F 150 4WD Pickup V8-351 5.8L (1982)
Compression Check: Testing and Inspection
COMPRESSION TEST
1. Ensure oil in crankcase is of the correct viscosity and at proper level and battery is properly charged. Operate vehicle until engine is at normal
operating temperature. Turn OFF ignition switch, then remove all spark plugs.
2. Set throttle plates (and choke plates, if equipped) in wide-open position.
3. Install a compression gauge such as Rotunda Compression Tester 059-00009 or equivalent in No. 1 cylinder.
4. Install an auxiliary starter switch in starting circuit. With ignition switch in the OFF position, and using auxiliary starter switch, crank engine at
least five compression strokes and record highest reading. Note the approximate number of compression strokes required to obtain the highest
reading.
5. Repeat test on each cylinder cranking the engine approximately the same number of compression strokes.
TEST CONCLUSION
1. The indicated compression pressures are considered within specification if the lowest reading cylinder is within 75 percent of the highest.
2. If one or more cylinders read low, squirt approximately one tablespoon of heavy SAE 50 weight or equivalent engine oil on top of the pistons in
the low reading cylinders. Repeat compression pressure check on these cylinders.
a. If compression improves considerably, piston rings are at fault.
b. If compression does not improve, valves are sticking or seating poorly.
c. If two adjacent cylinders indicate low compression pressures and squirting oil on pistons does not increase compression, cause may be a
cylinder head gasket leak between cylinders. Engine oil and/or coolant in cylinders could result from this problem.
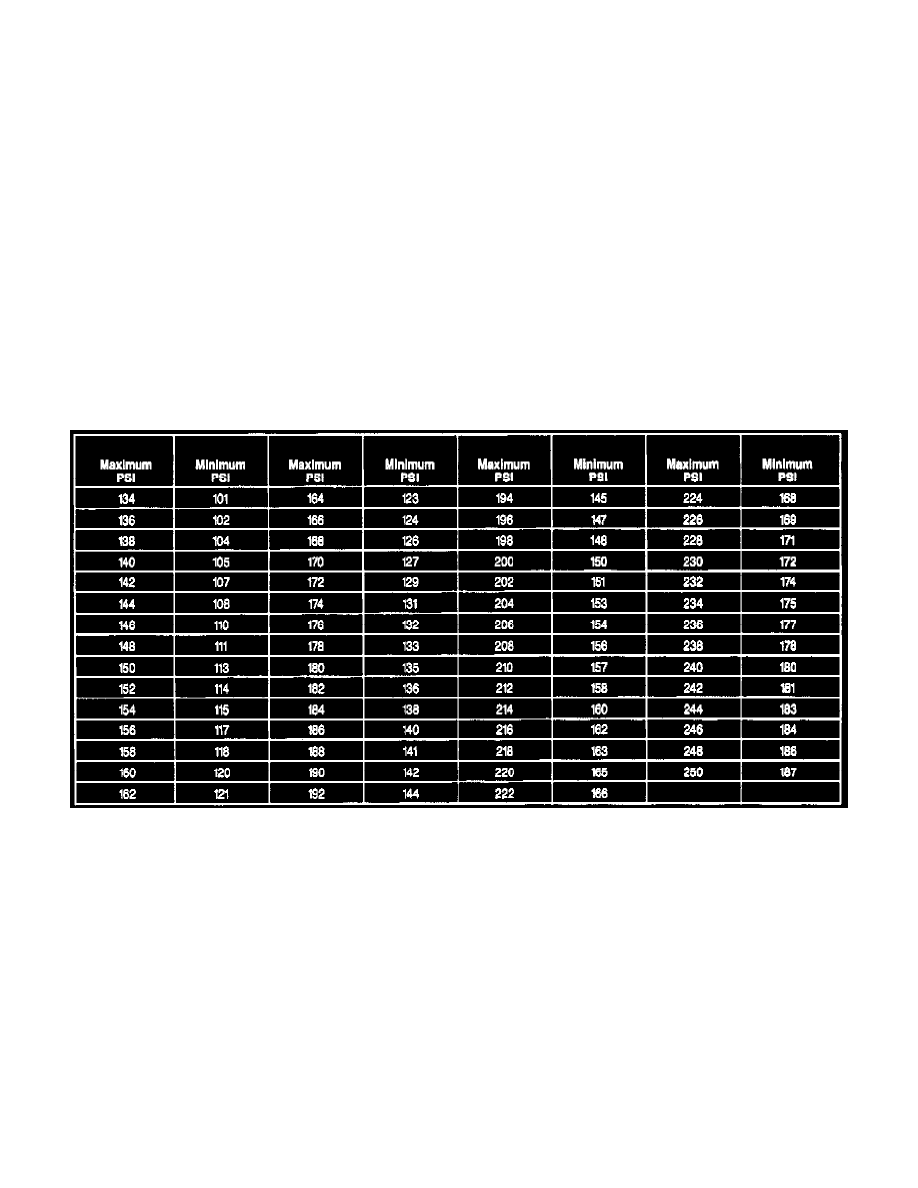
Compression Pressure Limit Chart
NOTE: Refer to the compression pressure limit chart for pressure specifications.
