F 150 4WD V8-4.6L VIN 8 (2010)
Fuel Injector: Description and Operation
ENGINE CONTROL COMPONENTS
Fuel Injectors
NOTICE: Do not apply battery positive (B+) voltage directly to the fuel injector electrical connector terminals. The solenoids may be
damaged internally in a matter of seconds.
The fuel injector is a solenoid-operated valve that meters fuel flow to the engine. The fuel injector is opened and closed a constant number of times
per crankshaft revolution. The amount of fuel is controlled by the length of time the fuel injector is held open.
The fuel injector is normally closed, and is operated by a 12-volt source from either the powertrain control module (PCM) power relay or fuel pump
relay. The ground signal is controlled by the PCM.
The injector is the deposit resistant injector (DRI) type and does not have to be cleaned. Install a new fuel injector if the flow is checked and found to
be out of specification.
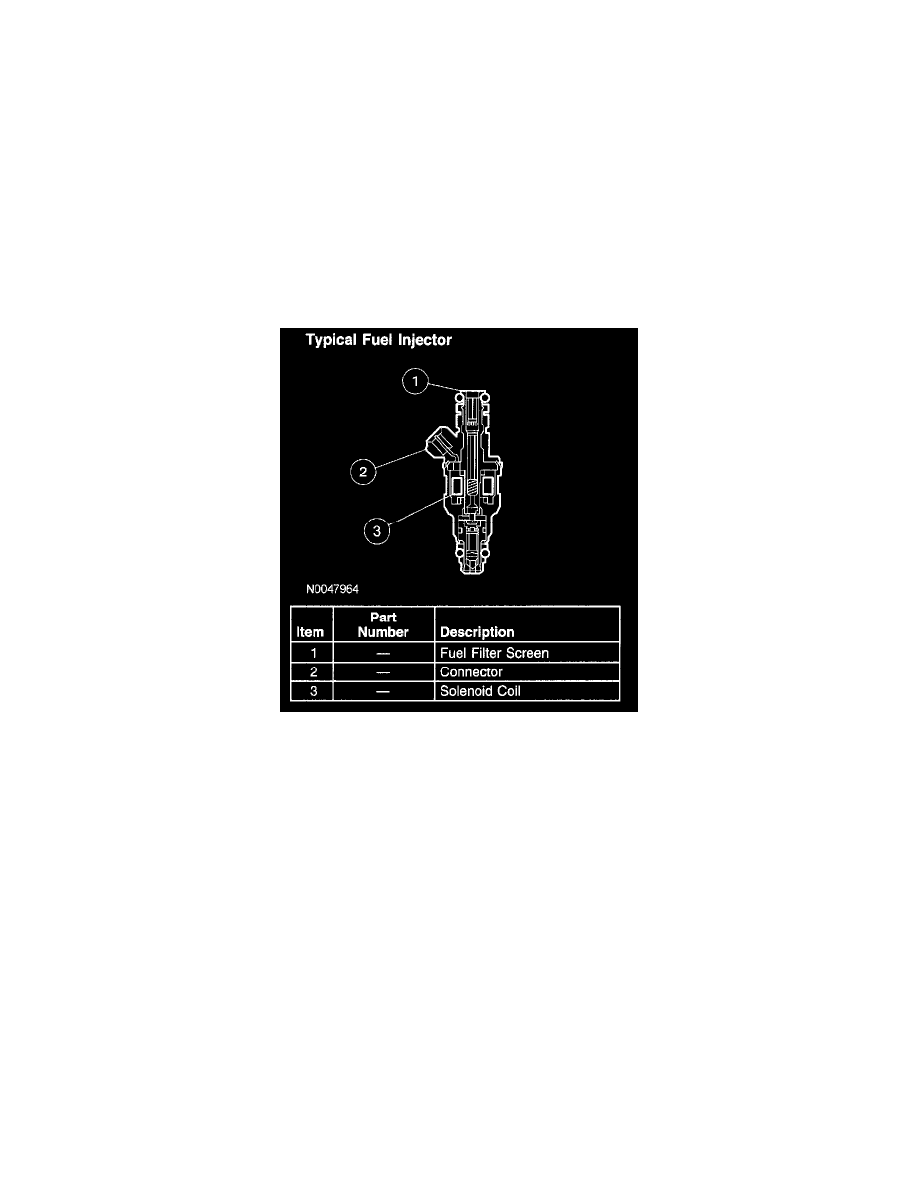
Typical Fuel Injector
Fuel Injectors - Direct Injection
The gasoline direct fuel injection fuel injector delivers fuel directly into the cylinder under high pressure. Each injector is controlled by 2 circuits from
the PCM.
A boosted voltage supply, up to 65 volts, is generated in the PCM and used to initially open the injector. The injector driver controls three transistor
switches that apply the boost voltage to open the injector and then modulates the current to hold the injector open. If boost voltage is unavailable, the
proper injector opening current may not be generated in the time required.
The PCM contains a smart driver that monitors and compares high side and low side injector currents to diagnose numerous concerns. Each fuel
injector high side circuit is paired inside the PCM with another fuel injector high side circuit. All injector concerns are reported with a single DTC per
injector.
