Ranger 2WD L4-2.3L VIN D (2001)
Catalytic Converter: Description and Operation
Catalyst and Exhaust Systems
Catalyst and Exhaust System
Overview
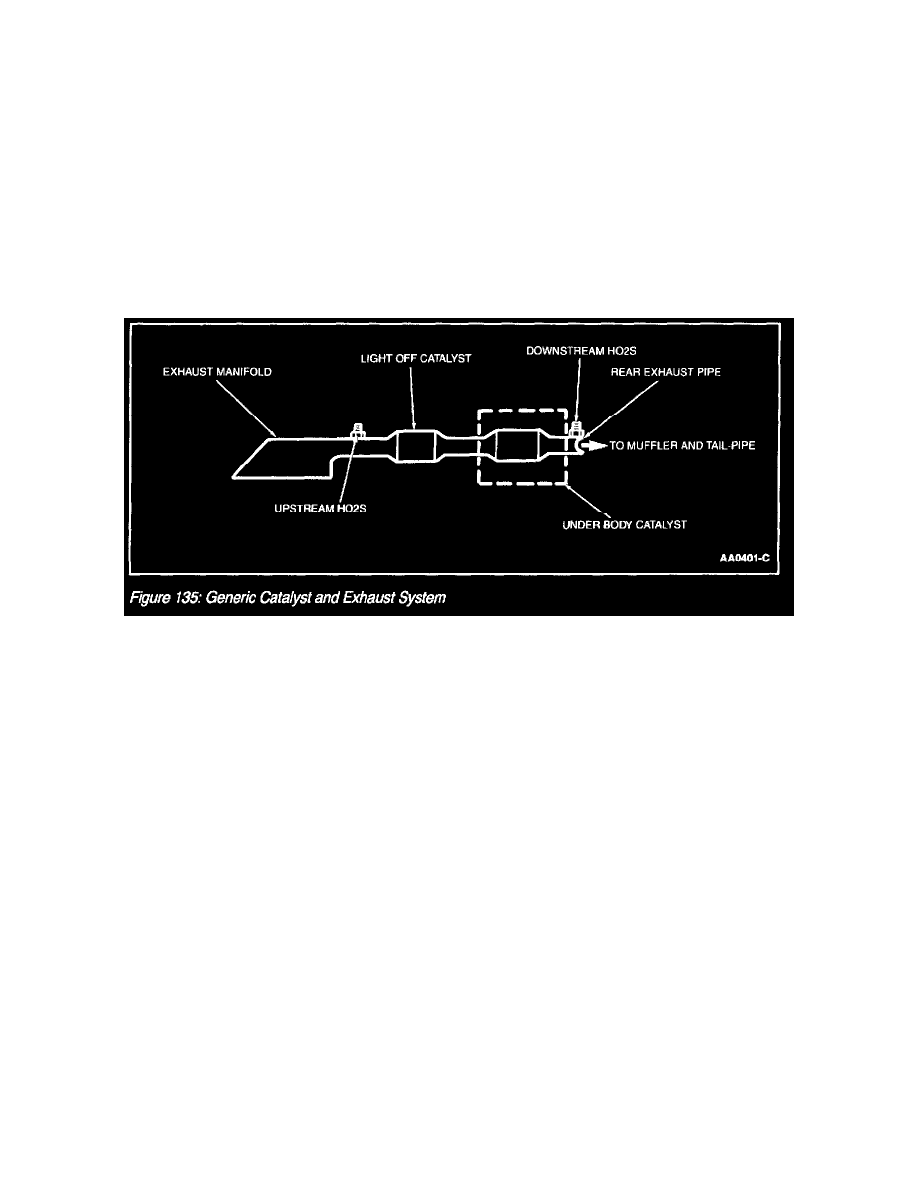
The Catalytic Converter and Exhaust Systems (Figure 135) work together to control the release of harmful engine exhaust emissions into the
atmosphere. The engine exhaust gas consists mainly of Nitrogen (N), Carbon Dioxide (CO2) and Water Vapor (H2O). However, it also contains
Carbon Monoxide (CO), Oxides Of Nitrogen (NOx), Hydrogen (H), and various unburned Hydrocarbons (HCs). CO, NO(x), and HCs are major air
pollutants, and their emission into the atmosphere must be controlled.
The exhaust system generally consists of an exhaust manifold, front exhaust pipe, upstream Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S), rear exhaust pipe,
downstream HO2S, a muffler and an exhaust tailpipe. The catalytic converter is installed between the front and rear exhaust pipes. Catalytic converter
efficiency is monitored by the On Board Diagnostic (OBD II) system.
Generic Catalyst and Exhaust System
Catalytic Converter
A catalyst is a material that remains unchanged when it initiates and increases the speed of a chemical reaction. A catalyst will also enable a
chemical reaction to occur at a lower temperature. The concentration of exhaust gas products released to the atmosphere must be controlled. The
catalytic converter assists in this task. It contains a catalyst in the form of a specially treated honeycomb structure saturated with catalytically
active precious metals. As the exhaust gases come in contact with the catalyst, they are changed into mostly harmless products. The catalyst
initiates and speeds up heat producing chemical reactions of the exhaust gas components so they are used up as much as possible.
Exhaust System
The purpose of the exhaust system is to convey engine emissions from the exhaust manifold to the atmosphere. Engine exhaust emissions are
directed from the engine exhaust manifold to the catalytic converter through the front exhaust pipe. An HO2S is mounted on the front exhaust pipe
before the catalyst. The catalytic converter reduces the concentration of Carbon Monoxide (CO), unburned Hydrocarbons (HCs) and Oxides of
Nitrogen (NO) in the exhaust emissions to an acceptable level. The reduced exhaust emissions are directed from the catalytic converter to a
muffler through the rear exhaust pipe. Another HO2S is mounted on the rear exhaust pipe. Lastly, the exhaust emissions are directed to the
atmosphere through an exhaust tailpipe.
HARDWARE
The downstream HO2S may be located after the light off catalyst or underbody catalyst. The underbody catalyst may be in-line with the light off
catalyst, or the underbody catalyst may be common to two light off catalysts, forming a "Y" pipe configuration. For an exact configuration of the
catalyst and exhaust system, refer to Exhaust System.
Three Way Catalytic Converter
The Three Way Catalytic (TWC) converter contains either platinum (Pt) and Rhodium (Rh) or Palladium (Pd) and Rhodium (Rh). The TWC
converter catalyzes the oxidation reactions of unburned HCs and CO and the reduction reaction of NO. The three-way conversion can be best
accomplished by always operating the engine air fuel/ratio at or close to stoichiometry.
Exhaust Manifold/Runners
The exhaust manifold runners collect exhaust gases from engine cylinders. The number of exhaust manifolds and exhaust manifold runners
depends on the engine configuration and number of cylinders.
