F 250 4WD Super Duty V10-6.8L (2002)
EGR Valve: Description and Operation
Electric Motor EGR System (EEGR)
Electric Motor EGR System (EEGR)
Highlights of the Electric System
^
EEGR valve is activated by an electric stepper motor not a vacuum motor (Rear of engine block).
^
No vacuum diaphragm is used.
^
No DPFE sensor is used.
^
No Orifice Tube/Assembly is used.
^
No EGR vacuum regulator solenoid is used.
^
A new Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor is used (called Thermal Manifold Absolute Pressure (TMAP) but the temperature function
is not used at this time) (located on top of the valve cover).
^
Engine coolant is routed through the assembly extending durability of the electric motor.
Overview
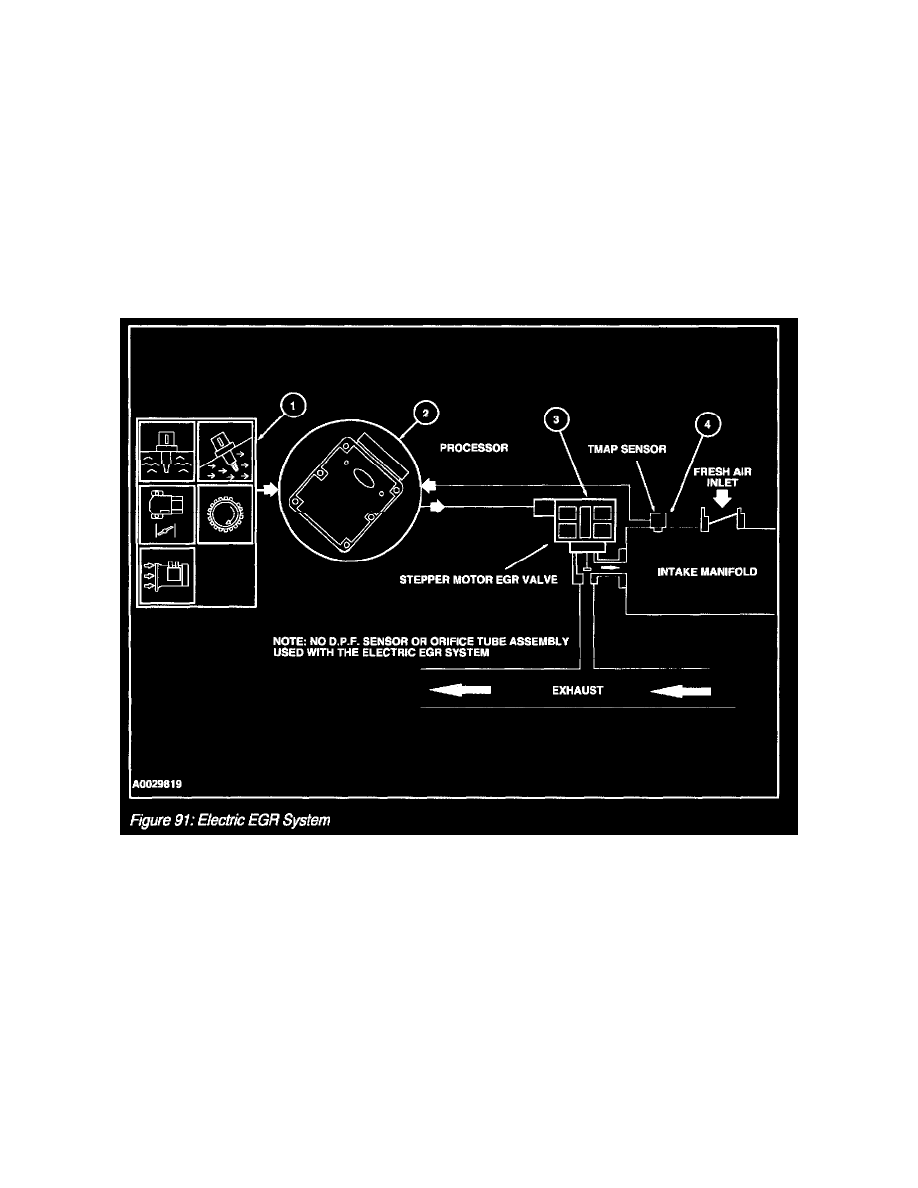
Electric EGR System
The electric EGR system uses exhaust gas recirculation to control the Oxides Of Nitrogen (NOx) emissions just like vacuum operated systems.
The only difference is the way in which the exhaust gas is controlled.
The Electric EGR system consists of an electric motor/EGR valve integrated assembly, a PCM, and connecting wiring. Additionally a MAP sensor
is also required. Operation of the system is as follows (Figure 91):
1. The EEGR system receives signals from the Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) or Cylinder Head Temperature (CHT) sensor, throttle
position (TP) sensor, mass air flow (MAF) sensor, crankshaft position (CKP) sensor and the manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor to
provide information on engine operating conditions to the PCM. The engine must be warm, stable and running at a moderate load and rpm
before the EEGR system is activated. The PCM will deactivate EGR during idle, extended wide open throttle or whenever a failure is
detected in an EEGR component or EGR required input.
2. The PCM calculates the desired amount of EGR for a given set of engine operating conditions.
3. The PCM in turn will output signals to the EEGR motor to move (advance or retract) a certain number of discrete steps. The electric
stepper motor will directly actuate the EGR valve, independent of engine vacuum. The EGR valve is commanded from 0 to 52 discrete
increments or "steps" to get the EGR valve from a fully closed to full or partially open position. The position of the EGR valve determines
the EGR flow.
