LTD Country Squire V8-302 5.0L VIN F TBI (1983)
Catalytic Converter: Description and Operation
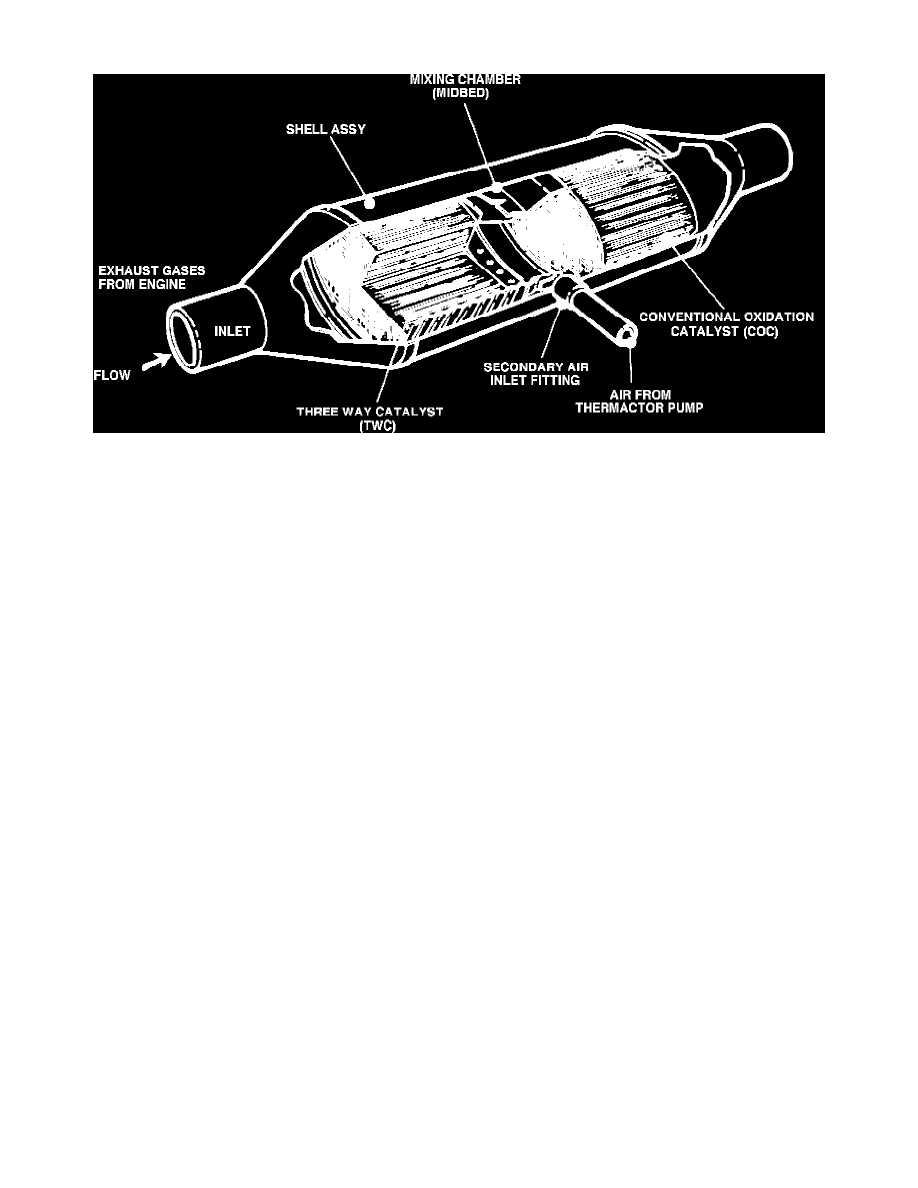
Fig. 15 Dual catalytic converter
This converter consists of two catalytic converters in one shell, with a mixing chamber in between the two, Fig. 15. Each converter is composed of
a ceramic ``honeycomb'' coated with a rhodium/platinum catalyst designed to control oxides of nitrogen (NOx), unburned hydrocarbons (HC) and
carbon monoxide (CO), and is therefore called a ``three-way catalyst'' (TWC). The rear converter is coated with platinum catalyst and is called a
``conventional'' oxidation catalyst'' (COC) converter. The platinum catalyst is also called a ``two-way catalyst'' since it only acts on two of the
major pollutants, HC and CO.
The TWC converter acts on the exhaust gases from the engine. As the gases flow from the TWC to the COC converter, they mix with air from the
thermactor pump injected into the mixing chamber or ``midbed.'' This air is required for proper oxidation of HC and CO in the COC converter.
