F 250 4WD Pickup L6-300 4.9L (1982)
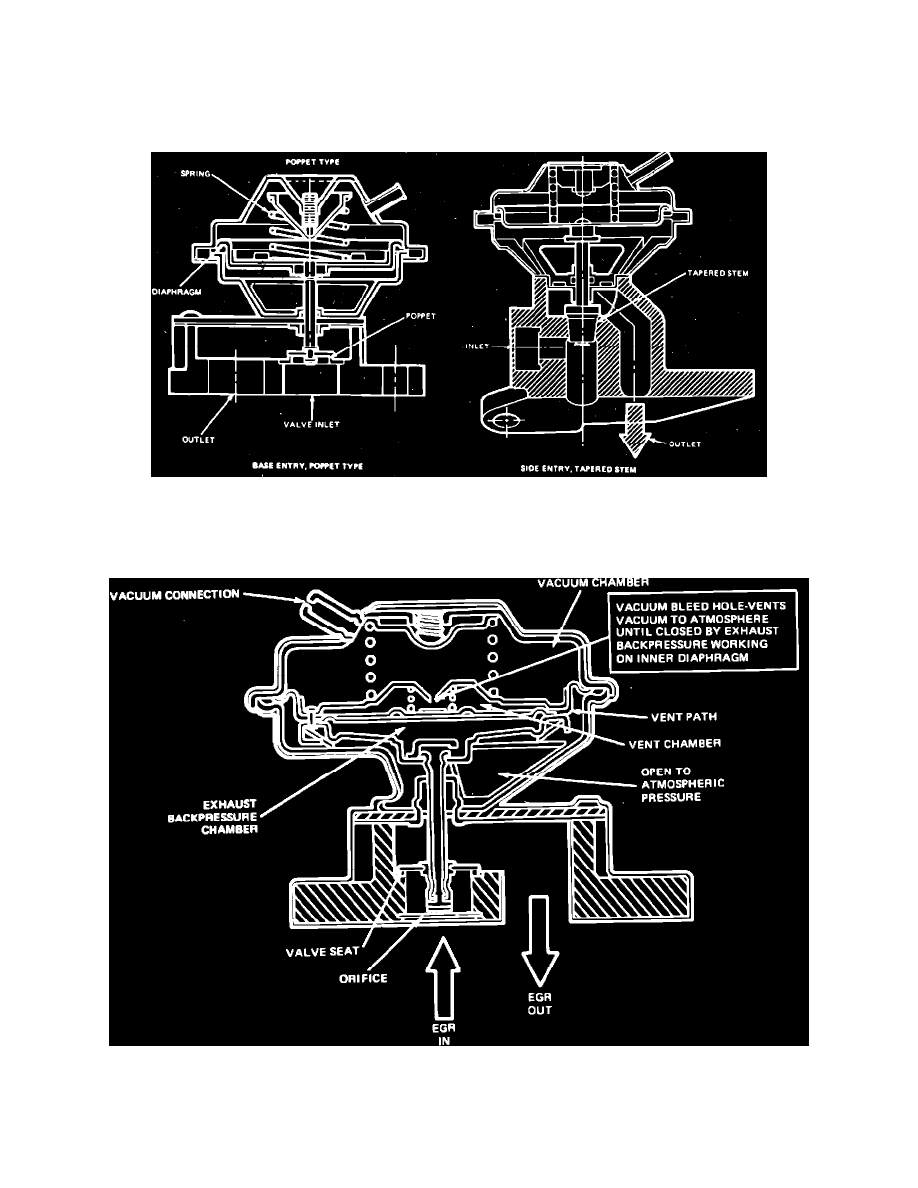
Fig. 6 EGR valve position sensor
This sensor, Fig. 6, is used to monitor the EGR valve pintle position. The computer applies a reference voltage to the EVP sensor, and the
resulting signal from the EVP sensor is proportional to the amount of exhaust gases flowing through the EGR valve pintle into the intake manifold.
Depending on the input from this and other sensors, the computer can increase or decrease EGR flow by activating or deactivating a pair of
solenoid vacuum valves.
Fig. 49 Ported type EGR valves
Ported type valves, Fig. 49, may be of the poppet or tapered stem design and can have base or side entry. The two passages connecting the exhaust
system to intake manifold are blocked by a valve which is opened by vacuum and closed by spring pressure.
Fig. 50 Integral back pressure transducer EGR valve
The integral back pressure transducer valve, Fig. 50, cannot be opened by vacuum until the bleed hole is closed by exhaust back pressure. When
open, the valve oscillates at a level dependent on the exhaust back pressure flowing through the orifice. Valve opening increases as signal vacuum
and exhaust back pressure increases.
