Five Hundred AWD V6-3.0L VIN 1 (2005)
Pressure Feedback Exhaust Sensor: Description and Operation
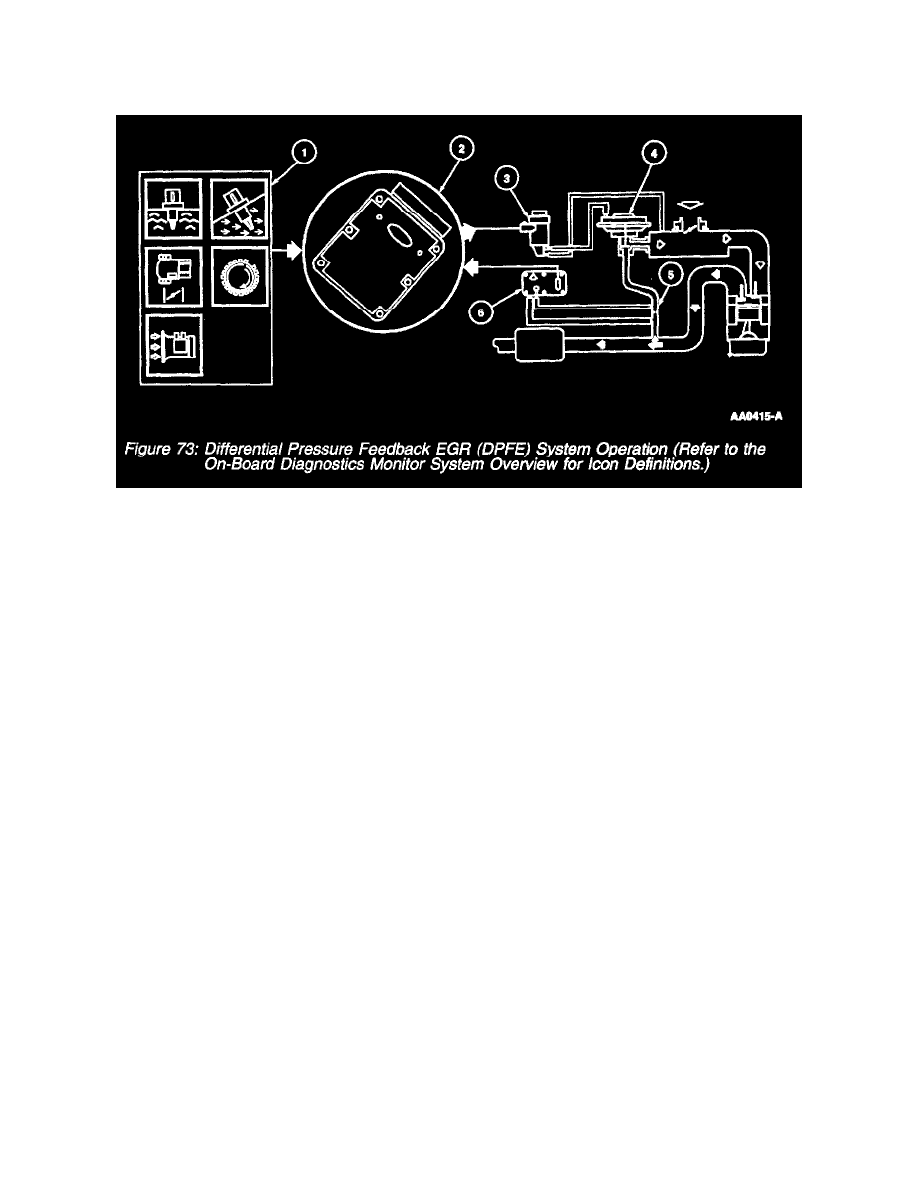
Differential Pressure Feedback EGR (DPFE) System
DIFFERENTIAL PRESSURE FEEDBACK EGR (DPFE) SYSTEM
Differential Pressure Feedback EGR (DPFE) System Operation
The differential pressure feedback EGR system consists of a differential pressure feedback EGR sensor, EGR vacuum regulator (EVR) solenoid, EGR
valve, orifice tube assembly, powertrain control module (PCM), and connecting wires and vacuum hoses. Operation of the system is as follows:
1. The DPFE system receives signals from the engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor or cylinder head temperature (CHT) sensor, intake air
temperature (IAT) sensor, throttle position (TP) sensor, mass air flow (MAF) sensor, and crankshaft position (CKP) sensor to provide information
on engine operating conditions to the PCM. The engine must be warm, stable, and running at a moderate load and RPM before the EGR system is
activated. The PCM deactivates EGR during idle, extended wide open throttle, or whenever a failure is detected in an EGR component or EGR
required input.
2. The PCM calculates the desired amount of EGR flow for a given engine condition. It then determines the desired pressure drop across the
metering orifice required to achieve that flow and outputs the corresponding signal to the EVR solenoid.
3. The EVR solenoid receives a variable duty cycle signal (0 to 100%). The higher the duty cycle the more vacuum the solenoid diverts to the EGR
valve.
4. The increase in vacuum acting on the EGR valve diaphragm overcomes the valve spring and begins to lift the EGR valve pintle off its seat, causing
exhaust gas to flow into the intake manifold.
5. Exhaust gas flowing through the EGR valve must first pass through the EGR metering orifice. With one side of the orifice exposed to exhaust
backpressure and the other to the intake manifold, a pressure drop is created across the orifice whenever there is EGR flow. When the EGR valve
closes, there is no longer flow across the metering orifice and pressure on both sides of the orifice is the same. The PCM constantly targets a
desired pressure drop across the metering orifice to achieve the desired EGR flow.
6. The DPFE sensor measures the actual pressure drop across the metering orifice and relays a proportional voltage signal (0 to 5 volts) to the PCM.
The PCM uses this feedback signal to correct for any errors in achieving the desired EGR flow.
