set amount of air flow to the engine through the idle air passage and PCV valve. The IAC valve
assembly provides additional air when commanded by the powertrain control module (PCM) to maintain the proper engine idle speed under varying
conditions. The IAC valve assembly mounts directly to the throttle body assembly in most applications, but is remote-mounted to the intake manifold in
some applications. Idle speed is controlled by the PCM and cannot be adjusted.
NOTE: The traditional idle air adjust procedure as well as throttle return screw are no longer used on OBD II applications.
Throttle rotation is controlled by a cam/cable linkage to slow the initial opening rate of the throttle plate. The TP sensor monitors throttle position and
provides an electrical signal to the PCM. Some throttle body applications provide an air supply channel upstream of the throttle plate to provide fresh air
to the Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) or IAC systems. Other throttle body applications provide individual vacuum taps downstream of the throttle
plate for PCV return, Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR), Evaporative Emission (EVAP), and miscellaneous control signals.
Throttle Body System Hardware
The major components of the throttle body assembly include the TP sensor, IAC valve assembly, and throttle body housing assembly.
Throttle Position Sensor
The TP sensor monitors throttle position and provides an electrical signal to the PCM. It is monitored by the OBD II system for component integrity,
system functionality, and faults that can cause emissions levels to exceed standards set in government regulations. For additional information on the
TP sensor, refer to Electronic EC System Hardware-PCM Inputs.
Idle Air Control Valve
Nippondenso Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve Assembly
