Fusion AWD V6-3.0L (2009)
catalyst.
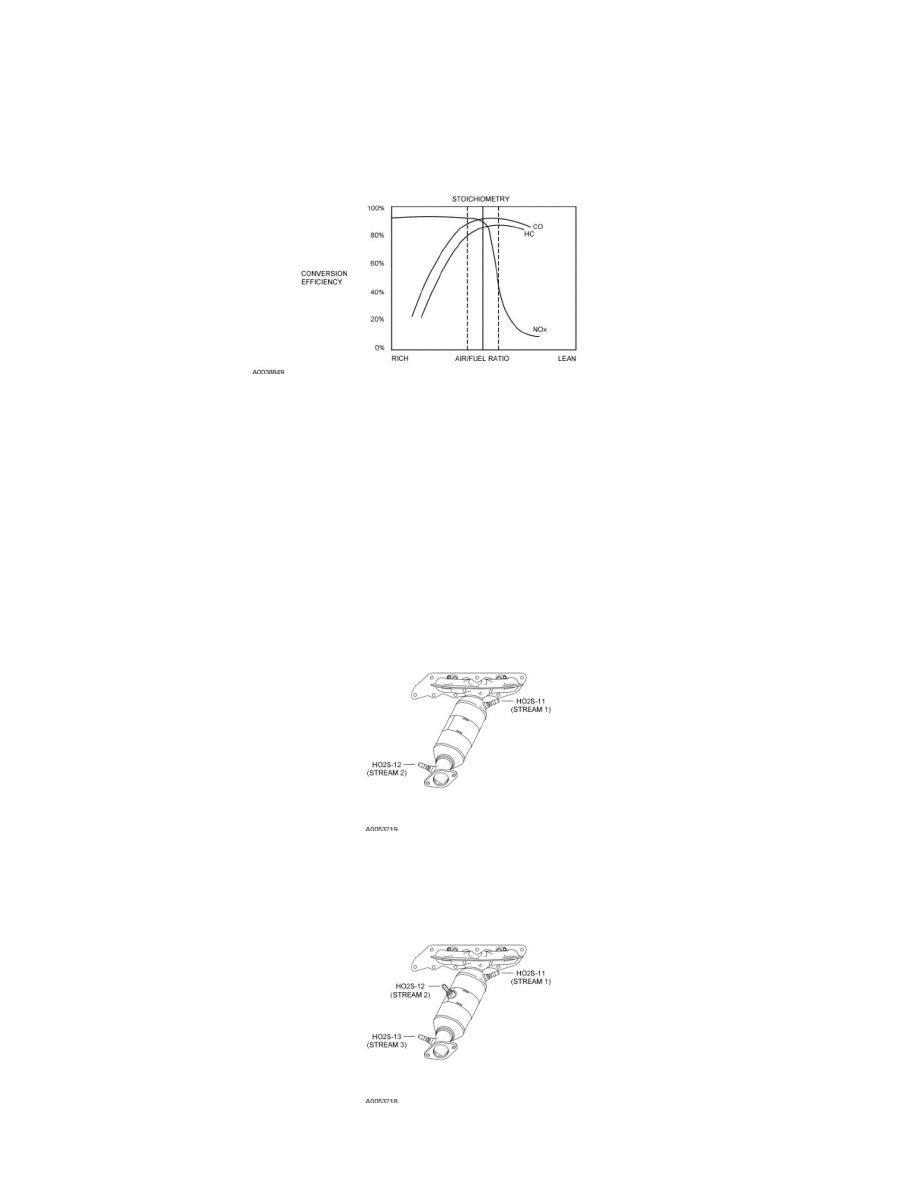
Three Way Catalytic Converter (TWC) Conversion Efficiency
A TWC requires a stoichiometric fuel ratio, 14.7 pounds of air to 1 pound of fuel (14.7:1), for high conversion efficiency. In order to achieve these high
efficiencies, the air/fuel ratio must be tightly controlled with a narrow window of stoichiometry. Deviations outside of this window greatly decrease the
conversion efficiency. For example a rich mixture decreases the HC and CO conversion efficiency while a lean mixture decreases the NOx conversion
efficiency.
TWC Conversion Efficiency Chart
TWC Conversion Efficiency Chart
Exhaust System
The purpose of the exhaust system is to convey engine emissions from the exhaust manifold to the atmosphere. Engine exhaust emissions are directed
from the engine exhaust manifold to the catalytic converter through the front exhaust pipe. A HO2S is mounted on the front exhaust pipe before the
catalyst. The catalytic converter reduces the concentration of CO, unburned HCs, and NOx in the exhaust emissions to an acceptable level. The reduced
exhaust emissions are directed from the catalytic converter past another HO2S mounted in the rear exhaust pipe and then on into the muffler. Finally, the
exhaust emissions are directed to the atmosphere through an exhaust tailpipe.
On some PZEV, there is a total of three HO2Ss in the exhaust stream. One near the exhaust manifold (stream 1), one in the middle of the light-off
catalyst (stream 2), and the third (stream 3) is mounted after the light-off catalyst.
Typical Bank 1 Catalyst 2 H2OS Configuration
Typical Bank 1 Catalyst 2 HO2S Configuration
Typical Bank 1 Catalyst 3 H2OS Configuration
