Granada L4-140 2.3L VIN A 2-bbl (1982)
ELECTRODE - Posts or plates which have an electrical potential with respect to each other, such as in a spark plug or battery. Electrodes are either
positive or negative.
ELECTROLYTE - Active chemical filler in a battery.
ELECTROMAGNETIC - Refers to a device which incorporates both electronic and magnetic principles together in its operation.
ELECTROMECHANICAL - Refers to a device which incorporates both electronic and mechanical principles together in its operation.
ELECTROMECHANICAL INSTRUMENT CLUSTER - Instrument cluster, first introduced on Taurus/Sable models, that utilizes magnetic gauges and
an "overlapping subassemblies" design. Use of the "overlapping sub-assemblies" design eases service because individual gauge sub-assemblies can be
removed as individual pieces.
ELECTRON - Negatively charged portion of an atom that orbits around the nucleus of the atom.
ELECTRONIC - An operation, produced or caused by the action of electrons or by devices which function as a result of electron action. Electronic is
often used to describe the control of systems or devices by the use of small electrical signals and various semiconductor devices and circuits.
EMF - Electromotive force or voltage.
EMITTER - One of three elements or terminals of a transistor that emits the electrons that the collector collects.
ENABLE - A type of microcomputer decision which results in an automotive system being activated and permitted to operate.
ENERGIZED - Having the electrical current or electrical source turned on.
F
FAILURE MODE EFFECTS MANAGEMENT (FMEM) STRATEGY - EEC IV strategy designed to reduce the adverse effects that may be caused by
an EEC system sensor failure. Should a sensor fail, the ECA substitutes a good sensor signal in its place. This allows the engine to keep running so that
the vehicle can be driven to the dealer for service.
FIELD (A/C) - A coil with many turns of wire located behind the clutch rotor. Current passing through this coil sets up a magnetic field and causes the
clutch to engage.
FIELD - Magnetic lines of force orientated from north to south as in a magnetic field. A magnetic field may be natural as with a permanent magnet or
created when electricity flows in a wire.
FIELD COIL - A coil of insulated wire usually wound around an iron core. Current flowing in the coil produces a magnetic field. Also called "field
winding." FILAMENT - A resistance in a light bulb which glows and produces light when a current is forced through it.
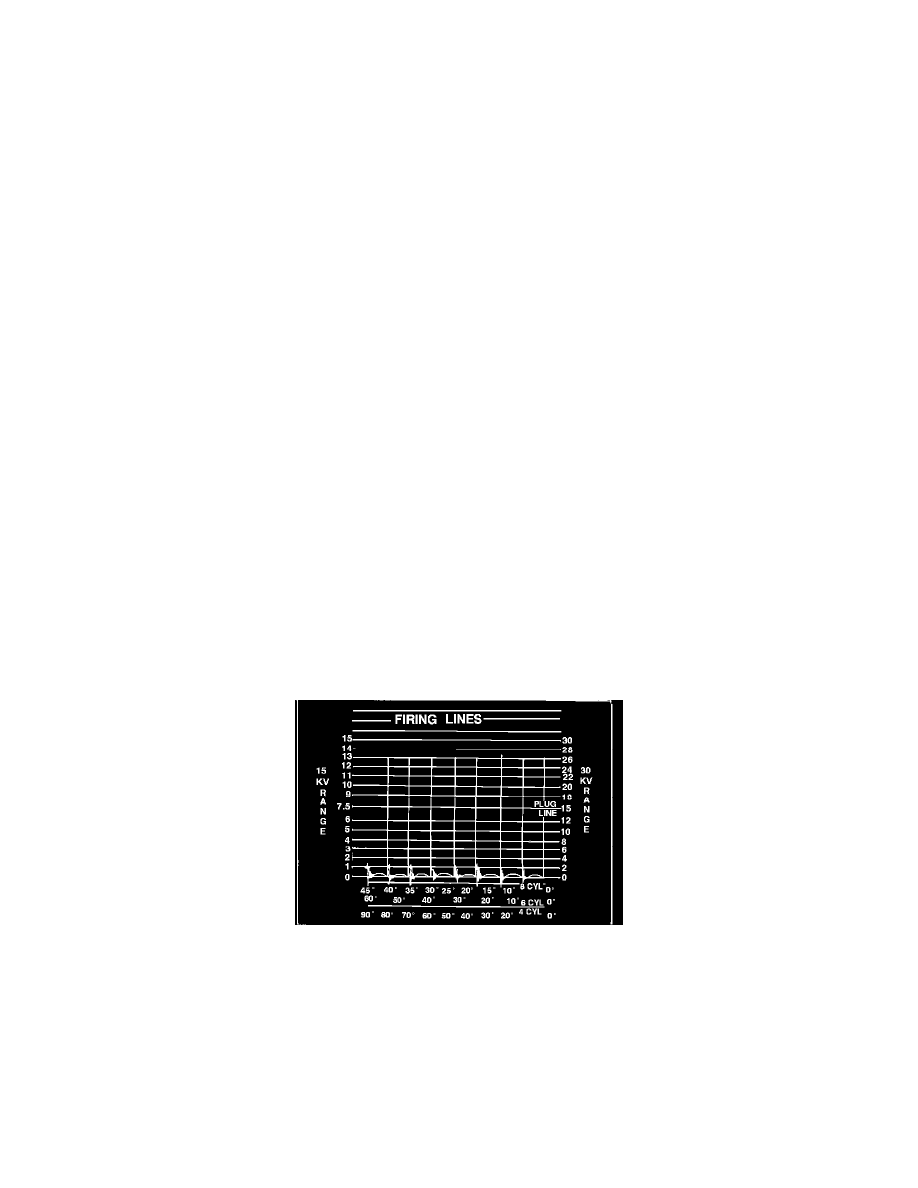
FIRING LINE
FIRING LINE - The total amount of voltage being expended through the secondary circuit.
FLUX - Electric or magnetic lines of force passing or flowing in a magnetic field. Also, material used to cause joining metal to adhere to both parts to be
joined.
FOUR-WAY FLASHERS - See "hazard warning system."
FREE ELECTRON - Electrons that are not bound to a certain atom but are free to move around from atom to atom.
FREQUENCY - Refers to the number of times something repeats itself (such as a signal from a sensor) in one second.
