F 350 2WD Super Duty V10-6.8L (2009)
Intake Air Temperature Sensor: Description and Operation
Engine Control Components
Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor
The IAT sensor is a thermistor device in which resistance changes with temperature. The electrical resistance of a thermistor decreases as the
temperature increases, and the resistance increases as the temperature decreases. The varying resistance affects the voltage drop across the sensor
terminals and provides electrical signals to the PCM corresponding to temperature.
Thermistor-type sensors are considered passive sensors. A passive sensor is connected to a voltage divider network so that varying the resistance of the
passive sensor causes a variation in total current flow. Voltage that is dropped across a fixed resistor in a series with the sensor resistor determines the
voltage signal at the PCM. This voltage signal is equal to the reference voltage minus the voltage drop across the fixed resistor.
The IAT sensor provides air temperature information to the PCM. The PCM uses the air temperature information as a correction factor in the calculation
of fuel, spark, and air flow.
The IAT sensor provides a quicker temperature change response time than the ECT or CHT sensor.
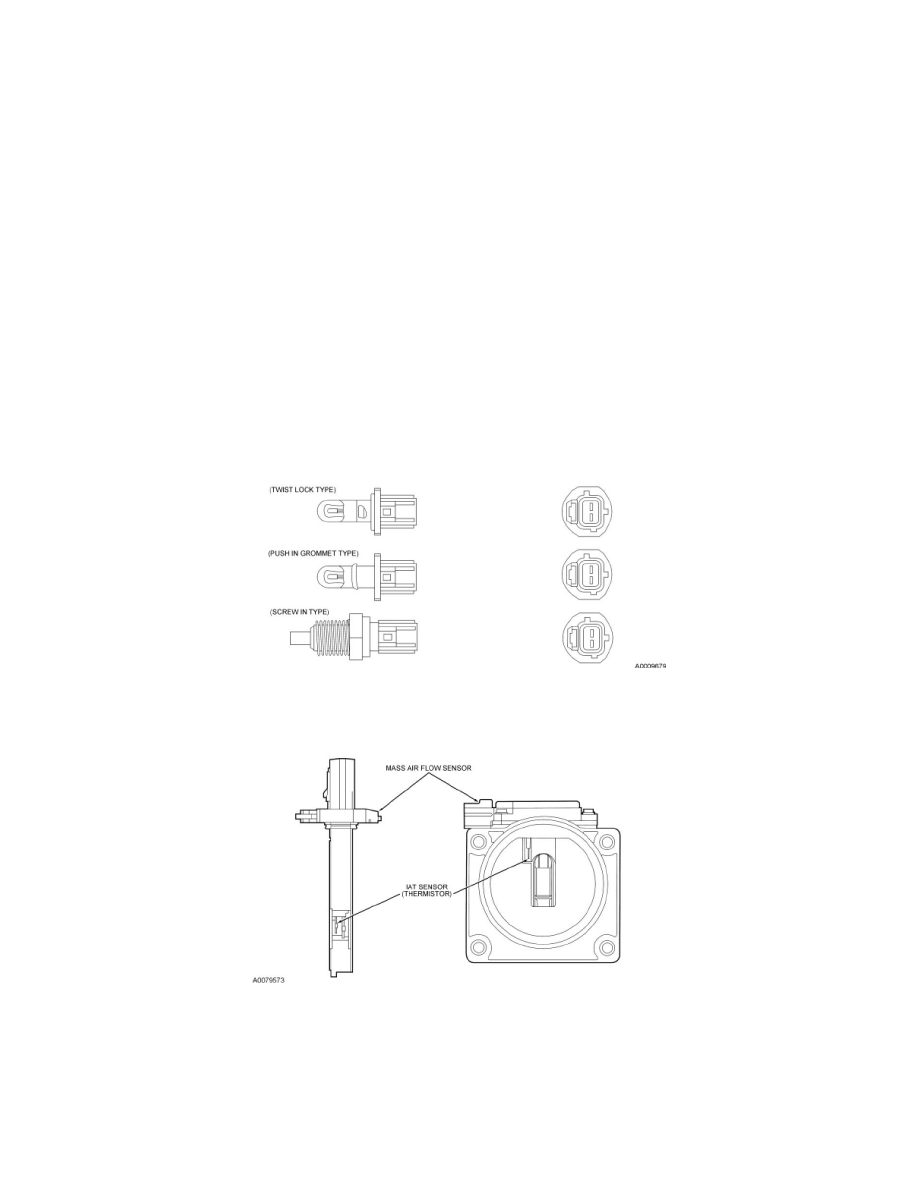
Currently there are two types of IAT sensors used, a stand-alone/non-integrated type and a integrated type. Both types function the same, however the
integrated type is incorporated into the mass air flow (MAF) sensor instead of being a stand alone sensor.
Supercharged vehicles use two IAT sensors. Both sensors are thermistor type devices and operate as described above. One is located before the
supercharger at the air cleaner for standard OBD/cold weather input, while a second sensor (IAT2) is located after the supercharger in the intake
manifold. The IAT2 sensor located after the supercharger provides air temperature information to the PCM to control spark and to help determine charge
air cooler (CAC) efficiency.
Typical Stand-Alone/Non-Integrated Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensors
Typical Stand-Alone/Non-Integrated Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensors
Typical Integrated Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor Incorporated Into a Drop-in or Flange-type MAF Sensor
Typical Integrated Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor Incorporated Into a Drop-in or Flange-type MAF sensor
