Fusion FWD V6-3.0L (2009)
Diagrams/Diagrams By Number
Refer to Wiring Diagram Set 131, Parking Aid for schematic and connector information. See: Diagrams/Electrical Diagrams/Diagrams By Number
Normal Operation
The Parking Aid Module (PAM) communicates with the scan tool through the Medium Speed Controller Area Network (MS-CAN). Circuits VDB06
(GY/OG) (MS-CAN +) and VDB07 (VT/OG) (MS-CAN -) provide the network connection to the PAM. Voltage for the PAM is provided by circuit
CBP35 (YE/GY). Circuit GD133 (BK) provides ground.
This pinpoint test is intended to diagnose the following:
-
Fuse
-
Wiring, terminals or connectors
-
PAM
PINPOINT TEST J: THE PAM DOES NOT RESPOND TO THE SCAN TOOL
NOTICE: Use the correct probe adapter(s) when making measurements. Failure to use the correct probe adapter(s) may damage the
connector.
NOTE: Failure to disconnect the battery when instructed will result in false resistance readings. Refer to Battery.
-------------------------------------------------
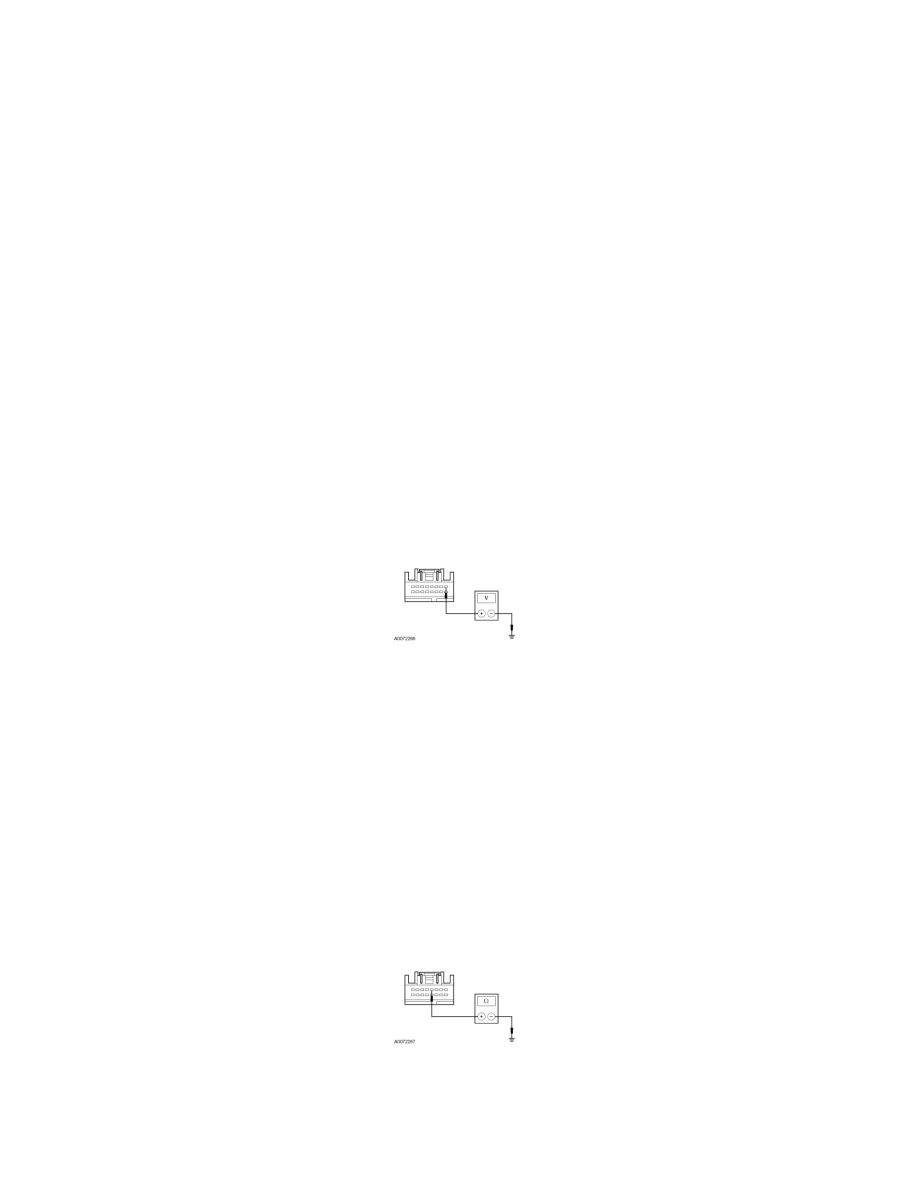
J1 CHECK THE PAM VOLTAGE SUPPLY CIRCUIT FOR AN OPEN
-
Ignition OFF.
-
Disconnect: PAM C4014.
-
Ignition ON.
-
Measure the voltage between the PAM C4014-1, circuit CBP19 (BN/WH), harness side and ground.
-
Is the voltage greater than 10 volts?
Yes
GO to J2.
No
VERIFY the Smart Junction Box (SJB) fuse 28 (10A) is OK. If OK, REPAIR the circuit. TEST the system for normal operation. If not OK, REFER to
the Wiring Diagrams to identify the possible causes of the circuit short.
-------------------------------------------------
J2 CHECK THE PAM GROUND CIRCUIT FOR AN OPEN
-
Ignition OFF.
-
Disconnect: Negative Battery Cable.
-
Measure the resistance between the PAM C4014-4, circuit GD171 (BK/GY), harness side and ground.
-
Is the resistance less than 5 ohms?
Yes
GO to J3.
