F 350 4WD Super Duty V8-6.4L DSL Turbo (2008)
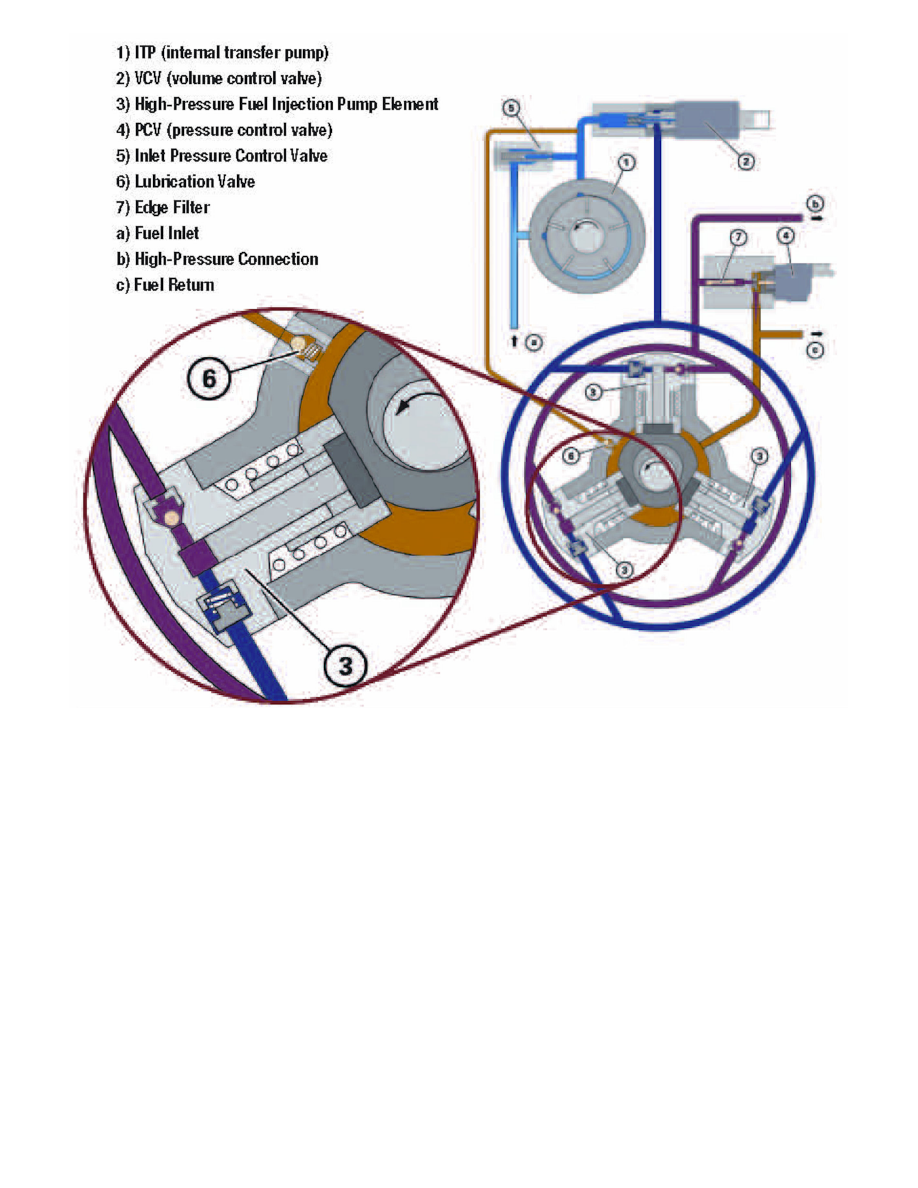
High Pressure Pump Operation
^ After being filtered at the engine mounted fuel filter fuel is directed to the high pressure fuel injection pump.
^ Before fuel enters the Volume Control Valve (VCV) the pressure is stepped up by the Internal Transfer Pump (ITP). The ITP is located inside the
high pressure fuel injection pump and is driven by its main shaft.
^ The VCV controls how much fuel enters the three (3) main pump pistons.
^ A portion of the fuel leaving the ITP is sent to a lubrication valve which allows fuel to lubricate and cool the internal mechanical components of the
high pressure fuel injection pump.
^ The high pressure fuel injection pump main shaft has an offset journal that actuates each of the three (3) pistons as the shaft rotates.
^ The offset journal of the main shaft utilizes a free-spinning hub to make contact with the three (3) pistons.
^ The pistons start their compression stroke via the offset journal and are returned to rest via spring pressure.
^ The pistons receive fuel from the VCV through a one way check valve. Fuel is drawn into the cylinder while the piston is returning to rest.
^ The outlet check valve ball is closed while fuel is being drawn in due to the suction (low pressure area) of the piston returning to rest and the pressure
exerted by the other two pistons.
^ Once the piston starts its compression stroke the inlet check valve closes via spring and fuel pressure and the outlet check valve opens due to
increasing fuel pressure forcing the check valve ball away from its seat.
^ The pressure control valve (PCV) controls the pressure in the system by restricting fuel flow to the return line (pressure is the resistance to flow).
High Pressure Fuel Injection Pump & Cover
^ The high pressure fuel injection pump is installed in the crankcase.
^ The pump is a three (3) piston rotary style pump that is driven by the rear gear train.
^ Each bank of cylinders has its own pump outlet and high pressure fuel supply tube.
